Understanding the EFS UI Application in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the EFS UI Application in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the EFS UI Application in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the EFS UI Application in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide

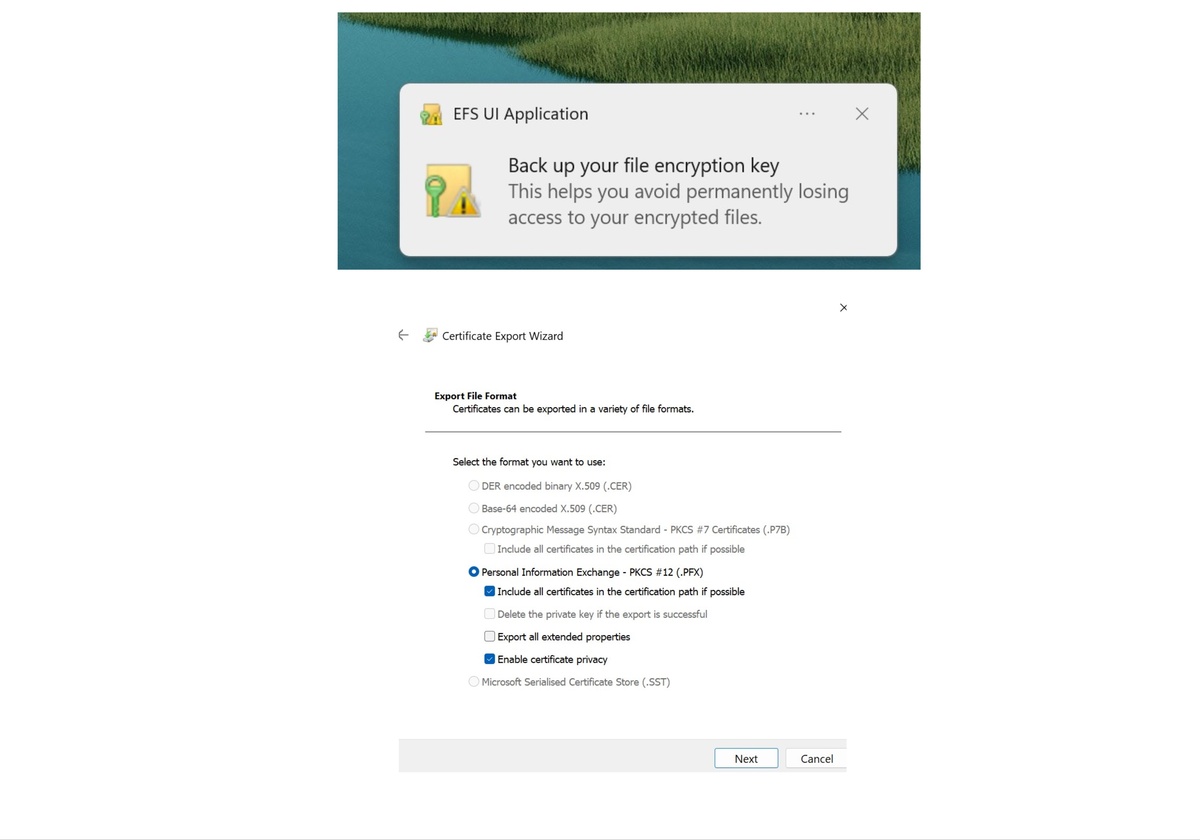
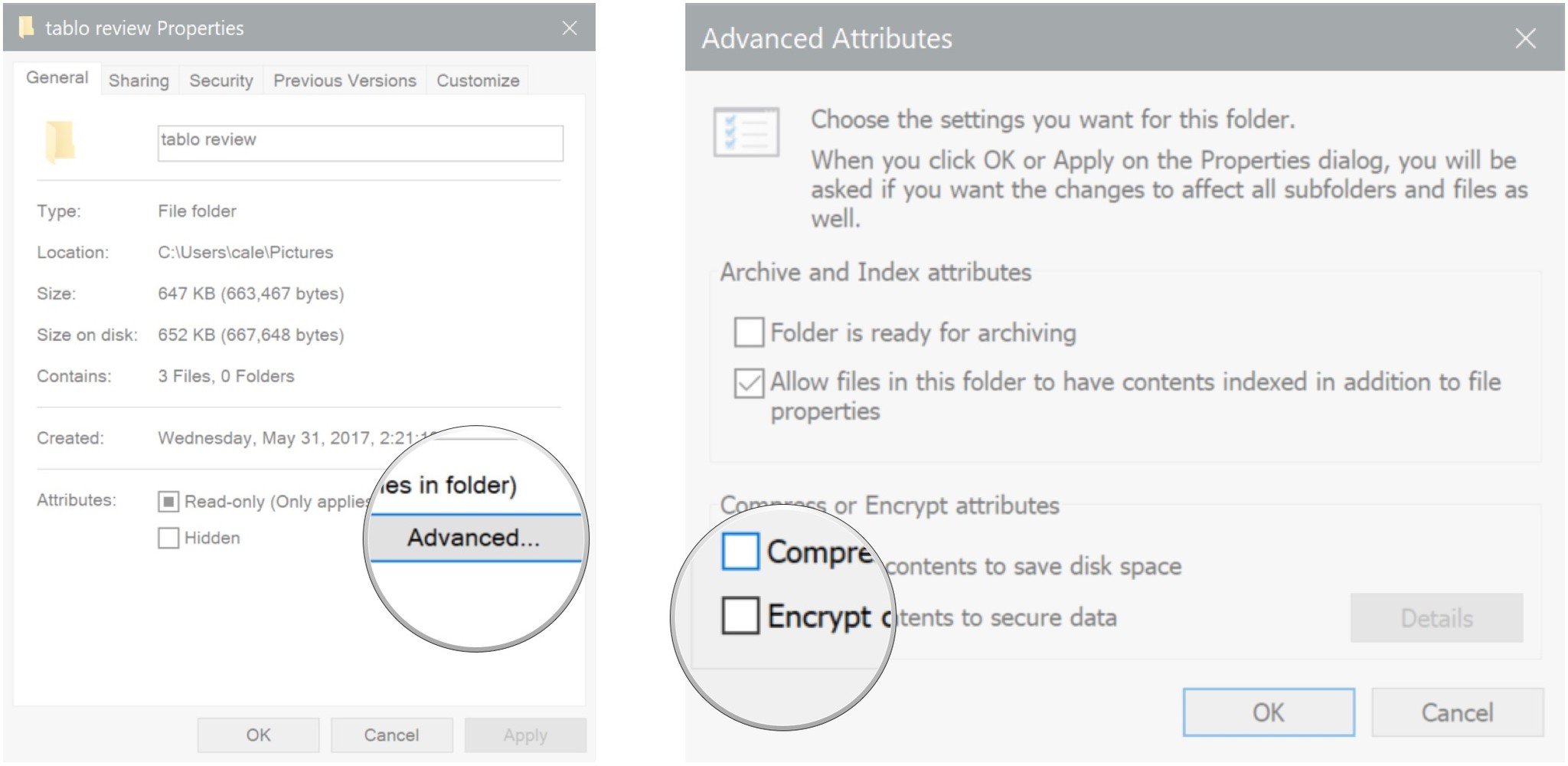
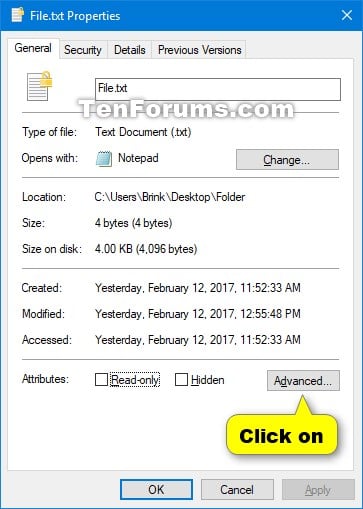
The Windows 10 operating system, known for its user-friendly interface and robust features, offers a powerful tool for data encryption: Encrypting File System (EFS). This built-in feature allows users to safeguard sensitive data stored on their local drives, ensuring its privacy and security. EFS, however, is not directly accessible through a dedicated graphical user interface (GUI) within Windows 10. Instead, it relies on the command-line interface (CLI) and relies on other tools for its management.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of EFS, its functionalities, and its importance in securing sensitive data within the Windows 10 environment. It will explore the methods of managing EFS, its strengths and limitations, and offer insights into its practical applications.
