Windows 10 and Security: Understanding Built-in Protection and Its Limitations
Related Articles: Windows 10 and Security: Understanding Built-in Protection and Its Limitations
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Windows 10 and Security: Understanding Built-in Protection and Its Limitations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 and Security: Understanding Built-in Protection and Its Limitations

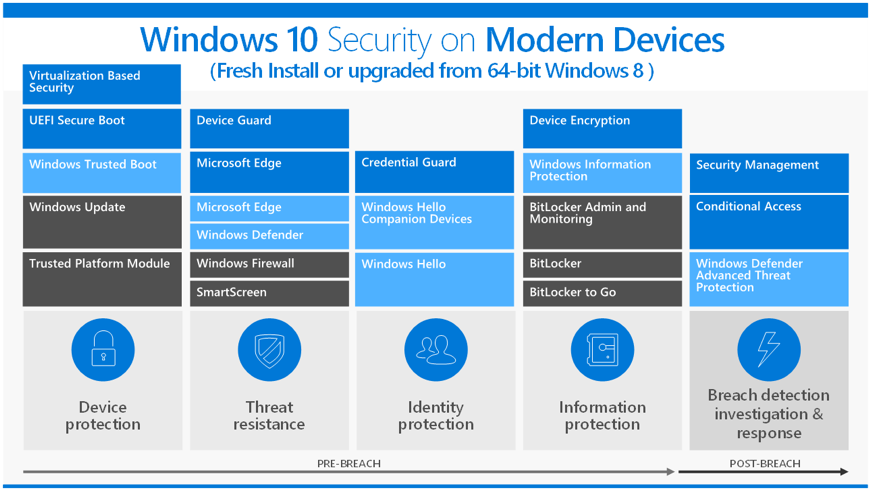
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, presenting a dynamic and challenging environment for users. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, ensuring robust security measures is paramount. Windows 10, the widely used operating system, incorporates a suite of security features designed to safeguard users and their data. While these features provide a foundational level of protection, it is crucial to understand their limitations and the necessity of supplementing them with additional security measures.
