Understanding High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
![How To Fix High Disk Usage in Windows 10 [Solved] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/JFe_dl8-lyU/maxresdefault.jpg)
The Windows 10 operating system is renowned for its user-friendly interface and robust functionality. However, users often encounter an issue that can significantly impact their computing experience: high disk usage. This phenomenon, often characterized by a disk drive persistently operating at near 100% capacity, can lead to system sluggishness, application freezes, and overall performance degradation. Understanding the root causes of this issue and implementing effective solutions is crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient computing environment.
Causes of High Disk Usage in Windows 10:
High disk usage in Windows 10 can be attributed to a variety of factors, ranging from resource-intensive applications to underlying system processes. Identifying the specific culprit is the first step towards resolving the issue. Here are some common causes:
1. Resource-Intensive Applications:
- Large File Transfers: Transferring large files, such as videos, images, or software installations, can temporarily strain the disk drive.
- Background Processes: Some applications, even when not actively used, may run background processes that consume significant disk resources. This can include antivirus software, cloud synchronization tools, or software updates.
- Disk-Intensive Applications: Certain applications, such as video editing software, photo editing programs, or gaming platforms, are inherently disk-intensive due to their reliance on large file sizes and complex processing.
2. System Processes:
- Disk Defragmentation: This process, which rearranges fragmented data on the hard drive to improve access speed, can temporarily increase disk usage.
- Indexing: Windows Indexing Service creates an index of files and folders to facilitate faster searches. This process can be resource-intensive, particularly when indexing large datasets.
- System Updates: Windows updates, including feature updates and security patches, can require significant disk space and processing power, leading to temporary high disk usage.
3. Disk Errors and Faults:
- Bad Sectors: Damaged sectors on the hard drive can cause the system to repeatedly attempt to access and write data to these sectors, leading to high disk usage.
- File System Errors: Errors in the file system, such as corruption or inconsistencies, can also contribute to high disk usage.
- Hardware Issues: Physical problems with the hard drive, such as failing components or faulty connections, can lead to increased disk activity and performance degradation.
4. Insufficient Disk Space:
- Limited Storage: When the hard drive is nearing its storage capacity, the system may struggle to allocate sufficient space for new files and processes, resulting in high disk usage.
- Excessive Temporary Files: Temporary files created by applications and system processes can accumulate over time, consuming valuable disk space and contributing to high disk usage.
Diagnosing High Disk Usage:
To effectively address high disk usage, it is essential to identify the specific cause. Windows 10 provides various tools and methods to diagnose the issue:
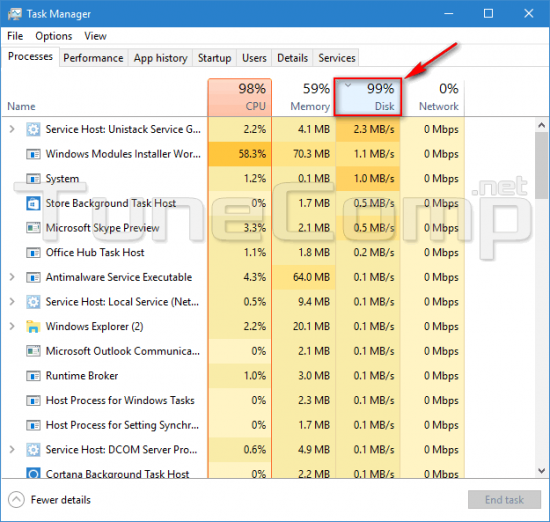
1. Task Manager:
- Open Task Manager: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Navigate to the Performance Tab: Select the "Performance" tab.
- Monitor Disk Usage: Observe the "Disk" section, which displays the overall disk usage in real-time.
- Identify Resource-Intensive Processes: Click on the "Disk" column to sort processes by disk usage. This will highlight the applications or system processes consuming the most disk resources.
