Understanding and Resolving Memory-Related Errors in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Resolving Memory-Related Errors in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Resolving Memory-Related Errors in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding and Resolving Memory-Related Errors in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding and Resolving Memory-Related Errors in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Anatomy of Memory Errors in Windows 11
- 3.2 Recognizing the Symptoms of Memory Errors
- 3.3 Addressing Memory Errors: A Systematic Approach
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Tips for Preventing Memory Errors
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding and Resolving Memory-Related Errors in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide

Windows 11, like any operating system, relies heavily on system resources, particularly memory (RAM). When the operating system encounters a situation where it lacks sufficient memory to perform its tasks, it signals this issue through various error messages, often collectively referred to as "out of memory" errors. These errors can manifest in different ways, impacting user experience and potentially causing system instability.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of memory-related errors in Windows 11, exploring their causes, symptoms, and effective solutions. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and addressing the root cause, users can effectively mitigate these errors and ensure a smooth and efficient computing experience.
The Anatomy of Memory Errors in Windows 11
Memory errors in Windows 11 are essentially signals that the operating system is struggling to allocate enough RAM to handle the current workload. This can be due to various factors, including:
1. Insufficient RAM: This is the most straightforward cause. If the system’s total RAM is inadequate for the programs and processes running concurrently, the operating system will struggle to allocate sufficient memory, leading to errors.
2. Memory Leaks: Programs can sometimes fail to release memory they no longer need, causing a gradual accumulation of unused memory. This "memory leak" can eventually exhaust available RAM, triggering errors.
3. Hardware Malfunctions: Faulty RAM modules or other hardware components can lead to memory allocation issues, resulting in system errors.
4. Operating System Issues: Corrupted system files or outdated drivers can interfere with memory management, leading to errors.
5. Excessive Program Usage: Running numerous programs simultaneously, especially resource-intensive ones, can easily overwhelm available RAM, causing errors.
6. Background Processes: Numerous background processes, including system updates, virus scans, and other services, can consume significant memory, contributing to errors.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Memory Errors
Memory errors in Windows 11 can manifest in several ways, providing clues about the underlying issue:
1. Slow Performance: The system might become sluggish, applications may load slowly, and responsiveness might be significantly reduced.
2. Frequent Crashes: Programs may crash unexpectedly, or the entire system might freeze and require a restart.
3. Error Messages: Windows may display error messages indicating insufficient memory, such as "Out of memory," "Not enough memory," or "Virtual memory too low."
4. Blue Screen of Death (BSOD): In severe cases, the system might display a blue screen with error codes, indicating a critical system failure often related to memory issues.
5. Unresponsive Applications: Programs may freeze or become unresponsive, indicating they are struggling to access sufficient memory.
Addressing Memory Errors: A Systematic Approach
Resolving memory errors requires a methodical approach, starting with the most likely causes and progressing to more complex solutions:
1. Close Unnecessary Programs: The simplest step is to close any programs you are not actively using. This releases memory back to the system, potentially resolving the issue.
2. Restart Your Computer: Restarting the computer often clears temporary files and frees up memory, allowing the system to operate more efficiently.
3. Check Available RAM: To determine if you have sufficient RAM, navigate to Settings > System > About. Observe the amount of installed RAM and compare it to your system requirements. Consider upgrading your RAM if it is insufficient for your needs.
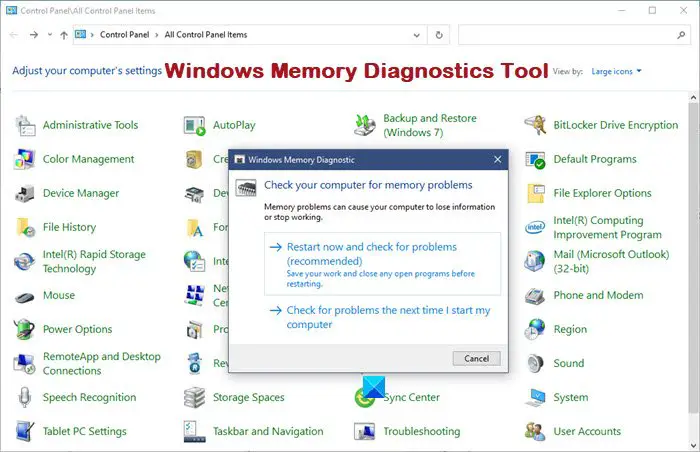
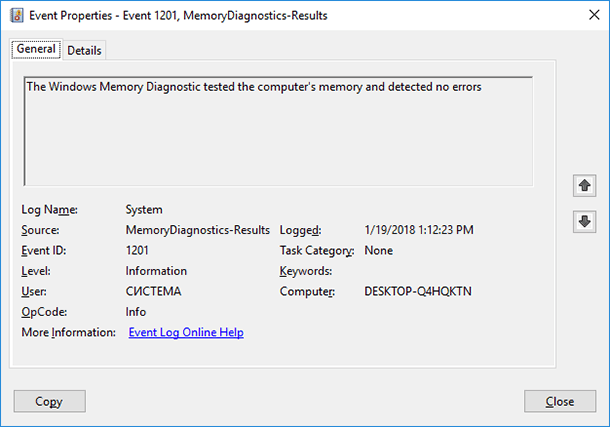
4. Run a Memory Diagnostic Tool: Windows includes a built-in memory diagnostic tool that can detect hardware memory errors. Access it by searching for "Windows Memory Diagnostic" in the search bar. Run the tool and follow the prompts.
