Understanding CPU Throttling in Windows 11: Balancing Performance and Power Consumption
Related Articles: Understanding CPU Throttling in Windows 11: Balancing Performance and Power Consumption
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding CPU Throttling in Windows 11: Balancing Performance and Power Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding CPU Throttling in Windows 11: Balancing Performance and Power Consumption
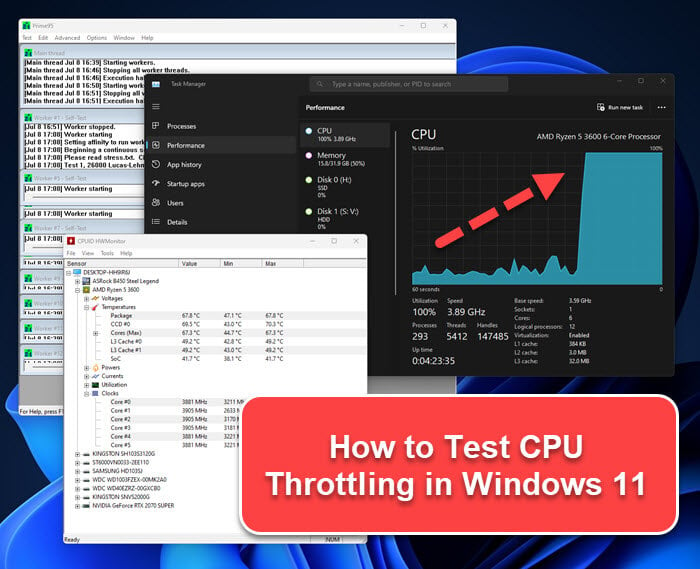
Modern computers are designed to be versatile machines, capable of handling demanding tasks like gaming and video editing while also offering long battery life for mobile devices. This delicate balance is achieved through various mechanisms, including CPU throttling.
CPU throttling is a process where the operating system or hardware dynamically adjusts the clock speed and power consumption of the central processing unit (CPU). This adjustment is made in response to various factors, primarily to manage heat dissipation, conserve power, and prevent system instability. While it might sound like a limitation, CPU throttling is a crucial feature that ensures your computer operates smoothly and efficiently.
How CPU Throttling Works in Windows 11:
Windows 11 utilizes a sophisticated system for managing CPU performance. It incorporates several key components:
- Power Plans: Windows 11 offers various power plans, such as "Balanced," "High Performance," and "Power Saver." Each plan defines different CPU throttling thresholds, balancing performance and power consumption.
- Thermal Management: When the CPU temperature reaches a critical threshold, Windows 11 automatically reduces the CPU clock speed to prevent overheating. This ensures the longevity of the hardware and prevents system crashes.
- Processor Performance States: Windows 11 defines several processor performance states, each with different clock speeds and power consumption levels. The operating system dynamically adjusts the performance state based on the workload and system resources.
- Windows 11 Power Options: These settings allow users to fine-tune CPU throttling behavior. Users can adjust the minimum and maximum processor state, the power saving mode, and the sleep timer.
Benefits of CPU Throttling:
- Improved Battery Life: By reducing CPU power consumption, throttling significantly extends battery life on laptops and tablets.
- Reduced Heat Generation: Throttling prevents excessive heat buildup, extending the lifespan of your CPU and other components.
- Enhanced System Stability: By preventing the CPU from reaching critical temperatures, throttling reduces the risk of system crashes and freezes.
- Optimized Performance: While throttling reduces peak performance, it ensures a smoother and more consistent user experience by preventing sudden performance drops caused by overheating.
When CPU Throttling Can Be a Concern:
While generally beneficial, CPU throttling can sometimes hinder performance, particularly in demanding applications. If you notice significant performance degradation, especially during resource-intensive tasks, it might be due to excessive throttling.
