Understanding CPU Temperature Monitoring in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding CPU Temperature Monitoring in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding CPU Temperature Monitoring in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding CPU Temperature Monitoring in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of computer hardware, maintaining optimal operating temperatures is crucial for ensuring reliable performance and longevity. The Central Processing Unit (CPU), the brain of any computer, is particularly susceptible to overheating, which can lead to performance degradation, system instability, and even hardware damage. Recognizing this, Windows 10 offers several built-in tools and third-party applications designed to monitor CPU temperature, providing users with valuable insights into their system’s thermal health.
The Importance of CPU Temperature Monitoring
Understanding CPU temperature is essential for several reasons:
- Performance Optimization: Elevated CPU temperatures can significantly impact performance. When a CPU operates beyond its optimal temperature range, it may throttle its speed to prevent overheating, resulting in slower processing and reduced responsiveness.
- System Stability: Excessive heat can lead to system instability, causing crashes, freezes, and other unexpected behaviors.
- Hardware Protection: Sustained high temperatures can damage the CPU itself, leading to irreversible hardware failure.
- Early Warning System: Monitoring CPU temperature allows users to identify potential issues before they escalate into critical problems, enabling proactive troubleshooting and preventative measures.
Methods for Monitoring CPU Temperature in Windows 10
Windows 10 provides several methods for monitoring CPU temperature, each with its own strengths and limitations:
1. Task Manager:
