Windows 10 and Android App Compatibility: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Windows 10 and Android App Compatibility: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Windows 10 and Android App Compatibility: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 and Android App Compatibility: A Comprehensive Overview
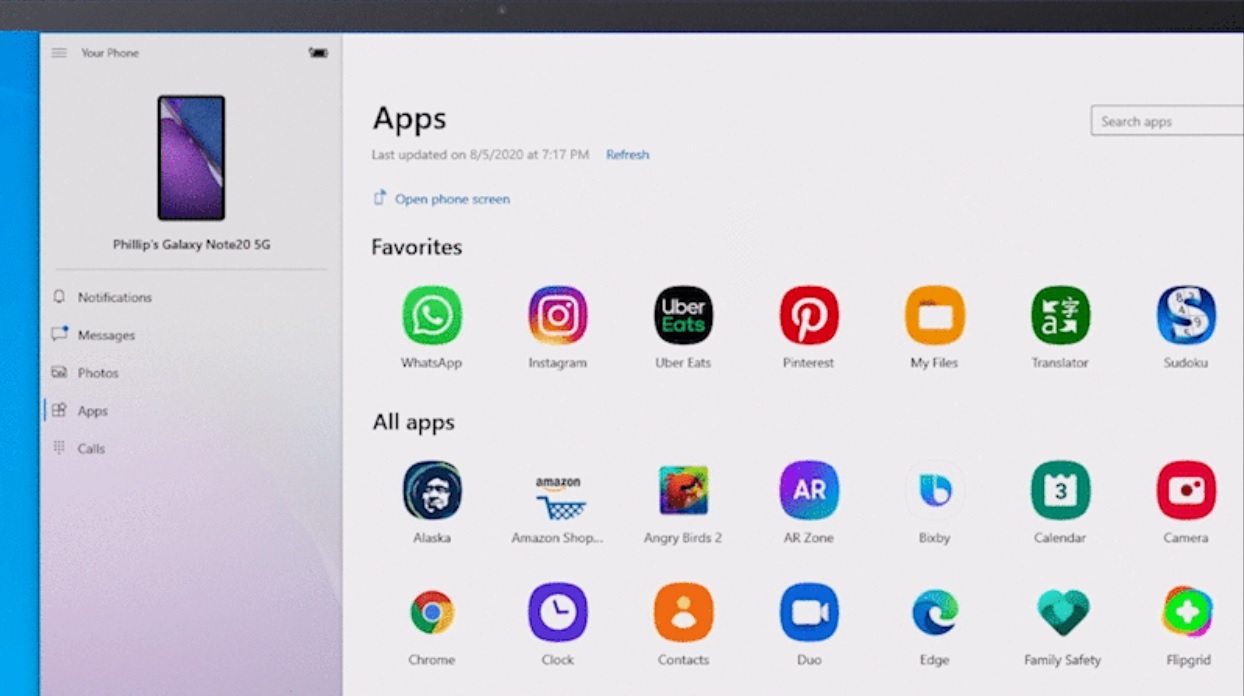
The world of computing has witnessed a surge in the demand for cross-platform compatibility. Users seek seamless integration between operating systems, enabling them to access a broader range of applications and services across their devices. In this context, the question of whether Windows 10 supports Android apps has become a significant point of interest.
While Windows 10 itself does not natively support Android apps, there are alternative solutions and platforms that bridge the gap between these two ecosystems. This article will delve into the intricacies of this compatibility, exploring the existing options, their limitations, and the potential benefits they offer.
The Challenge of Cross-Platform Compatibility
Windows 10, developed by Microsoft, and Android, an open-source operating system primarily used on mobile devices, are fundamentally distinct platforms. They utilize different programming languages, software architectures, and application distribution models. This inherent difference poses a challenge for direct compatibility between the two.
The Rise of Emulation and Virtualization
To overcome this challenge, several solutions have emerged, primarily relying on emulation and virtualization. These technologies allow users to create virtual environments within their Windows 10 systems, mimicking the Android operating system. This virtual environment enables the execution of Android apps designed for mobile devices.
Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA)
Microsoft, recognizing the growing demand for cross-platform compatibility, introduced the Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA) as part of Windows 11. WSA allows users to install and run Android apps directly on their Windows 11 machines. This integration leverages the power of the underlying Windows system, providing a more seamless and efficient experience compared to traditional emulators.
Third-Party Emulators
Prior to the introduction of WSA, third-party emulators like BlueStacks, NoxPlayer, and LDPlayer offered a means to run Android apps on Windows 10. These emulators provide a virtualized environment, allowing users to access the Google Play Store and install a wide range of Android applications. However, these emulators often require significant system resources, potentially impacting performance and stability.
Benefits of Running Android Apps on Windows 10
The ability to run Android apps on Windows 10 offers several advantages:
- Expanded App Ecosystem: Users gain access to a vast library of Android apps, including popular social media platforms, productivity tools, gaming apps, and more.
