Understanding the Windows 10 "E Drive" and its Significance
Related Articles: Understanding the Windows 10 "E Drive" and its Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Windows 10 "E Drive" and its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Windows 10 "E Drive" and its Significance
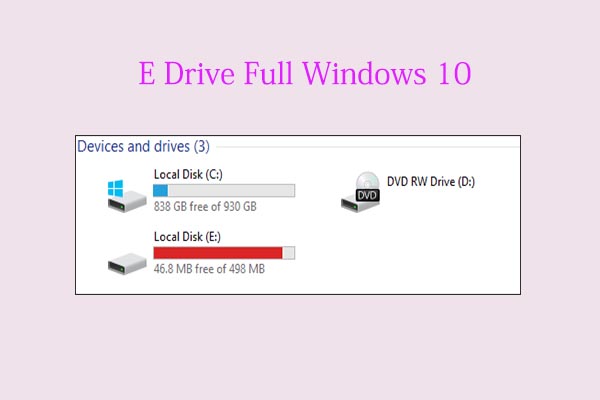
The term "E Drive" in relation to Windows 10 is not a standard or officially recognized component of the operating system. It’s a misconception that arises from a misunderstanding of how Windows manages storage and assigns drive letters.
Drive Letter Assignment in Windows:
Windows assigns drive letters to various storage devices, including internal hard drives, external drives, and removable media. The most common drive letter for the primary internal hard drive is "C," but this can vary depending on the system configuration.
The "E Drive" misconception often stems from situations where a user encounters a drive letter other than "C" for their primary hard drive. This can occur due to:
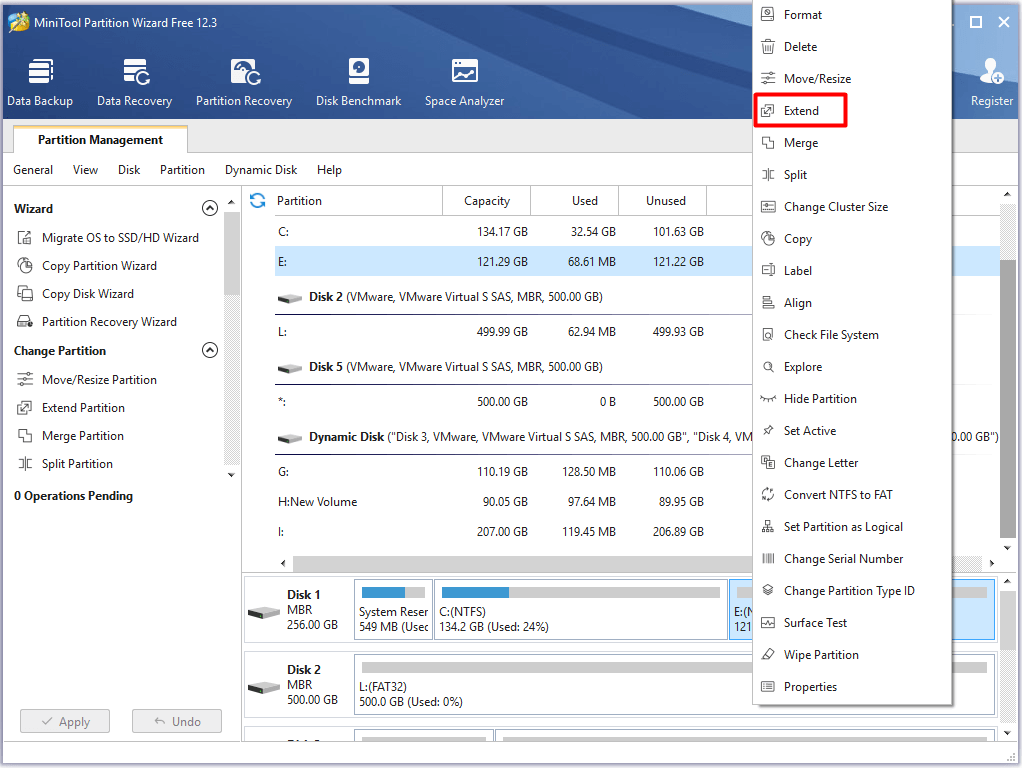
- Multiple Hard Drives: If a system has multiple hard drives, Windows will assign drive letters sequentially, starting with "C" for the first drive and progressing to "D," "E," and so on.