Identifying and Addressing CPU Throttling Issues:
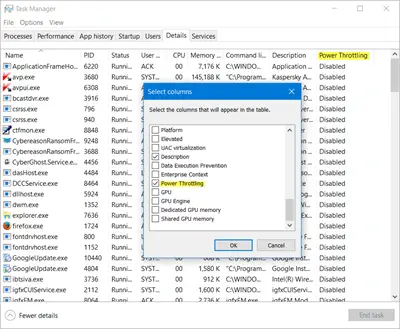
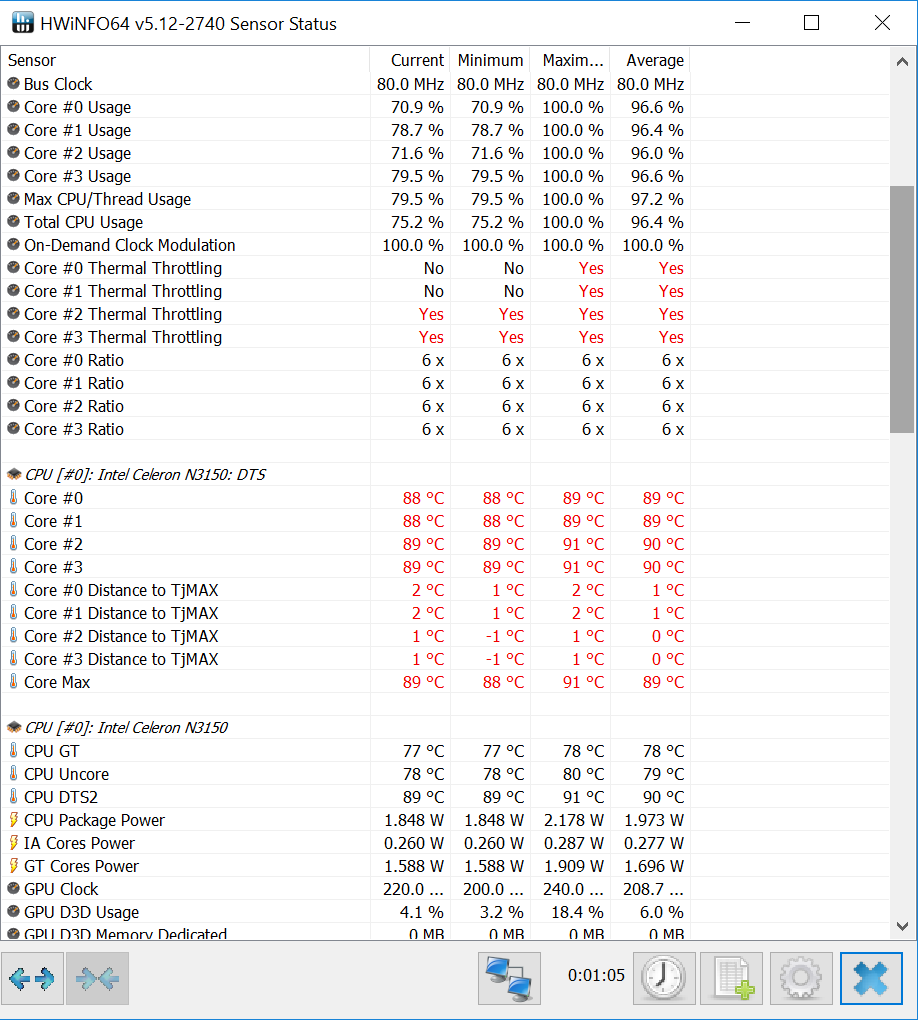
- Monitor CPU Temperature: Use system monitoring tools like Task Manager or third-party software to track CPU temperature. If it consistently reaches high levels, especially during normal usage, it might indicate excessive throttling.
- Check Power Plan Settings: Ensure that your current power plan is appropriate for your needs. If you are experiencing performance issues, consider switching to the "High Performance" plan.
- Adjust Power Options: In the Windows 11 Power Options, you can fine-tune CPU throttling behavior. Increase the minimum processor state to allow for more consistent performance.
- Update Drivers: Outdated drivers can sometimes cause CPU throttling issues. Ensure your drivers are up-to-date, particularly for your motherboard and chipset.
- Consider Hardware Upgrades: If you are experiencing frequent throttling issues, it might be due to insufficient cooling or an outdated CPU. Consider upgrading your cooling system or upgrading to a newer CPU with better thermal performance.