EFS: A Foundation for Data Security
EFS employs a robust encryption mechanism, utilizing the Windows Data Protection API (DPAPI) and the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm. When EFS is enabled, files and folders are encrypted using a unique key, rendering them inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. This key is tied to the user’s account, ensuring that only authorized users with the correct credentials can decrypt and access the protected data.
Why is EFS Important?
In a world increasingly reliant on digital information, data security is paramount. EFS plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive information by:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data, preventing unauthorized disclosure or breaches.
- Integrity: Protecting data from unauthorized modifications or tampering, maintaining its authenticity and reliability.
- Compliance: Meeting industry regulations and legal requirements for data protection, such as HIPAA for healthcare or GDPR for personal data.
Managing EFS: A Deeper Dive
While EFS lacks a dedicated GUI, its management can be accomplished through various methods:
-
Command-line Interface (CLI): The
ciphercommand is the primary tool for managing EFS. It allows users to encrypt, decrypt, and manage EFS-protected files and folders. - Group Policy: Administrators can utilize Group Policy to enforce EFS settings across an organization, ensuring consistent security practices.
- Third-Party Tools: Several third-party applications offer graphical interfaces for managing EFS, simplifying the process for users unfamiliar with command-line operations.
The Limitations of EFS
Despite its strengths, EFS has certain limitations that users should be aware of:
- Limited Scope: EFS primarily focuses on protecting data stored on local drives. It does not extend protection to data stored on network shares or cloud services.
- Key Management: The reliance on user accounts for key management can pose challenges in scenarios involving user account changes or deletions.
- Performance Impact: Encryption and decryption processes can impact system performance, particularly when dealing with large files or frequent data access.
Practical Applications of EFS
EFS proves valuable in various scenarios, including:
- Personal Data Protection: Securing sensitive documents, financial records, or personal information on personal computers.
- Business Data Security: Protecting confidential business data, such as customer records, financial reports, or intellectual property.
- Government and Enterprise Security: Meeting regulatory requirements and protecting sensitive data in government agencies and large enterprises.
FAQs Regarding EFS
1. Can EFS protect data stored on external drives?
EFS primarily protects data stored on local drives. To protect data on external drives, consider using third-party encryption software or BitLocker drive encryption.
2. What happens to encrypted data if a user account is deleted?
Data encrypted using EFS remains encrypted and inaccessible without the corresponding user account. This can be a challenge if the user account is deleted or the password is forgotten.
3. Can EFS be used to encrypt entire drives?
While EFS does not directly encrypt entire drives, BitLocker Drive Encryption, another feature within Windows 10, offers full-disk encryption capabilities.
4. Is EFS compatible with all file systems?
EFS is primarily compatible with the NTFS file system. It does not work with FAT32 or exFAT file systems.
5. How can I recover encrypted data if I forget my password?
Recovering encrypted data without the password is extremely difficult. It is crucial to maintain good password hygiene and consider using a password manager for secure storage.
Tips for Utilizing EFS Effectively
- Implement EFS selectively: Only encrypt files and folders containing truly sensitive data to minimize performance impact.
- Use strong passwords: Choose complex and unique passwords for user accounts to protect encrypted data.
- Backup encrypted data: Regularly backup encrypted data to ensure recovery in case of data loss or system failure.
- Consider alternative solutions: For data protection beyond local drives, explore cloud storage with built-in encryption or third-party encryption software.
- Stay informed about security updates: Regularly update Windows 10 to benefit from security patches and improvements that enhance EFS’s effectiveness.
Conclusion
EFS provides a powerful and convenient method for encrypting sensitive data within the Windows 10 environment. It offers a robust layer of security, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. However, it is crucial to understand its limitations and consider its appropriate applications. By implementing best practices and utilizing EFS strategically, users can significantly enhance the security of their data, safeguarding it from unauthorized access and potential threats.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the EFS UI Application in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!