- External Drives: When an external hard drive or USB drive is connected, Windows assigns it a drive letter, potentially resulting in "E" if the internal hard drive is already assigned "C" and another drive is assigned "D."
- Virtual Drives: Software like virtual machine applications can create virtual drives, which can be assigned drive letters, including "E."
The Significance of Drive Letters:
Drive letters serve as convenient labels for Windows to access and manage different storage locations. They allow users to easily navigate and access files on different drives. While drive letters can be changed, it’s generally recommended to leave the default assignments to avoid potential conflicts or issues.
Understanding the "E Drive" Misconception:
The "E Drive" misconception is often associated with the following:
- "E Drive" as a Hidden System Partition: Some users believe that Windows 10 has a hidden "E Drive" that contains important system files. This is incorrect. The system files are typically located on the "C" drive, and there’s no separate "E Drive" dedicated to system functions.
- "E Drive" as a Recovery Partition: The recovery partition, containing tools for restoring Windows to a previous state, is usually labeled with a different drive letter, often "D" or "F," depending on the system configuration.
- "E Drive" as a Temporary Storage Location: Some users mistakenly believe that the "E Drive" is used for temporary storage, such as temporary files or swap files. These files are usually stored in the "C" drive’s "Temp" folder or other designated locations.
Clearing the Confusion:
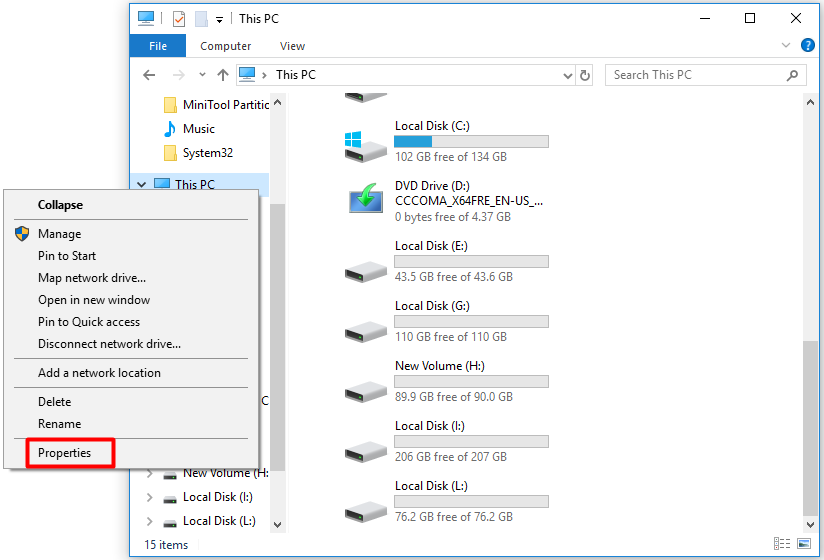
It’s crucial to understand that the "E Drive" doesn’t exist as a separate dedicated drive in Windows 10. The drive letter "E" is simply a potential assignment for a different storage device. If you encounter a "E Drive" in your system, it’s likely an external drive, a virtual drive, or a second internal hard drive.
Conclusion:
The misconception surrounding the "E Drive" in Windows 10 highlights the importance of understanding how Windows assigns drive letters and manages storage. By accurately identifying the source of the "E Drive" in a given system, users can avoid confusion and ensure proper file management practices.
FAQs on Drive Letters and Storage Management in Windows 10:
Q: What is the difference between a physical drive and a logical drive?
A: A physical drive refers to the actual hardware component, like a hard disk drive or a solid-state drive. A logical drive, on the other hand, is a partition created on the physical drive, which is then assigned a drive letter and treated as a separate storage space by Windows.
Q: Can I change drive letters in Windows 10?
A: Yes, you can change drive letters in Windows 10. However, it’s generally recommended to avoid changing the drive letter assigned to the primary hard drive (usually "C") to prevent potential issues with system files and applications.
Q: What happens if I delete a logical drive?
A: Deleting a logical drive erases all data stored on that partition. It’s essential to back up any important data before deleting a logical drive.
Q: How can I create a new logical drive?
