Windows Security: A Comprehensive Look at its Malware Protection Capabilities
Related Articles: Windows Security: A Comprehensive Look at its Malware Protection Capabilities
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Windows Security: A Comprehensive Look at its Malware Protection Capabilities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows Security: A Comprehensive Look at its Malware Protection Capabilities
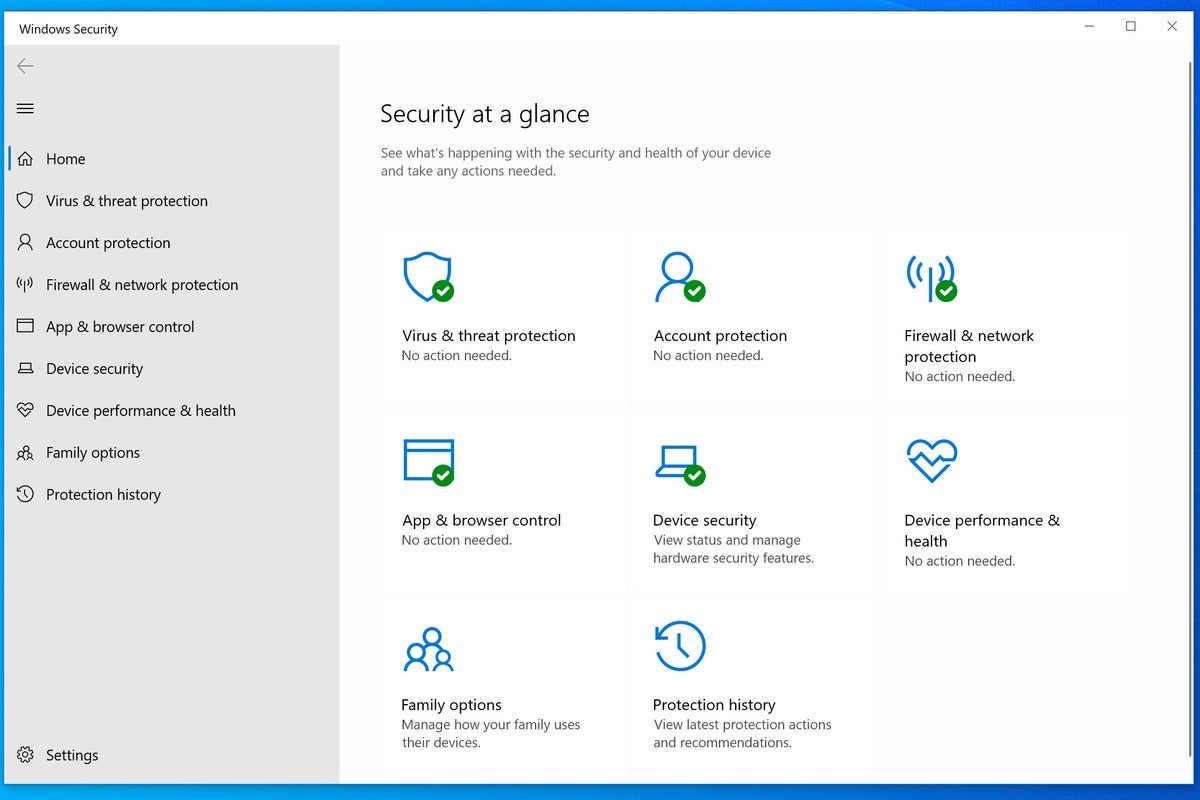
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, with cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated. Malware, encompassing viruses, worms, ransomware, and trojans, poses a significant risk to computer systems and personal data. Windows, the dominant operating system globally, has integrated security features to combat these threats. This article delves into the capabilities of Windows Security, analyzing its effectiveness in safeguarding against malware and exploring its key features.
Understanding Windows Security
Windows Security, formerly known as Windows Defender, is a comprehensive security suite built into Windows operating systems. It offers a multi-layered approach to protecting users from malware, encompassing real-time protection, threat detection, and system hardening features.
