Windows and Malware: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your System
Related Articles: Windows and Malware: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your System
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Windows and Malware: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your System. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Windows and Malware: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your System
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Windows and Malware: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your System
- 3.1 Windows’ Built-in Security Features: A Multi-Layered Defense
- 3.2 Beyond Built-in Protection: User Responsibility and Additional Measures
- 3.3 FAQ: Understanding Common Questions About Windows and Malware
- 3.4 Tips for Safeguarding Your Windows System
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Proactive Approach to Windows Security
- 4 Closure
Windows and Malware: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your System
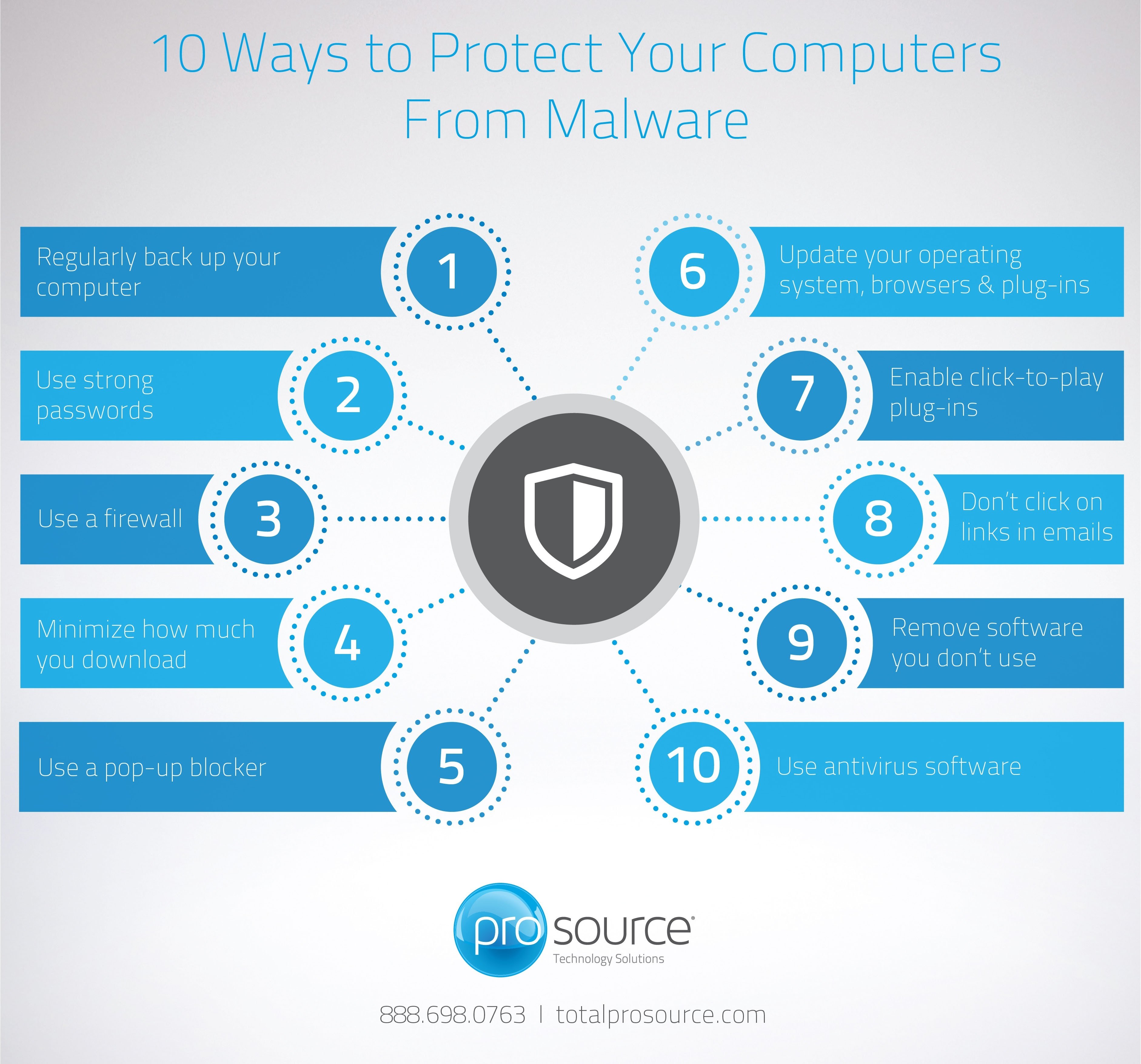
The ubiquitous nature of computers and the internet has made digital security a paramount concern. Malware, short for malicious software, poses a constant threat, seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in operating systems and applications to steal data, disrupt operations, or gain unauthorized access. Windows, as the dominant operating system for personal computers, is a primary target for malware developers. While Windows has evolved significantly in its security features, it is crucial to understand the mechanisms it employs to combat these threats and how users can further enhance their system’s resilience.
