Understanding Malware and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Malware and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Malware and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Malware and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
The question of whether Windows 11 harbors malware is a complex one, demanding a nuanced understanding of both the operating system and the nature of malicious software. While no operating system is inherently immune to malware, Windows 11, like its predecessors, offers robust security features and a continuously evolving defense against threats. This article aims to demystify the relationship between Windows 11 and malware, providing a comprehensive overview of the threats, vulnerabilities, and countermeasures involved.
What is Malware?
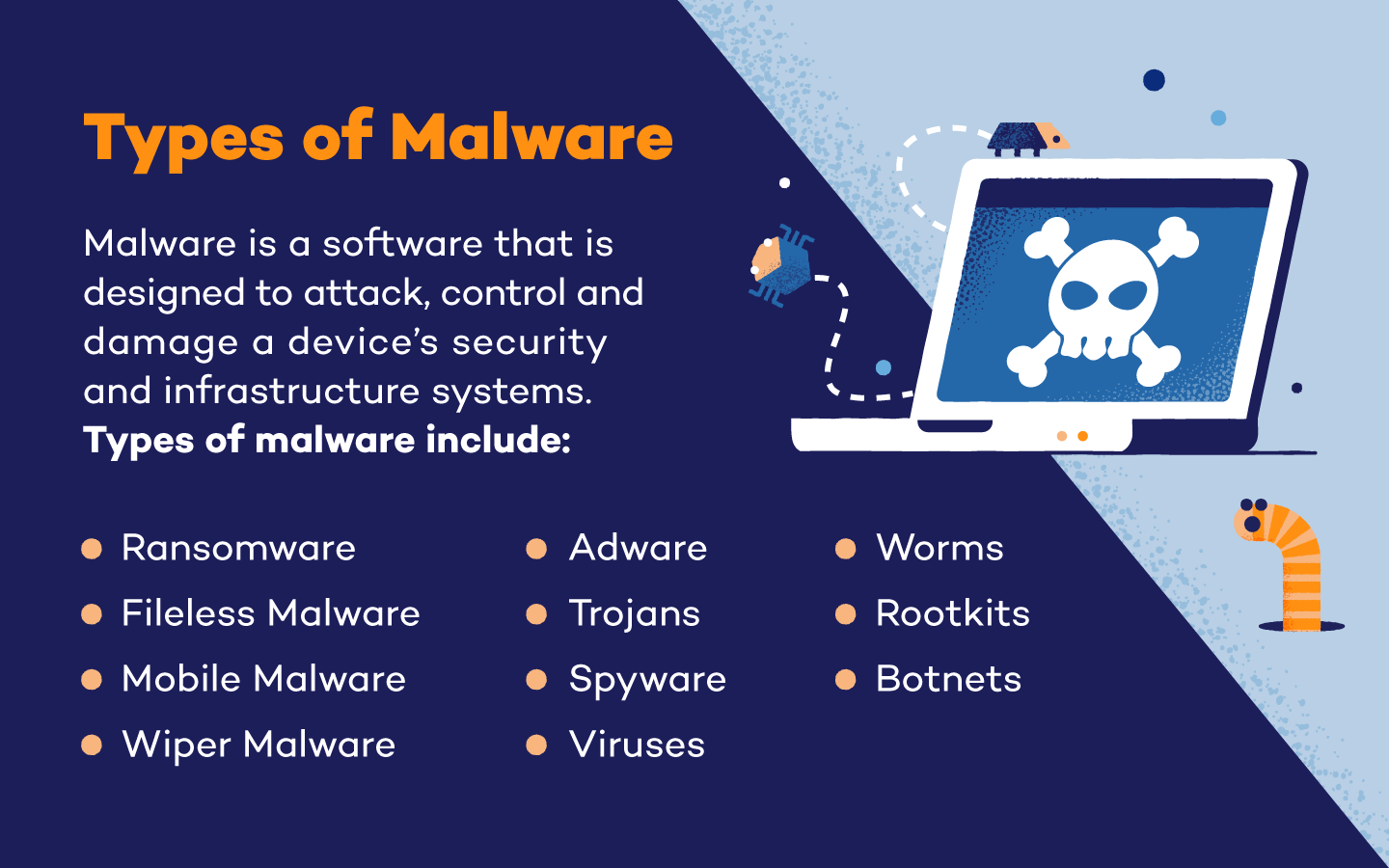
Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a broad spectrum of harmful programs designed to infiltrate and compromise computer systems. These programs can manifest in various forms, each with its unique modus operandi:
- Viruses: These programs replicate themselves, spreading to other files and programs, often causing damage to data or system performance.
- Worms: Similar to viruses, worms can self-propagate, but they spread across networks, exploiting vulnerabilities in network protocols to infect multiple devices.
- Trojan Horses: Disguised as legitimate software, Trojan horses often contain malicious payloads that can steal data, control the infected system, or launch further attacks.
- Spyware: Designed to monitor and steal user data, spyware can record keystrokes, capture screenshots, or track browsing history.
- Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts a user’s files, rendering them inaccessible, and demands a ransom for decryption.
- Adware: This intrusive software displays unwanted advertisements, often without the user’s consent, and can sometimes lead to other malware infections.
Windows 11 Security Features:
Windows 11 incorporates a comprehensive suite of security features designed to mitigate the risks posed by malware:
- Windows Defender: This built-in antivirus program provides real-time protection against known threats, automatically scanning files and applications for malicious code.