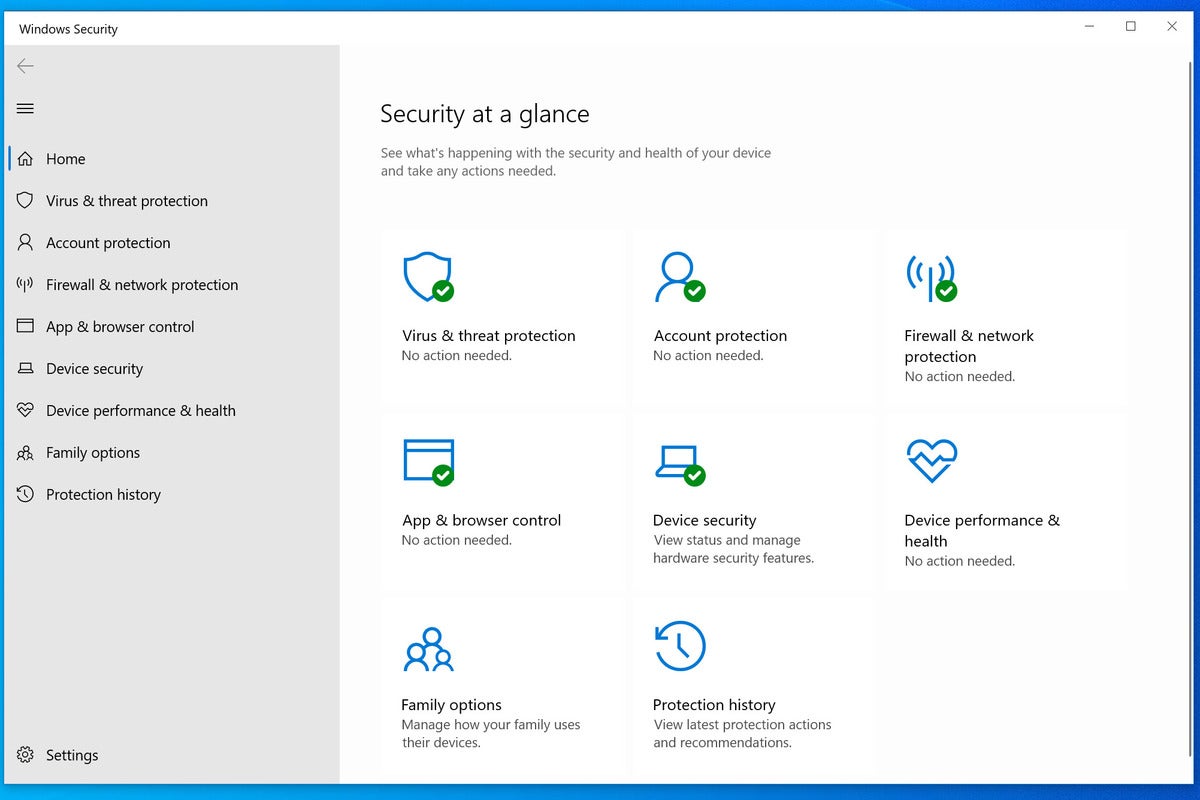
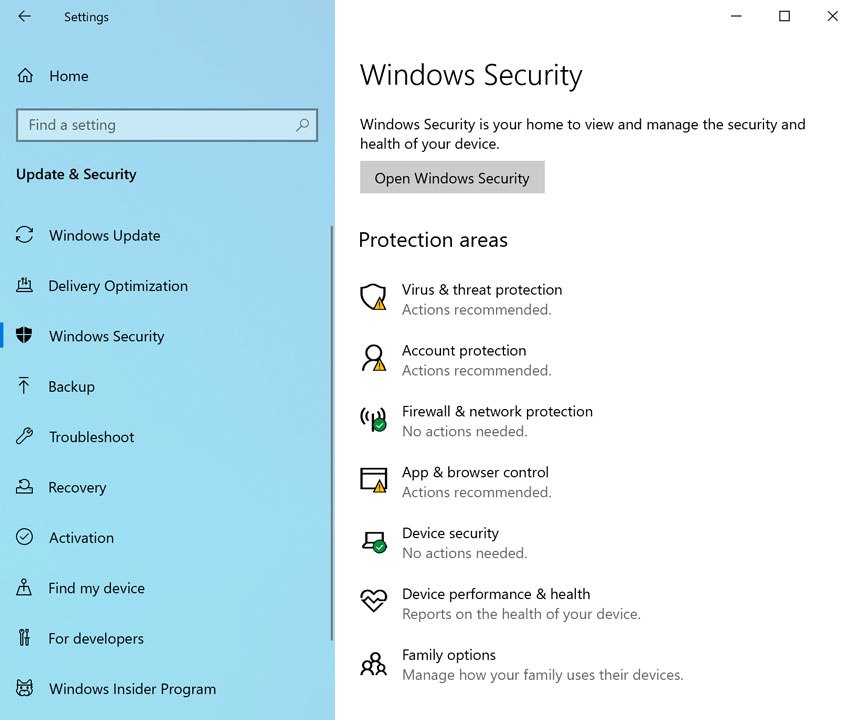
Windows Defender: The Core of Windows 10 Security
Windows Defender, the built-in antivirus software in Windows 10, plays a vital role in protecting against malware. It operates in real-time, constantly monitoring the system for suspicious activity and blocking potentially harmful files or programs. Windows Defender utilizes a multi-layered approach to security, encompassing:
- Real-time Protection: This feature scans files and applications as they are downloaded or executed, preventing malware from gaining access to the system.
- Cloud-Powered Protection: Leveraging Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure, Windows Defender receives constant updates on emerging threats, ensuring its threat detection capabilities remain up-to-date.
- Behavioral Analysis: Windows Defender analyzes the behavior of software, identifying suspicious patterns that may indicate malicious activity.
