Windows 10 and Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Windows 10 and Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Windows 10 and Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 and Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide

Windows 10, Microsoft’s latest operating system, boasts a robust suite of security features designed to safeguard users from the ever-evolving threat of malware. While no system is completely impervious to malicious attacks, Windows 10 offers a multifaceted approach to defense, encompassing both proactive measures and reactive defenses. Understanding the intricacies of these security mechanisms is crucial for users seeking to protect their devices and data.
Understanding the Malware Threat:
Malware, a broad term encompassing viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware, poses a significant threat to computer systems. These malicious programs can infiltrate devices through various methods, including:
- Phishing: Deceptive emails or websites disguised as legitimate entities, enticing users to download infected files or divulge sensitive information.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Malware exploits security flaws in software applications or operating systems to gain unauthorized access.
- Drive-by Downloads: Users inadvertently download malware by visiting compromised websites that inject malicious code into their systems.
Windows 10’s Security Arsenal:
Windows 10 employs a layered approach to malware protection, encompassing:
1. Windows Defender Antivirus:
This built-in antivirus software acts as the first line of defense, continuously scanning the system for known threats. Windows Defender Antivirus utilizes a comprehensive database of malware signatures to identify and neutralize malicious files. It also leverages cloud-based intelligence to detect emerging threats, providing proactive protection against new and evolving malware variants.
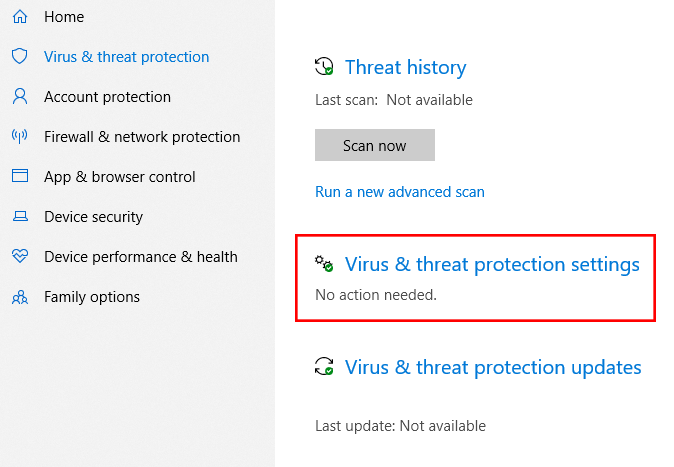
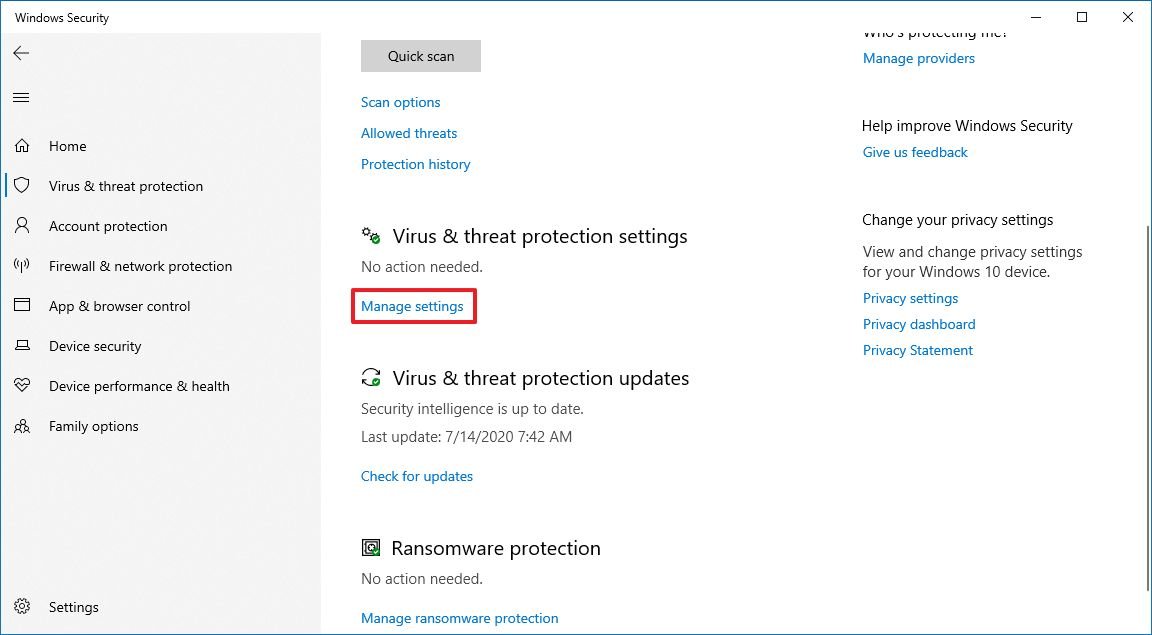
2. Windows Security:
This central hub consolidates various security settings, allowing users to manage antivirus protection, firewall settings, and device security features. Windows Security offers a user-friendly interface for configuring security options, enabling users to tailor their protection based on their specific needs.