Windows’ Built-in Security Features: A Multi-Layered Defense
Windows incorporates a multi-layered security framework to protect against malware. These features work in conjunction to identify, block, and remove malicious software:
1. Windows Defender Antivirus: This real-time antivirus engine, included by default in Windows, constantly scans files and applications for known malware signatures. It also utilizes cloud-based analysis to detect and block emerging threats. Windows Defender Antivirus is continuously updated with the latest malware definitions, ensuring its effectiveness against new and evolving threats.
2. Windows Security: This central hub provides access to various security settings and features, including:
- Firewall: Acts as a barrier between the computer and external networks, blocking unauthorized access attempts.
- SmartScreen: Filters potentially harmful websites and downloads, preventing access to known malicious content.
- App & Browser Control: Restricts the execution of untrusted applications and blocks potentially dangerous websites.
- Exploit Protection: Offers a range of mitigations against common attack vectors, such as buffer overflows and data execution prevention.
3. Windows Update: Regular updates are crucial for maintaining system security. Windows Update delivers security patches, bug fixes, and new features, addressing vulnerabilities exploited by malware.
4. Sandboxing: Windows offers a sandbox environment for testing potentially unsafe applications. By isolating the application from the main system, any malicious activity is contained within the sandbox, preventing damage to the user’s data and files.
5. User Account Control (UAC): This feature prompts users for permission before allowing applications to make changes to the system, mitigating unauthorized actions by malware.
Beyond Built-in Protection: User Responsibility and Additional Measures
While Windows offers robust security features, user behavior plays a crucial role in maintaining a secure system. Several practices can significantly enhance protection against malware:
1. Exercise Caution with Downloads and Emails: Be wary of suspicious attachments in emails, especially from unknown senders. Verify the source of downloaded software and only download from trusted websites.
2. Install Security Software: Consider using third-party antivirus software alongside Windows Defender Antivirus for an additional layer of protection. These solutions often offer advanced features like real-time threat detection, behavioral analysis, and vulnerability scanning.
3. Keep Software Updated: Regularly update all software, including operating system, applications, and drivers. Updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by malware.
4. Use Strong Passwords: Employ strong and unique passwords for all accounts. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts and consider using a password manager to store and manage passwords securely.
5. Enable Two-Factor Authentication: This extra layer of security adds an additional step to account login, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access.
6. Be Aware of Phishing Attacks: Phishing emails and websites attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Be cautious about clicking on links or providing personal information in suspicious emails or websites.
7. Regularly Back Up Data: Regularly back up important data to an external drive or cloud storage service. This safeguards against data loss in the event of a malware attack or system failure.
8. Educate Yourself About Malware: Stay informed about the latest malware threats and vulnerabilities. Understanding how malware operates and the common attack vectors can help you take proactive steps to protect your system.
FAQ: Understanding Common Questions About Windows and Malware
Q: Is Windows Defender Antivirus enough to protect my system?
A: While Windows Defender Antivirus provides a strong baseline of protection, it is not foolproof. Consider using a third-party antivirus solution for enhanced security, especially if you handle sensitive data or frequently browse the web.
Q: How do I know if my system is infected with malware?
A: Signs of malware infection include slow system performance, unusual pop-ups or error messages, unexpected program crashes, and unauthorized changes to system settings. Running a full system scan with a reputable antivirus software can help identify malware infections.
Q: Can I remove malware myself?
A: While some basic malware removal tools are available, it is generally recommended to consult with a security expert or use a professional malware removal tool. Attempting to remove malware manually can be complex and may inadvertently damage your system.
Q: What should I do if I suspect my system is infected?
A: If you suspect your system is infected, disconnect from the internet to prevent further damage. Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus software. If the infection persists, consider seeking professional assistance from a security expert or IT technician.
Q: How can I avoid downloading malware?
A: Be cautious when downloading software from the internet. Only download from trusted websites and verify the software’s authenticity. Use a reputable antivirus software to scan downloaded files before opening them.
Q: What are the latest malware threats?
A: The threat landscape is constantly evolving. Stay informed about the latest malware threats through reputable security news sources and keep your software up-to-date with the latest security patches.
Tips for Safeguarding Your Windows System
- Enable automatic updates: Ensure Windows Update is enabled and set to automatically download and install updates.
- Use a strong password manager: Store and manage your passwords securely using a reputable password manager.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Add an extra layer of security to your accounts by enabling two-factor authentication.
- Be cautious with public Wi-Fi networks: Avoid accessing sensitive information or performing online banking on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Install a VPN: Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and enhance privacy.
- Regularly review security settings: Periodically review your Windows security settings and ensure they are configured optimally.
- Stay informed about security threats: Stay updated on the latest malware threats and vulnerabilities through reputable security news sources.
Conclusion: A Proactive Approach to Windows Security
Windows offers a robust set of security features to combat malware threats. However, maintaining a secure system requires a proactive approach from users. By understanding the mechanisms behind Windows’ security features, implementing best practices, and staying informed about evolving threats, users can significantly reduce their risk of malware infection and safeguard their data and privacy. Remember, security is an ongoing process, and continuous vigilance is essential in the ever-evolving digital landscape.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows and Malware: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your System. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!