- Exploit Protection: This feature mitigates vulnerabilities in software by hardening the system against known attack methods.
- Firewall: The Windows Firewall acts as a barrier between the computer and the internet, blocking unauthorized access to the system.
Beyond Windows Defender: The Need for Additional Security
While Windows Defender provides a strong foundation for security, it is not a foolproof solution. The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats necessitates a multi-faceted approach to security, which often requires supplementing Windows Defender with additional measures.
- Limited Coverage: Windows Defender’s primary focus is on traditional malware such as viruses, worms, and trojans. It may not offer comprehensive protection against more sophisticated threats like ransomware, phishing attacks, or zero-day exploits.
- Proactive Protection: Relying solely on reactive measures, such as detecting and blocking known threats, can leave the system vulnerable to emerging threats.
- User Education: Even with advanced security software, user awareness and responsible online practices are critical for mitigating risks.
The Importance of Complementary Security Solutions
To achieve a robust security posture, it is recommended to implement a layered approach, combining Windows Defender with other security solutions:
- Third-Party Antivirus Software: Independent antivirus programs often offer more comprehensive protection, including advanced features such as anti-phishing, anti-spam, and parental controls.
- Firewall Software: Dedicated firewalls provide granular control over network traffic, enhancing security beyond the basic protection offered by the Windows Firewall.
- Password Manager: Strong and unique passwords are essential for online security, but managing them can be challenging. Password managers help users create and store secure passwords, simplifying password management and enhancing security.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): VPNs encrypt internet traffic, providing an extra layer of privacy and security when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping operating systems, applications, and antivirus software up-to-date is crucial for patching vulnerabilities and ensuring optimal security.
- Backups: Regular backups are essential for data recovery in case of a security breach or system failure.
FAQs on Windows 10 Security
1. Is Windows Defender Enough for Security?
While Windows Defender provides a solid foundation for security, it is not enough on its own. It is recommended to supplement it with additional security measures for comprehensive protection.
2. Should I Use Both Windows Defender and Third-Party Antivirus Software?
While both Windows Defender and third-party antivirus software can provide protection, running them simultaneously can cause conflicts and slow down the system. It is generally recommended to choose one or the other, ensuring that the chosen solution is reliable and up-to-date.
3. Can I Disable Windows Defender?
While disabling Windows Defender is possible, it is not recommended. It is crucial to have some form of antivirus protection, and Windows Defender provides a basic level of security. If you choose to use a third-party antivirus solution, ensure it provides comprehensive protection and does not conflict with Windows Defender.
4. How Do I Know if My System is Secure?
There are several ways to assess system security:
- Regularly check for updates: Ensure that the operating system, applications, and antivirus software are up-to-date.
- Monitor system performance: Unusual system behavior, such as slow performance or crashes, can indicate a security threat.
- Use a security scanner: Regularly run a security scan to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats.
- Be cautious online: Avoid clicking on suspicious links, opening attachments from unknown senders, and downloading software from untrusted sources.
Tips for Enhancing Windows 10 Security
- Use strong passwords: Create long, complex passwords that are difficult to guess.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to your phone.
- Be wary of phishing attacks: Phishing emails and websites often attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Keep software up-to-date: Regularly install software updates to patch vulnerabilities.
- Backup important data: Regular backups can help recover data in case of a security breach or system failure.
- Be cautious when using public Wi-Fi: Avoid accessing sensitive information or performing online banking on public Wi-Fi networks.
Conclusion
Windows 10 provides a solid foundation for security through its built-in features, such as Windows Defender. However, it is essential to recognize the limitations of these features and supplement them with additional security measures. A multi-layered approach, combining Windows Defender with third-party antivirus software, firewalls, password managers, and other security tools, is crucial for achieving comprehensive protection against the ever-evolving cyber threats. By implementing these measures and maintaining responsible online practices, users can significantly enhance their system security and protect their data.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows 10 and Security: Understanding Built-in Protection and Its Limitations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!