3. Windows Firewall:
Acting as a digital barrier, the Windows Firewall blocks unauthorized access to the device from external networks. It filters incoming and outgoing network traffic, preventing malicious programs from connecting to the internet or establishing communication with other devices.
4. SmartScreen:
This feature helps prevent users from downloading or visiting malicious websites. SmartScreen analyzes the reputation of websites and files before allowing access, warning users about potentially harmful content.
5. App & Browser Control:
Windows 10 allows users to restrict access to potentially harmful applications and websites. Users can configure specific settings to block access to certain apps or websites, providing an additional layer of protection.
6. Sandboxing:
Windows 10 includes a feature called "Windows Sandbox," which allows users to run untrusted applications in a secure, isolated environment. This prevents any malicious code from affecting the main operating system or data stored on the device.
7. Automatic Updates:
Microsoft regularly releases security updates for Windows 10, patching vulnerabilities and improving the operating system’s overall security posture. Automatic updates ensure that devices are equipped with the latest security features, mitigating potential risks.
Beyond the Basics: Enhancing Protection:
While Windows 10’s built-in security features provide a solid foundation, users can further strengthen their protection by adopting additional measures:
- Using Strong Passwords: Employ complex passwords, including a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, for all accounts.
- Enabling Two-Factor Authentication: This extra layer of security requires users to provide an additional code, usually sent to their mobile device, when logging in.
- Being Cautious of Phishing: Exercise caution when clicking on links or opening attachments in emails, especially those from unknown senders.
- Keeping Software Up-to-Date: Regularly update all software applications, including operating systems, to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security.
- Using a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts internet traffic, making it harder for malicious actors to intercept data.
- Installing a Third-Party Antivirus: While Windows Defender Antivirus provides solid protection, users may consider installing a reputable third-party antivirus solution for additional security layers.
FAQs about Windows 10 and Malware Protection:
Q: Is Windows 10 completely safe from malware?
A: No operating system is completely immune to malware. While Windows 10 offers robust security features, it’s essential to adopt good security practices and stay vigilant to minimize risks.
Q: Does Windows 10 automatically protect against all malware?
A: Windows 10’s built-in security features provide strong protection against known malware. However, new threats emerge constantly, and users need to remain proactive in updating software and practicing safe online habits.
Q: How do I know if my computer is infected with malware?
A: Signs of malware infection include slow performance, unexpected pop-ups, unusual programs running in the background, and changes in browser settings. Running a full system scan with Windows Defender Antivirus or a third-party antivirus solution can help identify malware infections.
Q: What should I do if I suspect my computer is infected with malware?
A: If you suspect malware infection, disconnect the device from the network, run a full system scan with antivirus software, and consider contacting a cybersecurity professional for assistance.
Tips for Staying Safe from Malware:
- Be wary of unsolicited emails and attachments: Avoid clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Verify website authenticity: Ensure that websites you visit are legitimate by checking for secure connections (HTTPS) and verifying the domain name.
- Download software from trusted sources: Only download software from reputable websites and developers to avoid installing malicious applications.
- Practice safe browsing habits: Avoid clicking on suspicious links, downloading files from untrusted sources, and visiting websites known for malware distribution.
- Keep your devices and software up-to-date: Regularly update your operating system, software applications, and antivirus software to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security.
- Use a strong password and enable two-factor authentication: Secure your accounts with complex passwords and enable two-factor authentication for an extra layer of security.
- Be cautious of free Wi-Fi networks: Avoid accessing sensitive information or making online transactions on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Install a reputable antivirus solution: Consider using a third-party antivirus solution for additional protection beyond Windows Defender Antivirus.
Conclusion:
Windows 10 provides a comprehensive suite of security features designed to protect users from malware. However, users must remain vigilant and adopt good security practices to minimize risks. By understanding the threat of malware, leveraging Windows 10’s security features, and implementing additional security measures, users can significantly reduce their vulnerability to malicious attacks and safeguard their devices and data.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows 10 and Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!