- Accessibility: Built-in to Windows 10, readily accessible through Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Functionality: Provides basic CPU temperature information in the "Performance" tab.
- Limitations: Limited to core temperature readings, does not offer detailed historical data or customizable alerts.
2. Event Viewer:
- Accessibility: Accessible through the Windows search bar or the Administrative Tools folder.
- Functionality: Logs system events, including temperature-related warnings and errors.
- Limitations: Not a real-time monitoring tool, relies on system logs for historical data.
3. Command Prompt (PowerShell):
- Accessibility: Accessible through the Windows search bar or the "Run" dialog (Win+R).
- Functionality: Provides CPU temperature information through specific commands like "wmic sensors get Temperature".
- Limitations: Requires familiarity with command-line syntax, not user-friendly for casual users.
4. Third-Party Monitoring Software:
- Accessibility: Widely available from various developers, downloadable from online repositories.
- Functionality: Offers advanced features like real-time monitoring, customizable alerts, historical data visualization, and comprehensive system monitoring.
- Limitations: Requires installation and configuration, potential for resource usage and conflicts with other software.
Popular Third-Party CPU Monitoring Applications:
Several third-party applications provide comprehensive CPU temperature monitoring capabilities, including:
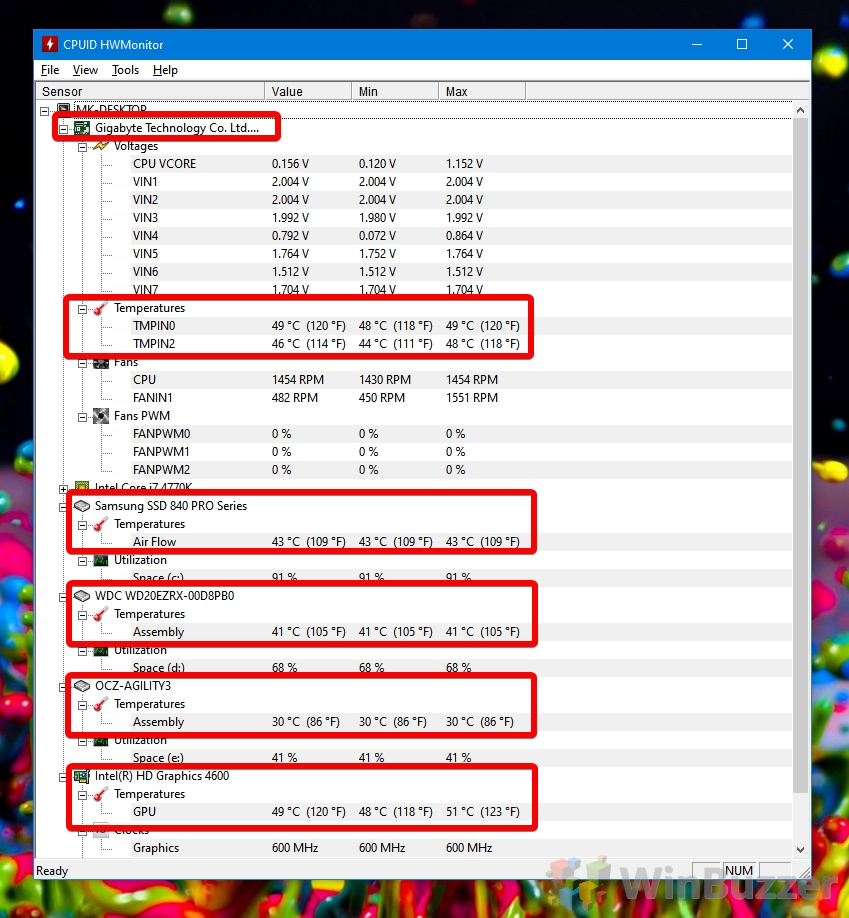
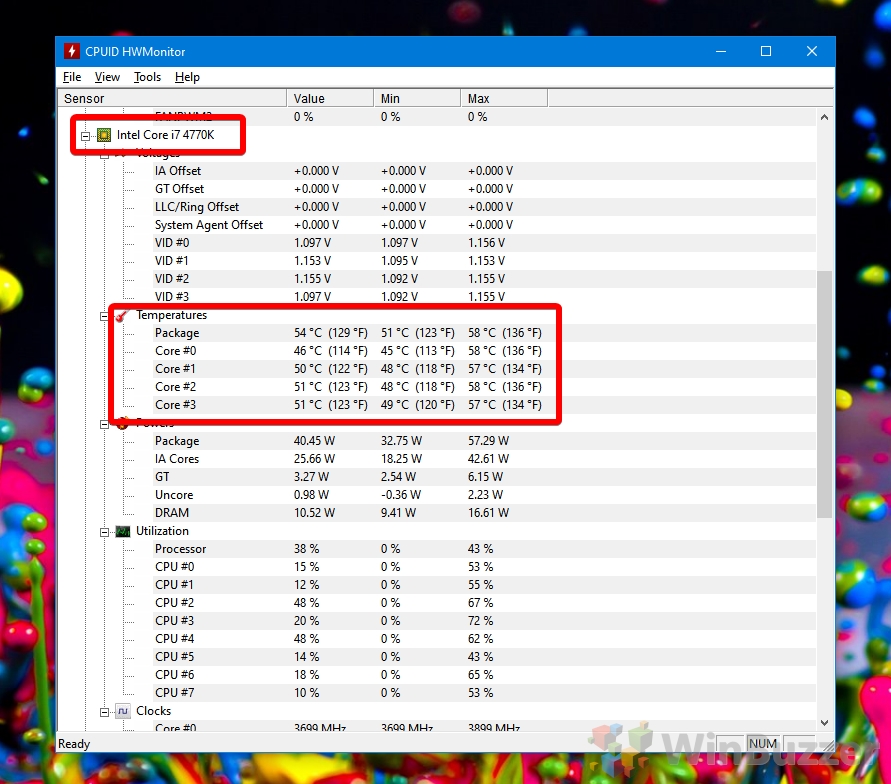
- HWMonitor: Free, open-source software known for its detailed hardware information, including CPU temperature, fan speeds, and voltage readings.
- SpeedFan: Free software that allows users to monitor and control fan speeds based on temperature readings.
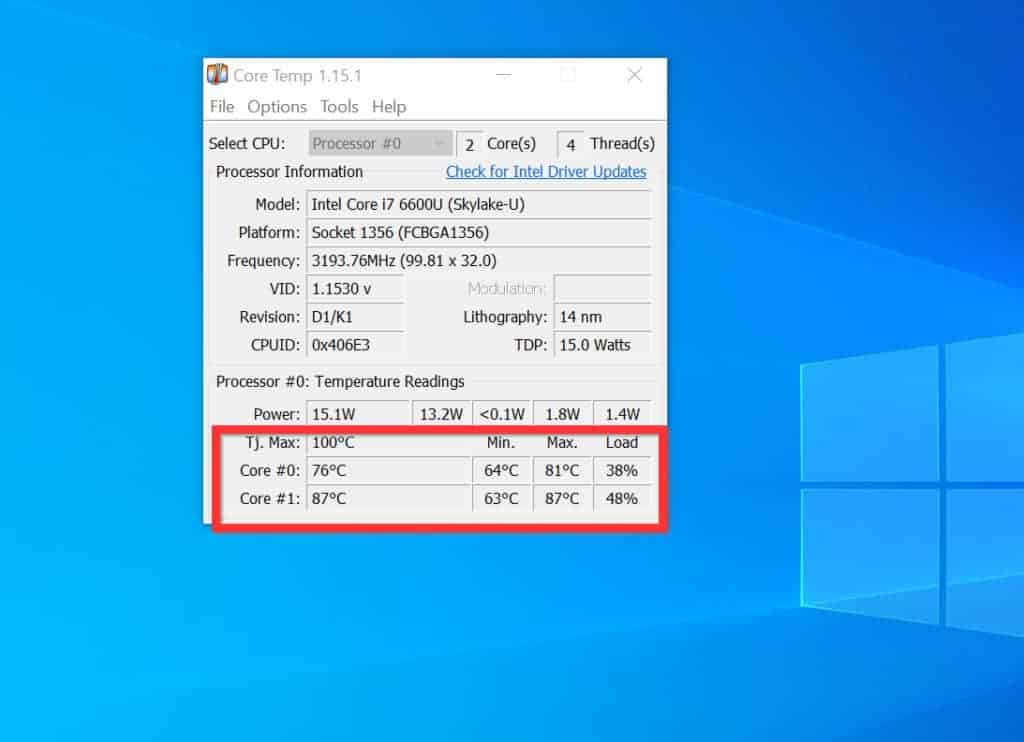
- Core Temp: Free software that provides real-time CPU temperature readings, including individual core temperatures.