FAQs about CPU Throttling in Windows 11:
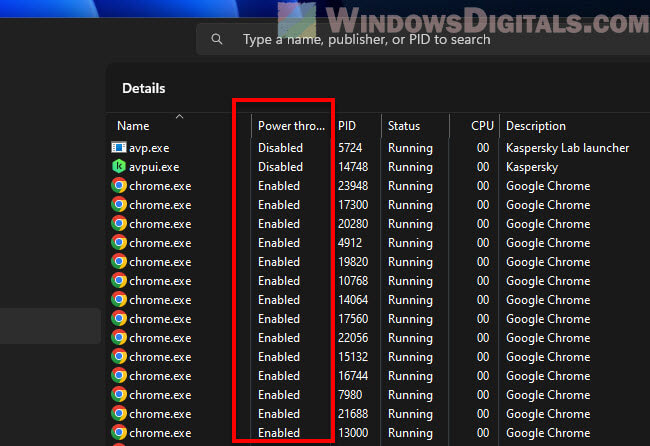
Q: How can I tell if my CPU is being throttled?
A: There are several ways to identify CPU throttling:
- System Performance: Noticeable performance drops, especially during resource-intensive tasks.
- CPU Clock Speed: Observe the CPU clock speed in Task Manager. If it consistently drops below its maximum frequency, it might indicate throttling.
- CPU Temperature: Monitor the CPU temperature using system monitoring tools. High temperatures often indicate throttling.
Q: Is CPU throttling harmful to my computer?
A: No, CPU throttling is a built-in safety mechanism designed to protect your computer from damage. It prevents overheating and ensures the longevity of your hardware.
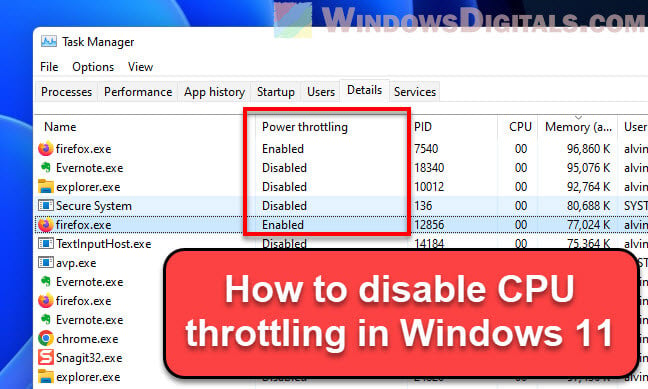
Q: Can I disable CPU throttling in Windows 11?
A: While you can adjust the throttling behavior, completely disabling it is not recommended. It can lead to overheating and potential damage to your CPU.
Q: What is the difference between CPU throttling and CPU undervolting?
A: CPU throttling is a process where the operating system or hardware dynamically adjusts the CPU clock speed and power consumption. Undervolting is a manual process where users lower the voltage supplied to the CPU, which can reduce power consumption and heat generation.
Q: How can I improve CPU performance in Windows 11?
A: To improve CPU performance in Windows 11, consider the following:
- Optimize Power Plan: Choose the "High Performance" power plan for maximum performance.
- Adjust Power Options: Increase the minimum processor state to ensure consistent performance.
- Update Drivers: Keep your drivers up-to-date, particularly for your motherboard and chipset.
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Close applications that are not actively in use to free up resources for demanding tasks.
- Clean Up Your Hard Drive: Remove unnecessary files and programs to improve disk performance.
- Consider Hardware Upgrades: If you are facing persistent performance issues, consider upgrading your CPU, RAM, or SSD.
Tips for Optimizing CPU Performance in Windows 11:
- Use Task Manager: Regularly monitor your CPU usage and identify resource-intensive processes.
- Optimize Background Processes: Disable unnecessary background processes and services to free up resources for demanding tasks.
- Enable Performance Mode: If your system supports it, enable the "Performance Mode" in the power options for maximum CPU performance.
- Keep Your System Clean: Regularly clean your system from malware and unwanted programs to ensure smooth performance.
- Update Windows 11: Ensure your Windows 11 operating system is up-to-date to benefit from the latest performance optimizations and security patches.
Conclusion:
CPU throttling is a vital feature in Windows 11, ensuring a balance between performance and power consumption. While it can sometimes limit peak performance, it plays a crucial role in maintaining system stability, extending battery life, and protecting your hardware. By understanding the principles of CPU throttling and utilizing the available optimization options, users can ensure their Windows 11 systems operate efficiently and reliably.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding CPU Throttling in Windows 11: Balancing Performance and Power Consumption. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!