A: You can create a new logical drive using the Disk Management tool in Windows 10. This involves partitioning unallocated space on a physical drive.
Q: What are the benefits of using multiple logical drives?
A: Using multiple logical drives can help organize files, improve performance by separating data, and enhance data security by creating separate partitions for critical data.
Tips for Managing Drive Letters and Storage in Windows 10:
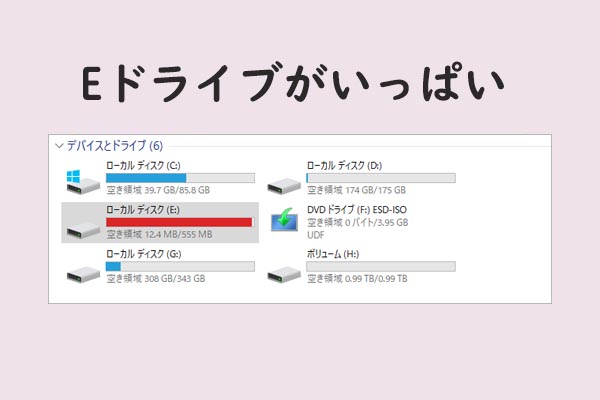
- Monitor Disk Space: Regularly check your disk space to ensure you have enough storage available for your files and applications.
- Optimize Disk Space: Use Disk Cleanup and other tools to remove unnecessary files and free up disk space.
- Defragment Hard Drives: Defragmenting hard drives can improve performance by organizing fragmented files.