- MSI Afterburner: Popular software for overclocking and monitoring, offering detailed hardware monitoring capabilities, including CPU temperature.
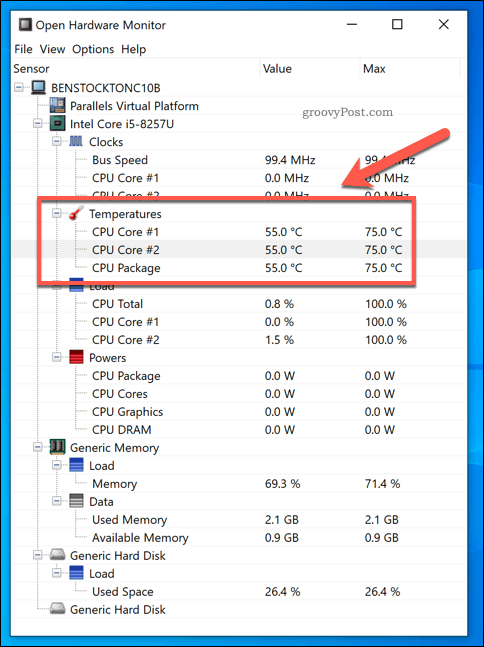
- Open Hardware Monitor: Free, open-source software offering real-time monitoring of various hardware components, including CPU temperature.
Understanding CPU Temperature Readings
CPU temperature readings typically vary depending on the CPU model, workload, and ambient temperature. Generally, the following temperature ranges are considered acceptable:
- Idle: Around 30-40°C (86-104°F).
- Light Load: Up to 50-60°C (122-140°F).
- Heavy Load: Up to 70-80°C (158-176°F).
- Maximum Safe Temperature: Varies depending on the CPU model, but typically around 90-100°C (194-212°F).
Tips for Maintaining Optimal CPU Temperatures
- Proper Airflow: Ensure adequate airflow around the computer case, allowing hot air to escape and cool air to enter.
- Dust Removal: Regularly clean the computer case and internal components to prevent dust buildup, which can hinder airflow and increase temperatures.
- Thermal Paste Application: Ensure proper thermal paste application on the CPU cooler, ensuring optimal heat transfer.
- Fan Speed Control: Adjust fan speeds to maintain optimal temperatures, especially during heavy workloads.
- Overclocking: Avoid excessive overclocking, as it can increase CPU temperatures and potentially damage the hardware.
- System Monitoring: Regularly monitor CPU temperature and identify potential issues before they escalate.
FAQs Regarding CPU Temperature Monitoring
Q: What is the ideal CPU temperature for optimal performance?
A: The ideal CPU temperature varies depending on the specific CPU model and workload. Generally, temperatures below 70°C (158°F) under heavy load are considered acceptable.
Q: What are the signs of an overheating CPU?
A: Signs of an overheating CPU include system crashes, freezes, slow performance, and unusual noises from the computer.
Q: Can I damage my CPU by leaving it running at high temperatures for a long time?
A: Yes, sustained high temperatures can damage the CPU. If temperatures exceed the maximum safe operating temperature for an extended period, it can lead to irreversible hardware failure.
Q: How often should I monitor my CPU temperature?
A: It is advisable to monitor your CPU temperature regularly, especially during heavy workloads or when you suspect potential overheating issues.
Q: Can I use multiple CPU temperature monitoring tools simultaneously?
A: It is generally not recommended to use multiple CPU temperature monitoring tools simultaneously, as they may conflict with each other or consume excessive system resources.
Conclusion
Monitoring CPU temperature is a crucial aspect of computer maintenance, ensuring optimal performance, system stability, and hardware longevity. Windows 10 offers several built-in tools and third-party applications that provide valuable insights into CPU thermal health. By utilizing these resources, users can identify potential overheating issues early on, enabling proactive troubleshooting and preventative measures, ultimately safeguarding their computer systems from performance degradation and hardware damage.
![How To Check CPU Temperature on Windows 10[Updated 2020] - ISORIVER](https://i0.wp.com/isoriver.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/screenshot.3-1.png?resize=515%2C502u0026ssl=1)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding CPU Temperature Monitoring in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!