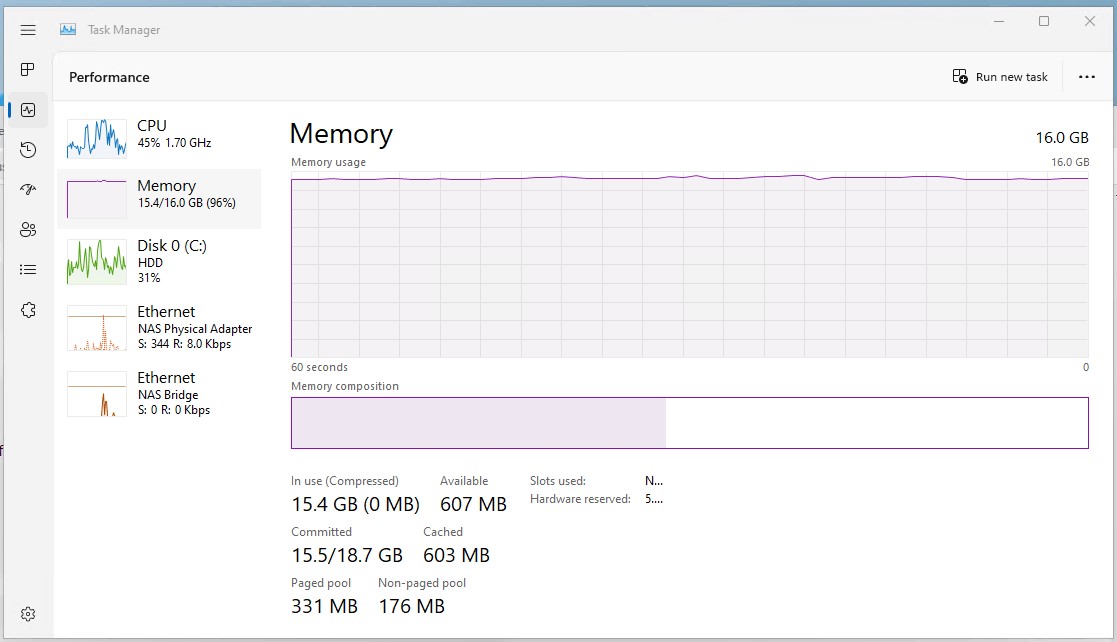
5. Check for Memory Leaks: Utilize tools like Task Manager or Resource Monitor to identify programs consuming excessive memory. If you suspect a memory leak, try updating or reinstalling the program.
6. Scan for Malware: Malware can consume system resources, including memory. Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program to eliminate any malicious software.
7. Optimize System Performance: Windows offers various performance optimization options. Access Settings > System > About > Advanced system settings > Performance. Adjust settings to prioritize performance over visual effects, potentially freeing up memory.
8. Increase Virtual Memory: Virtual memory allows the system to use hard drive space as temporary memory. Navigate to Settings > System > About > Advanced system settings > Performance > Advanced > Change. Adjust virtual memory settings, ensuring sufficient space for optimal performance.
9. Update Drivers: Outdated drivers can cause memory-related issues. Update all drivers, particularly for graphics cards and other resource-intensive components.
10. Repair or Replace Hardware: If memory errors persist despite other efforts, consider inspecting your RAM modules for physical damage. If necessary, replace faulty modules with compatible ones.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between physical memory (RAM) and virtual memory?
A: Physical memory (RAM) is the computer’s primary memory, directly accessible by the CPU. Virtual memory uses hard drive space as temporary memory when physical memory is insufficient.
Q2: How much RAM do I need for Windows 11?
A: The minimum requirement for Windows 11 is 4GB of RAM, but for a smooth experience, 8GB or more is recommended. The actual amount needed depends on the applications you use and your multitasking habits.
Q3: Can I increase RAM on my laptop?
A: Some laptops allow RAM upgrades, while others have soldered RAM that cannot be upgraded. Check your laptop’s specifications or consult the manufacturer’s website for details.
Q4: Is it safe to increase virtual memory?
A: While increasing virtual memory can help temporarily alleviate memory issues, excessive allocation can slow down system performance due to frequent hard drive access.
Q5: How do I know if my RAM is faulty?
A: Running a memory diagnostic tool can identify hardware errors. Symptoms like frequent crashes, blue screens, or slow performance might also indicate faulty RAM.
Tips for Preventing Memory Errors
1. Monitor Resource Usage: Regularly check resource usage using Task Manager or Resource Monitor to identify programs consuming excessive memory.
2. Limit Background Processes: Disable unnecessary background processes and services to free up memory.
3. Avoid Overloading the System: Limit the number of programs running simultaneously, especially resource-intensive ones.
4. Keep Your System Clean: Regularly clean temporary files and unused programs to free up disk space and improve system performance.
5. Regularly Update Windows: Windows updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes, which can enhance memory management.
6. Consider a RAM Upgrade: If you frequently encounter memory errors, upgrading your RAM can provide a long-term solution.
Conclusion
Memory errors in Windows 11, while frustrating, are often resolvable. By understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the symptoms, and employing the systematic approach outlined above, users can effectively address these errors and maintain a stable and efficient computing experience. Regularly monitoring system resources, optimizing system performance, and addressing potential hardware issues proactively can prevent memory errors and ensure a smooth workflow. Remember, a well-maintained system with adequate RAM is the foundation for a seamless and productive Windows 11 experience.
![Fix High RAM Memory Usage Issue on Windows 11/10 [10 Practical Fixes] (2022)](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/high-memory-usage-error.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Resolving Memory-Related Errors in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!