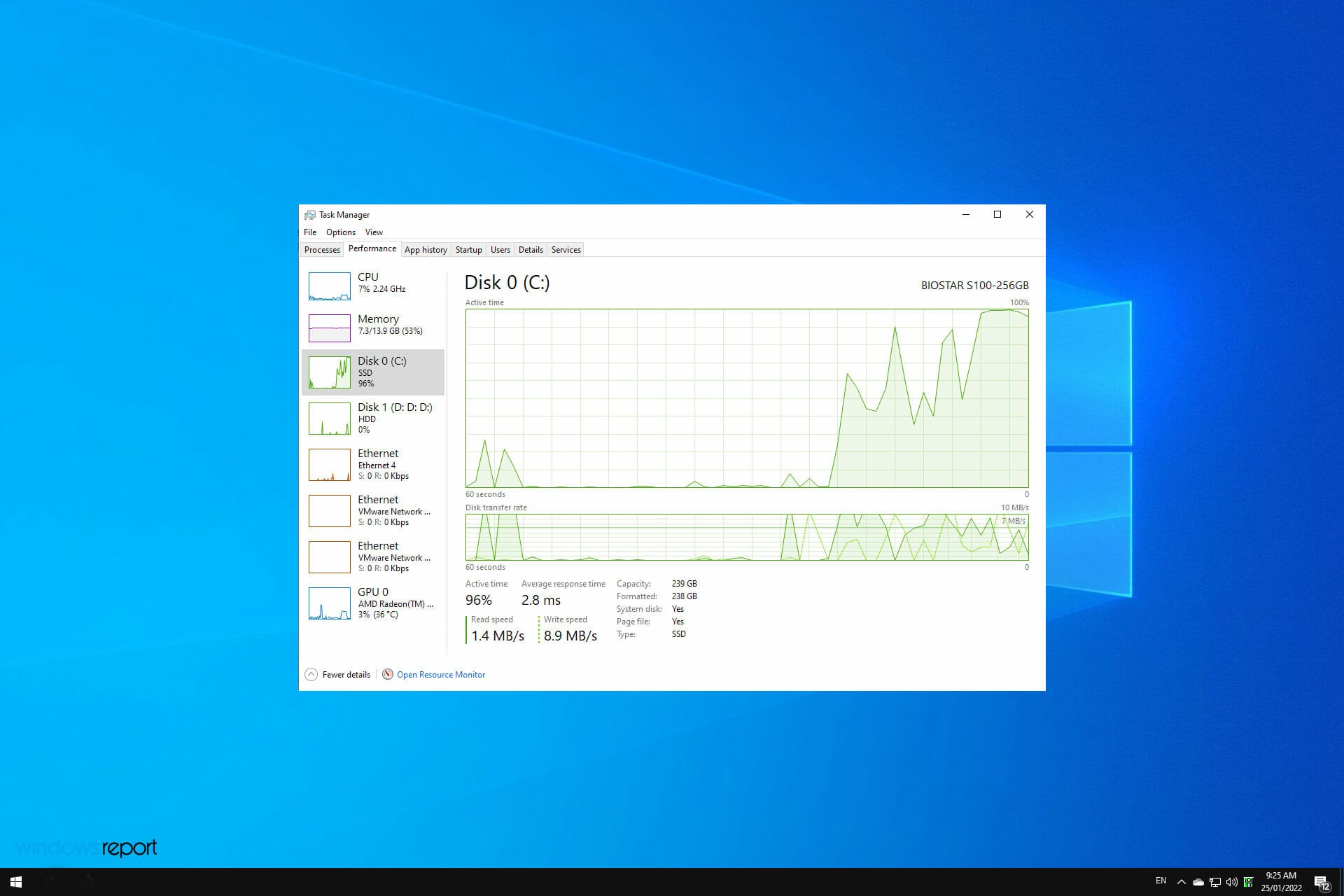
2. Resource Monitor:
- Open Resource Monitor: Search for "Resource Monitor" in the Start menu.
- Navigate to the Disk Activity Tab: Select the "Disk Activity" tab.
- Analyze Disk Usage: The "Disk Activity" tab provides a detailed breakdown of disk usage, including read and write operations, disk queue length, and I/O requests.