Key Components of Windows Security
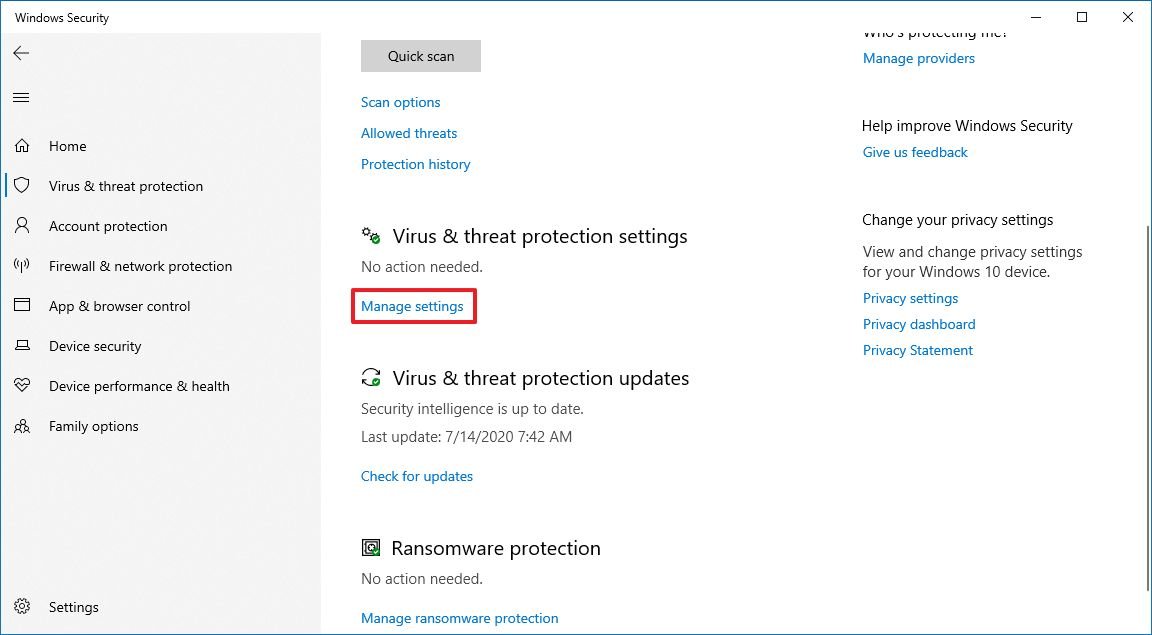
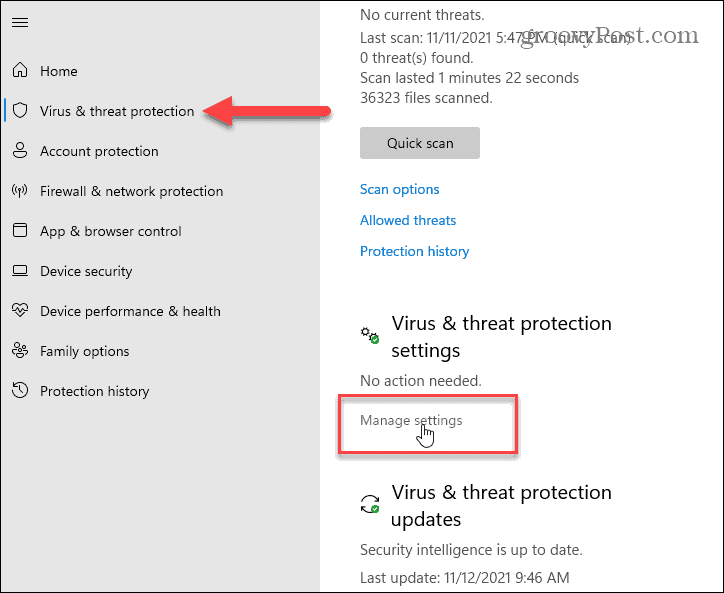
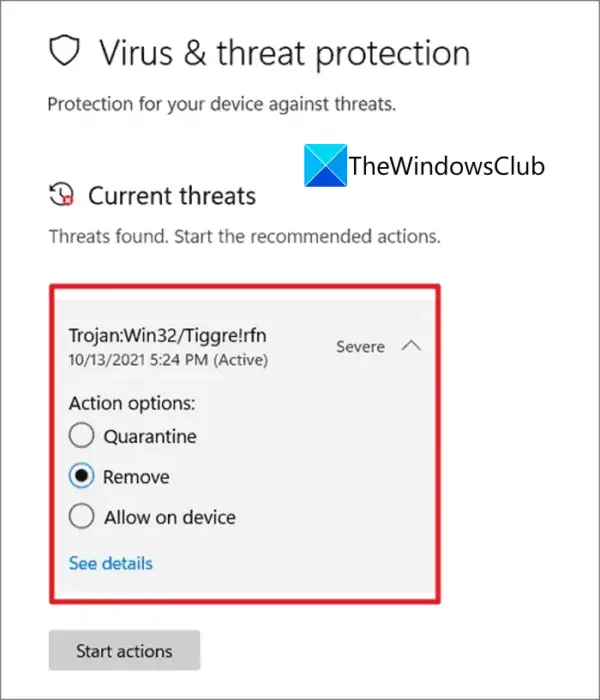
- Real-time Protection: This core feature constantly monitors the system for suspicious activities, analyzing files, programs, and websites in real-time. It uses a vast database of known malware signatures and heuristics to identify and block threats before they can cause harm.