- Back Up Important Data: Regularly back up your important files to an external drive or cloud storage service.
- Use Disk Management Tool: Utilize the Disk Management tool to create, delete, and manage partitions and drive letters.
Conclusion:
Understanding drive letters and storage management in Windows 10 is crucial for efficient file organization, data security, and system performance. By avoiding misconceptions and applying best practices, users can optimize their storage space and ensure a smooth computing experience.
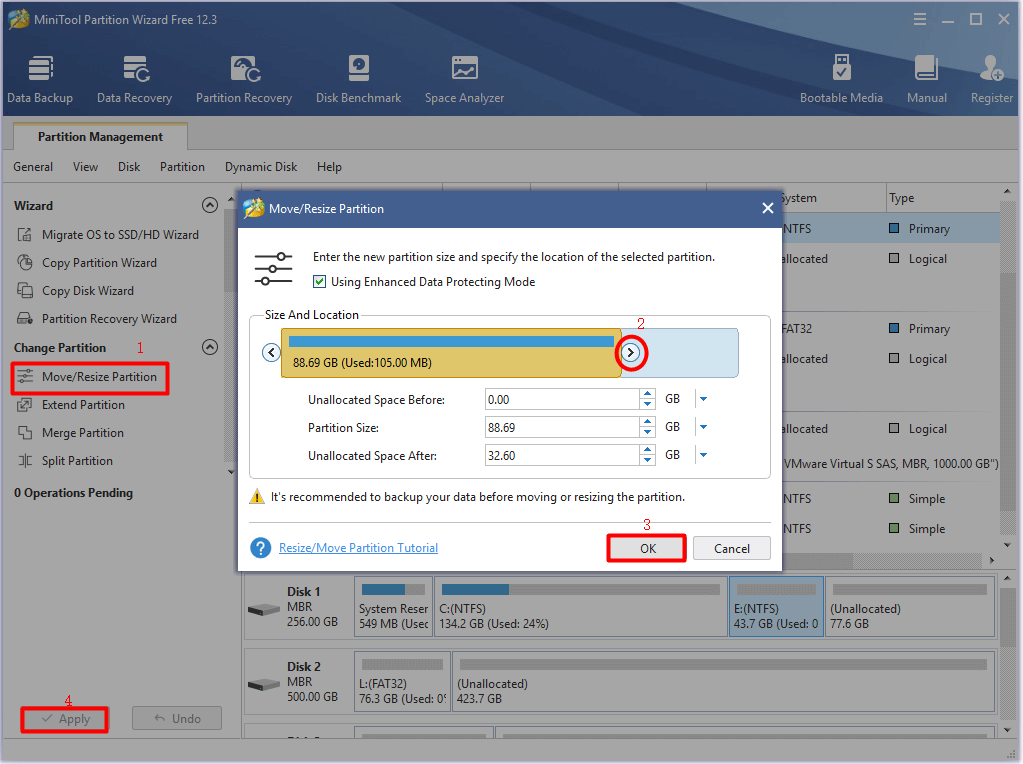
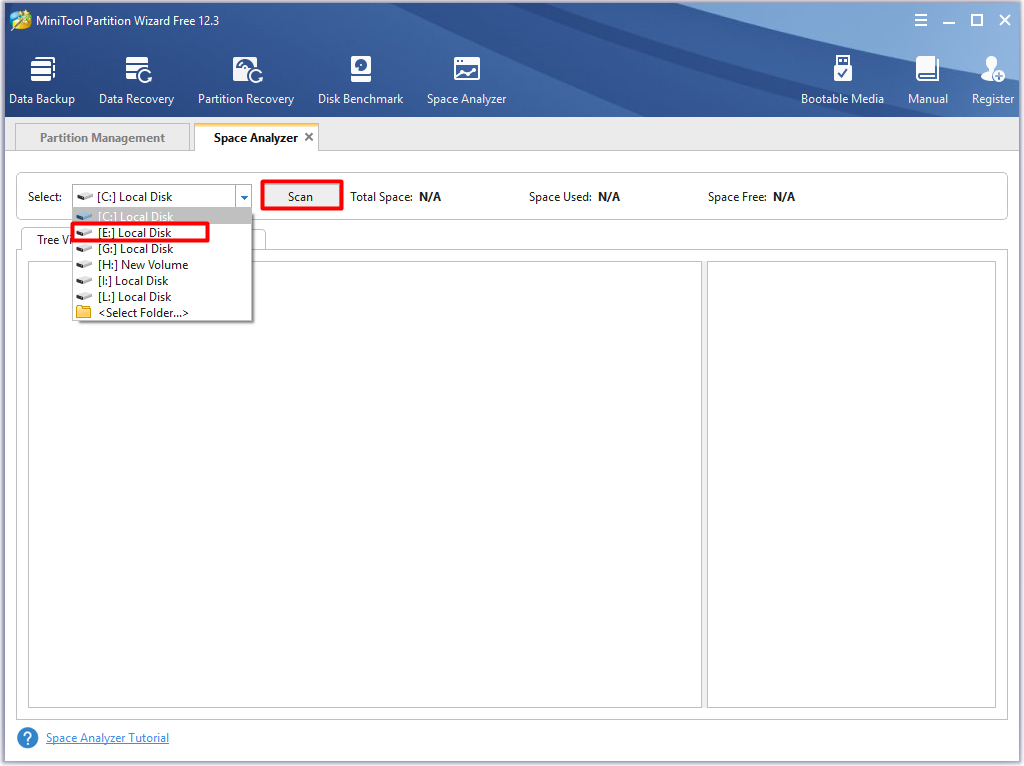
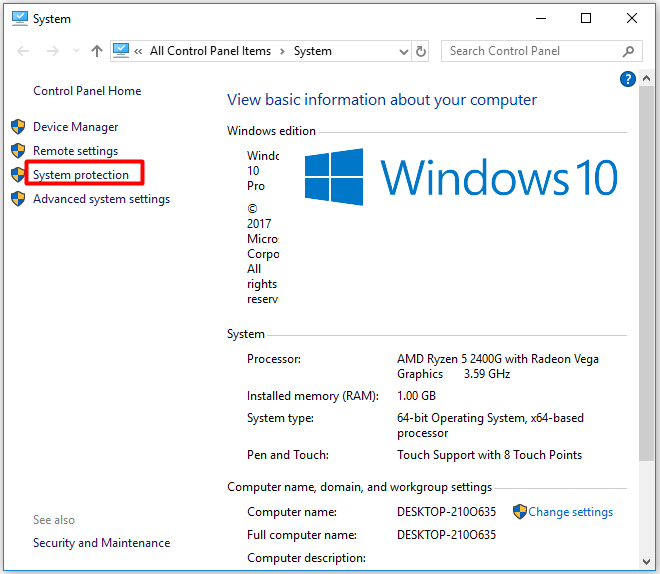
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Windows 10 "E Drive" and its Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!