3. Event Viewer:
- Open Event Viewer: Search for "Event Viewer" in the Start menu.
- Navigate to Windows Logs: Expand the "Windows Logs" section.
- Examine System and Application Logs: Review the "System" and "Application" logs for error messages or warnings related to disk activity or performance.
4. Disk Management:
- Open Disk Management: Search for "Disk Management" in the Start menu.
- Check Disk Health: Examine the disk health status and look for any errors or warnings.
- Analyze Disk Space: Analyze the available disk space and identify any potential storage limitations.
Resolving High Disk Usage:
Once the cause of high disk usage is identified, appropriate solutions can be implemented to restore optimal performance:
1. Addressing Resource-Intensive Applications:
- Close Unused Applications: Close any applications that are not actively being used, as they may be running background processes that consume disk resources.
- Disable Unnecessary Background Processes: In Task Manager, navigate to the "Startup" tab and disable any applications that are not essential for system operation.
- Adjust Application Settings: Review the settings of resource-intensive applications and adjust any options that may be consuming excessive disk resources. For example, disable automatic updates or background synchronization.
2. Optimizing System Processes:
- Defragment the Hard Drive: Run a disk defragmentation to rearrange fragmented data and improve disk performance.
- Adjust Indexing Settings: In the "Indexing Options" settings, exclude specific folders or file types from indexing to reduce the workload on the system.
- Schedule System Updates: Schedule system updates for off-peak hours to minimize their impact on system performance.
3. Addressing Disk Errors and Faults:
- Run Disk Check: Use the "chkdsk" command to scan for and repair errors in the file system.
- Replace Faulty Hard Drive: If hardware issues are suspected, replace the faulty hard drive with a new one.
4. Managing Disk Space:
- Delete Unnecessary Files: Remove any unnecessary files, such as temporary files, downloads, or unused applications.
- Move Files to External Storage: Move large files, such as videos or photos, to an external hard drive to free up disk space.
- Upgrade to a Larger Hard Drive: If the hard drive is nearing its storage capacity, consider upgrading to a larger hard drive.
FAQs:
1. What is the normal disk usage in Windows 10?
- Normal disk usage varies depending on system configuration, applications, and user activity. However, a general guideline is that disk usage should remain below 50% during normal operations.
2. Can I disable Windows Indexing Service?
- Disabling Windows Indexing Service can improve performance but may also slow down file searches. It is recommended to disable indexing for specific folders or file types rather than disabling it completely.
3. Is high disk usage a sign of a failing hard drive?
- High disk usage can be a symptom of a failing hard drive, but it is not always the case. Other factors, such as resource-intensive applications or system processes, can also contribute to high disk usage.
4. How can I monitor disk usage in real-time?
- Task Manager and Resource Monitor provide real-time monitoring of disk usage. These tools can help identify resource-intensive processes and diagnose performance issues.
5. What are some common signs of a failing hard drive?
- Slow boot times, frequent application crashes, system freezes, clicking or grinding noises from the hard drive, and error messages related to disk access can be signs of a failing hard drive.
Tips:
- Monitor Disk Usage Regularly: Regularly monitor disk usage to identify potential performance issues.
- Run Disk Maintenance Tasks: Schedule regular disk defragmentation and disk check operations.
- Optimize Application Settings: Adjust application settings to minimize disk usage.
- Keep System Up-to-Date: Ensure that Windows and applications are updated to the latest versions.
- Manage Disk Space: Regularly clean up unnecessary files and manage storage space effectively.
Conclusion:
High disk usage in Windows 10 can significantly impact system performance and user experience. By understanding the common causes and implementing appropriate solutions, users can address this issue and restore optimal performance. Regular monitoring, system optimization, and effective disk space management are crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient computing environment.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-fix-100-disk-usage-in-windows-10-4583918-2-5c3d47fd46e0fb00015065c9.png)
![How To Fix High Disk Usage in Windows 10 [2020 Solution]](https://benisnous.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/How-To-Fix-High-Disk-Usage-in-Windows-10-2020.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!