- Threat Detection: Windows Security employs advanced detection techniques, including behavioral analysis, to identify malware that may not have been previously encountered. It analyzes program behavior, looking for suspicious patterns that might indicate malicious activity.
- System Hardening: Windows Security includes features that strengthen system security, such as controlling user accounts, managing firewall settings, and limiting access to sensitive data. These measures reduce the attack surface, making it more difficult for malware to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Automatic Updates: Regular updates are crucial for maintaining robust security. Windows Security automatically downloads and installs security updates, ensuring the system is protected against the latest threats.
- Cloud-Based Protection: Windows Security leverages Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure to enhance threat detection capabilities. It shares threat intelligence with other Windows users, enabling rapid identification and blocking of new and emerging malware.
Effectiveness of Windows Security
Windows Security has proven to be a highly effective tool for protecting against malware. Its real-time protection and threat detection capabilities, coupled with regular updates and cloud-based intelligence, create a robust defense against a wide range of threats.
Independent testing organizations, such as AV-Test and AV-Comparatives, consistently rank Windows Security among the top antivirus solutions. These organizations evaluate antivirus software based on their ability to detect and remove malware, their impact on system performance, and the false-positive rate.
Limitations and Considerations
While Windows Security offers excellent protection, it’s important to acknowledge its limitations:
- Zero-Day Threats: Windows Security may not be able to detect and block completely new malware, known as zero-day threats, before they are added to its database.
- User Behavior: User behavior plays a significant role in system security. Clicking on suspicious links, downloading files from untrusted sources, and neglecting security updates can compromise even the most robust antivirus solution.
- Advanced Threats: Some sophisticated malware, such as ransomware and advanced persistent threats (APTs), can evade traditional antivirus detection mechanisms. These threats require additional security measures, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, to be effectively mitigated.
Complementing Windows Security
While Windows Security provides a strong foundation for malware protection, it is not a substitute for comprehensive cybersecurity practices. Users should consider additional measures to enhance their security posture:
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication: Utilize strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication for critical accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all software, including operating systems, applications, and browsers, up to date with the latest security patches.
- Anti-Phishing Training: Be aware of phishing scams and avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Backups: Regularly back up important data to a separate location to ensure recovery in case of a malware attack.
- Network Security: Implement a robust firewall and use a virtual private network (VPN) when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks.
FAQs
Q: Is Windows Security enough to protect against all malware?
A: While Windows Security is highly effective, it cannot guarantee protection against all malware, especially emerging threats. It’s crucial to implement a comprehensive security strategy that includes additional measures like software updates, strong passwords, and user awareness.
Q: Should I install a third-party antivirus program alongside Windows Security?
A: Installing a third-party antivirus program alongside Windows Security might provide additional protection, but it can also lead to conflicts and performance issues. It’s best to consult with a cybersecurity expert to determine if a third-party solution is necessary.
Q: How do I know if my system is infected with malware?
A: Signs of malware infection include slow performance, unexpected crashes, unusual pop-ups, suspicious browser activity, and unauthorized software installations. If you suspect your system is infected, run a full system scan with Windows Security or a reputable third-party antivirus program.
Q: What should I do if I detect malware on my system?
A: If you detect malware, immediately disconnect from the internet to prevent further spread. Run a full system scan with Windows Security or a third-party antivirus program. Follow the instructions provided by the antivirus software to remove the malware. If you are unable to remove the malware yourself, consider contacting a professional cybersecurity firm.
Tips
- Keep Windows Security Enabled: Ensure that Windows Security is enabled and running on your system.
- Schedule Regular Scans: Schedule regular full system scans with Windows Security to detect and remove potential threats.
- Review Security Settings: Regularly review the security settings in Windows Security and adjust them according to your needs.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices by reading security blogs and news articles.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Report any suspicious activity, such as phishing emails or malware infections, to the relevant authorities.
Conclusion
Windows Security is a powerful tool that provides comprehensive protection against malware. Its real-time protection, threat detection, and system hardening features make it a valuable asset for safeguarding computer systems. However, it’s crucial to remember that no security solution is perfect. Users must adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity, including regular updates, strong passwords, and user awareness, to ensure their systems are adequately protected. By implementing a multi-layered security strategy that includes Windows Security and other best practices, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to malware attacks.
![[INFOGRAPHIC] Top 7 Secured Tips To Prevent Windows 10 From Virus Attack](https://www.pcerror-fix.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/windows-10-security-tips-1.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows Security: A Comprehensive Look at its Malware Protection Capabilities. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!