- Cross-Device Continuity: This allows users to seamlessly switch between their Windows 10 PC and Android devices, accessing the same apps and services across platforms.
- Improved Productivity: Users can leverage familiar Android apps on their Windows 10 PC for tasks such as messaging, note-taking, or browsing the web.
- Enhanced Gaming Experience: Android gaming apps can be enjoyed on a larger screen with enhanced controls and performance, thanks to the capabilities of Windows 10 hardware.
Limitations and Considerations
While running Android apps on Windows 10 offers several benefits, certain limitations and considerations remain:
- Compatibility Issues: Not all Android apps are guaranteed to run flawlessly on Windows 10. Some apps may exhibit performance issues, compatibility problems, or may not function at all.
- Performance Overhead: Emulation and virtualization processes can consume significant system resources, potentially leading to slower performance on the host Windows 10 system.
- Security Concerns: Running Android apps within a virtualized environment raises security concerns, as vulnerabilities in the emulator or the Android system could potentially expose the host Windows 10 system to risks.
FAQs
Q1: Can I run any Android app on Windows 10?
A: While many Android apps are compatible with Windows 10 through emulators or WSA, not all apps are guaranteed to work flawlessly. Some apps may require specific hardware features or Android API versions that are not fully supported within the virtual environment.
Q2: Is it safe to run Android apps on Windows 10?
A: Running Android apps on Windows 10 through emulators or WSA introduces potential security risks. It is essential to download apps from trusted sources like the Google Play Store and keep both the emulator and the host Windows 10 system updated with the latest security patches.
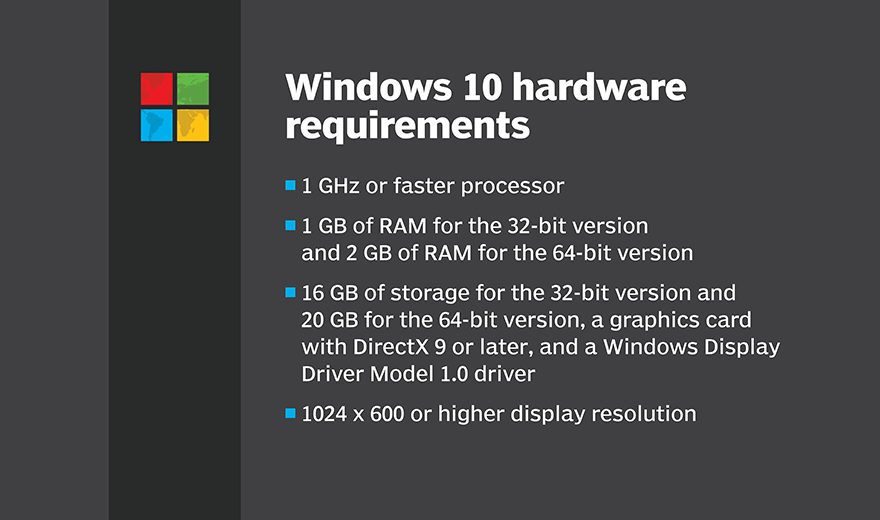
Q3: What are the system requirements for running Android apps on Windows 10?
A: The system requirements for running Android apps on Windows 10 vary depending on the specific emulator or platform used. Generally, a modern processor, ample RAM, and sufficient storage space are recommended.
Q4: Can I access Google Play Services on Windows 10?
A: Accessing Google Play Services on Windows 10 depends on the chosen method. WSA provides access to the Google Play Store and services. Third-party emulators may also offer access, but compatibility can vary.
Q5: Can I use Android apps alongside Windows apps?
A: Yes, Android apps can be used alongside Windows apps within the virtual environment provided by emulators or WSA. However, the interaction between the two ecosystems may be limited, and some features may not be fully compatible.
Tips for Running Android Apps on Windows 10
- Choose a reputable emulator: When using third-party emulators, select a well-established and reliable option with good user reviews and security measures.
- Update your system and emulator: Regularly update your Windows 10 system and the emulator software to ensure optimal compatibility and security.
- Check compatibility: Before installing an Android app, verify its compatibility with the emulator or WSA environment.
- Manage system resources: Monitor system resource usage, especially when running resource-intensive Android apps.
- Consider security measures: Employ antivirus software and other security measures to mitigate potential risks associated with running Android apps in a virtual environment.
Conclusion
While Windows 10 itself does not natively support Android apps, solutions like WSA and third-party emulators bridge the gap, enabling users to access a wider range of applications. This cross-platform compatibility offers significant benefits, including access to a larger app ecosystem, enhanced productivity, and a more seamless user experience across devices. However, users must be aware of potential limitations and security considerations when running Android apps within a virtual environment. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in cross-platform compatibility, further blurring the lines between operating systems and enhancing the user experience.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows 10 and Android App Compatibility: A Comprehensive Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!