- Windows Security: This centralized security hub offers a unified interface for managing various security settings, including firewall control, virus protection, and device security.
- Microsoft Defender SmartScreen: This feature helps protect against phishing websites and malicious downloads by analyzing website URLs and file reputations.
- Windows Sandbox: This secure environment allows users to safely run untrusted applications without affecting the main operating system.
- Microsoft Store: This curated app store provides a platform for verified applications, reducing the risk of downloading malware from untrusted sources.
Vulnerabilities and Exploits:
Despite these robust security measures, Windows 11, like any software, is not impervious to vulnerabilities. Exploits targeting zero-day vulnerabilities, which are previously unknown flaws, can bypass existing security measures and allow malware to gain access to the system.
Factors Contributing to Malware Infections:
Several factors contribute to malware infections, including:
- User Behavior: Clicking on suspicious links, downloading files from untrusted sources, or opening attachments from unknown senders can expose systems to malware.
- Outdated Software: Failing to update software regularly can leave systems vulnerable to exploits targeting known vulnerabilities.
- Weak Passwords: Using weak or easily guessable passwords can make accounts susceptible to brute-force attacks, allowing malware to gain unauthorized access.
- Unsecured Networks: Connecting to public Wi-Fi networks without proper security measures can expose devices to malware lurking on the network.
Preventing Malware Infections:
To minimize the risk of malware infections, users should adopt a proactive approach to security:
- Install and Update Security Software: Ensure that antivirus software, such as Windows Defender, is installed and regularly updated to protect against the latest threats.
- Practice Safe Browsing: Be wary of suspicious websites, avoid clicking on suspicious links, and verify the legitimacy of websites before providing personal information.
- Be Cautious with Downloads: Only download files from trusted sources and use a reputable antivirus program to scan downloaded files before opening them.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create complex and unique passwords for all accounts, and consider using a password manager to securely store them.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update operating systems, applications, and drivers to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Be Aware of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of emails or messages requesting personal information, and avoid clicking on links from unknown senders.
- Use a Firewall: Enable the built-in firewall to block unauthorized network access and prevent malware from connecting to external servers.
- Consider Additional Security Measures: Explore advanced security tools, such as a VPN for secure internet access, and a firewall for enhanced network protection.
Understanding the Importance of Cybersecurity:
The threat posed by malware is not to be taken lightly. Malware infections can lead to various consequences, including:
- Data Loss: Malware can steal sensitive information, such as financial details, passwords, and personal files.
- System Damage: Malware can corrupt files, damage system performance, or even render the computer unusable.
- Financial Loss: Malware can be used to steal money, either through fraudulent transactions or by holding data hostage through ransomware.
- Identity Theft: Stolen personal information can be used to create fake identities and commit fraud.
- Privacy Violation: Malware can monitor user activity, collect personal data, and track online behavior.
FAQs
Q: Can I get malware from downloading apps from the Microsoft Store?
A: While the Microsoft Store is a curated platform, it’s not entirely immune to malware. Although the store’s vetting process helps reduce the risk, malicious apps can sometimes slip through. It’s still essential to be cautious and research app developers before downloading.
Q: Does Windows 11 come pre-installed with malware?
A: No, Windows 11 itself does not come pre-installed with malware. However, it’s crucial to understand that the operating system is not a guarantee against infections. Malware can be introduced through various means, such as malicious websites, infected downloads, or vulnerabilities exploited by hackers.
Q: Can I remove malware from my Windows 11 computer myself?
A: While removing some malware might seem possible, attempting to do so manually can be risky. Malicious software often employs advanced techniques to hide itself and can be difficult to detect and remove without specialized tools. It’s generally recommended to use reputable antivirus software and follow their instructions for removing malware.
Q: How can I tell if my Windows 11 computer is infected with malware?
A: Several signs can indicate a potential malware infection:
- Slow Performance: If your computer is running significantly slower than usual, it could be a sign of malware consuming system resources.
- Unexpected Programs: If you notice unfamiliar programs running in the background or see strange icons on your desktop, it might be a sign of malware.
- Frequent Pop-ups: Excessive pop-up advertisements, especially those that appear even when you’re not browsing the internet, can indicate adware or other intrusive software.
- Unusual Network Activity: If your internet connection suddenly becomes slow or you notice high network activity, it could be a sign of malware communicating with external servers.
- Data Loss or Corruption: If you experience unexplained file deletions or data corruption, it could be a result of malware tampering with your files.
Tips for Protecting Your Windows 11 System:
- Keep your operating system and software updated: Regularly check for and install updates to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use a strong password manager: Store and manage your passwords securely to avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts.
- Be cautious of email attachments: Avoid opening attachments from unknown senders or those with suspicious content.
- Use a VPN for public Wi-Fi: Encrypt your internet traffic when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks to protect your data from snooping.
- Regularly back up your data: Create backups of important files to recover data in case of a malware infection.
- Educate yourself about cybersecurity: Stay informed about the latest threats and best practices for protecting your devices.
Conclusion:
While Windows 11 offers robust security features, it’s essential to understand that no operating system is completely immune to malware. By adopting proactive security measures, staying informed about threats, and practicing safe computing habits, users can significantly reduce their risk of malware infections. Remember that cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and continuous effort to protect your data and devices from harm.



![[Infographic] Types of Malware - Enabler Space](https://www.enablerspace.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Types-of-malware-infographic.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Malware and Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!