Understanding and Managing Windows 11’s Fast Startup Feature
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing Windows 11’s Fast Startup Feature
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing Windows 11’s Fast Startup Feature. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing Windows 11’s Fast Startup Feature
Windows 11, like its predecessor, Windows 10, incorporates a feature known as "Fast Startup" to expedite the boot process. This feature, designed to enhance user experience by reducing the time required to launch the operating system, operates by employing a hybrid shutdown method. Instead of completely shutting down the system, Fast Startup saves the system’s state to hibernation and then initiates a quick boot sequence upon restart. While this approach generally results in faster boot times, it can occasionally introduce complications and necessitate its disabling.
The Mechanics of Fast Startup
Fast Startup functions by leveraging a combination of hibernation and cold boot techniques. When the system is shut down, it does not fully power down all components. Instead, it saves the current kernel and user session data to a special hibernation file. This file, referred to as the "hiberfil.sys," resides in the root directory of the system drive. Upon restart, the system retrieves the saved data from this file, effectively resuming the previous session instead of starting from scratch. This process significantly reduces the time taken to reach the desktop, giving the impression of a much faster boot.
Circumstances Warranting Fast Startup Disabling
While Fast Startup generally enhances boot speed, certain scenarios may necessitate its deactivation. These scenarios often arise when users encounter specific technical difficulties or require access to advanced system functionalities. Here are some key instances where disabling Fast Startup might be beneficial:
- Troubleshooting System Issues: Fast Startup’s hybrid shutdown approach can sometimes interfere with troubleshooting efforts. For instance, if a system is experiencing boot errors, the saved state from Fast Startup might hinder the identification and resolution of the underlying issue. Disabling Fast Startup ensures a clean boot, allowing for more comprehensive diagnostics.
- Performing System Updates or Upgrades: When updating or upgrading the operating system, a clean boot is often recommended. Fast Startup, by preserving the system’s state, can potentially lead to conflicts or incomplete updates. Disabling Fast Startup ensures a fresh start, minimizing the risk of complications during the update process.
- Accessing Advanced Boot Options: Some advanced boot options, such as the Recovery Console or Safe Mode, might not be accessible with Fast Startup enabled. This is because Fast Startup bypasses the standard boot process, potentially preventing access to these critical tools. Disabling Fast Startup ensures full access to all boot options, providing greater flexibility in troubleshooting or performing system maintenance.
- Utilizing Legacy Boot Devices: Some older hardware, such as legacy hard drives or external devices, may not function optimally with Fast Startup enabled. The hibernation file created by Fast Startup can potentially interfere with these devices, leading to boot errors or data corruption. Disabling Fast Startup eliminates this potential conflict, allowing for seamless operation with legacy hardware.
- Improving System Security: While not directly related to security, disabling Fast Startup can indirectly enhance system security. By preventing the system from entering a hybrid shutdown state, it eliminates a potential vulnerability that could be exploited by malicious actors.
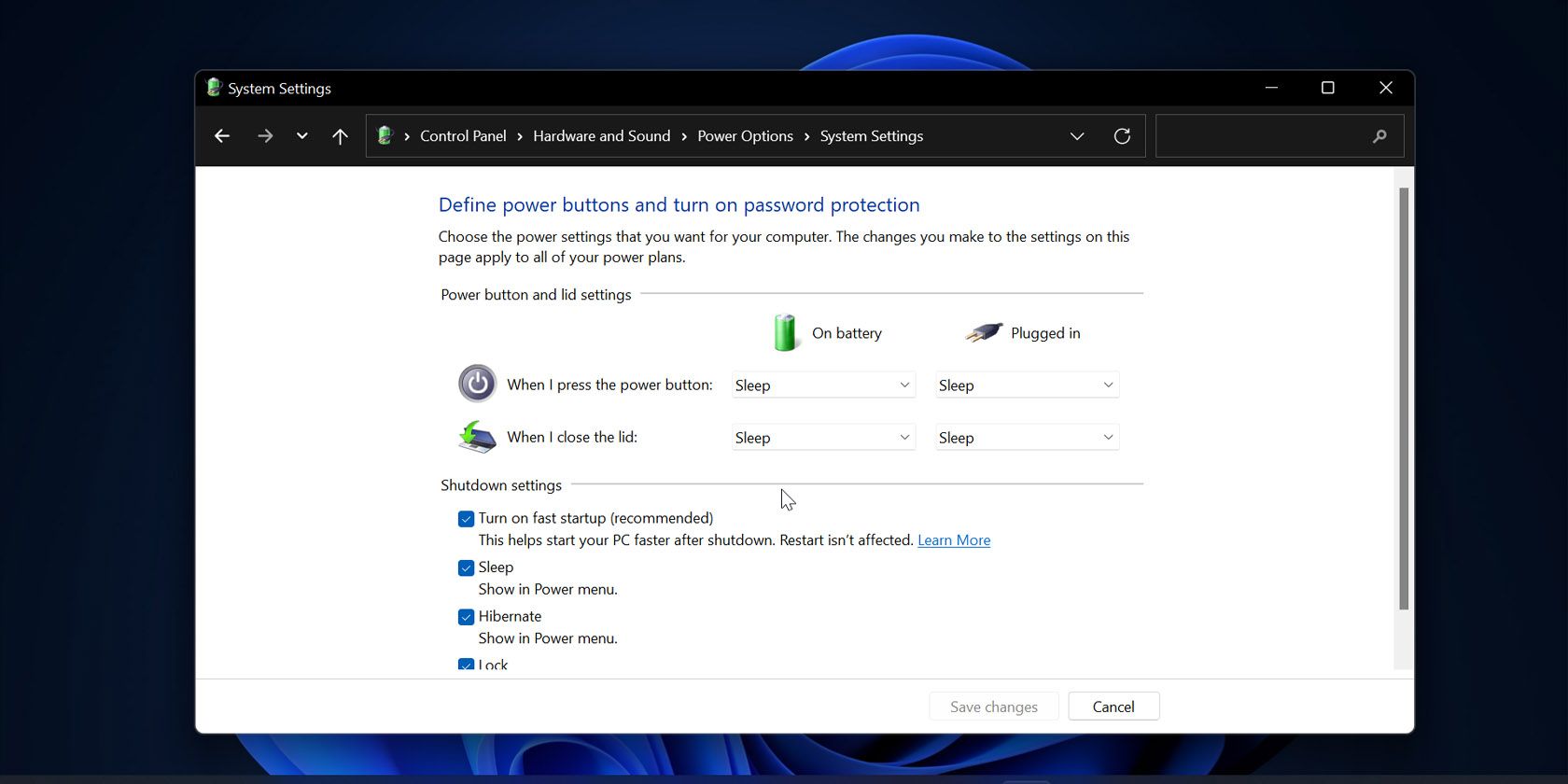
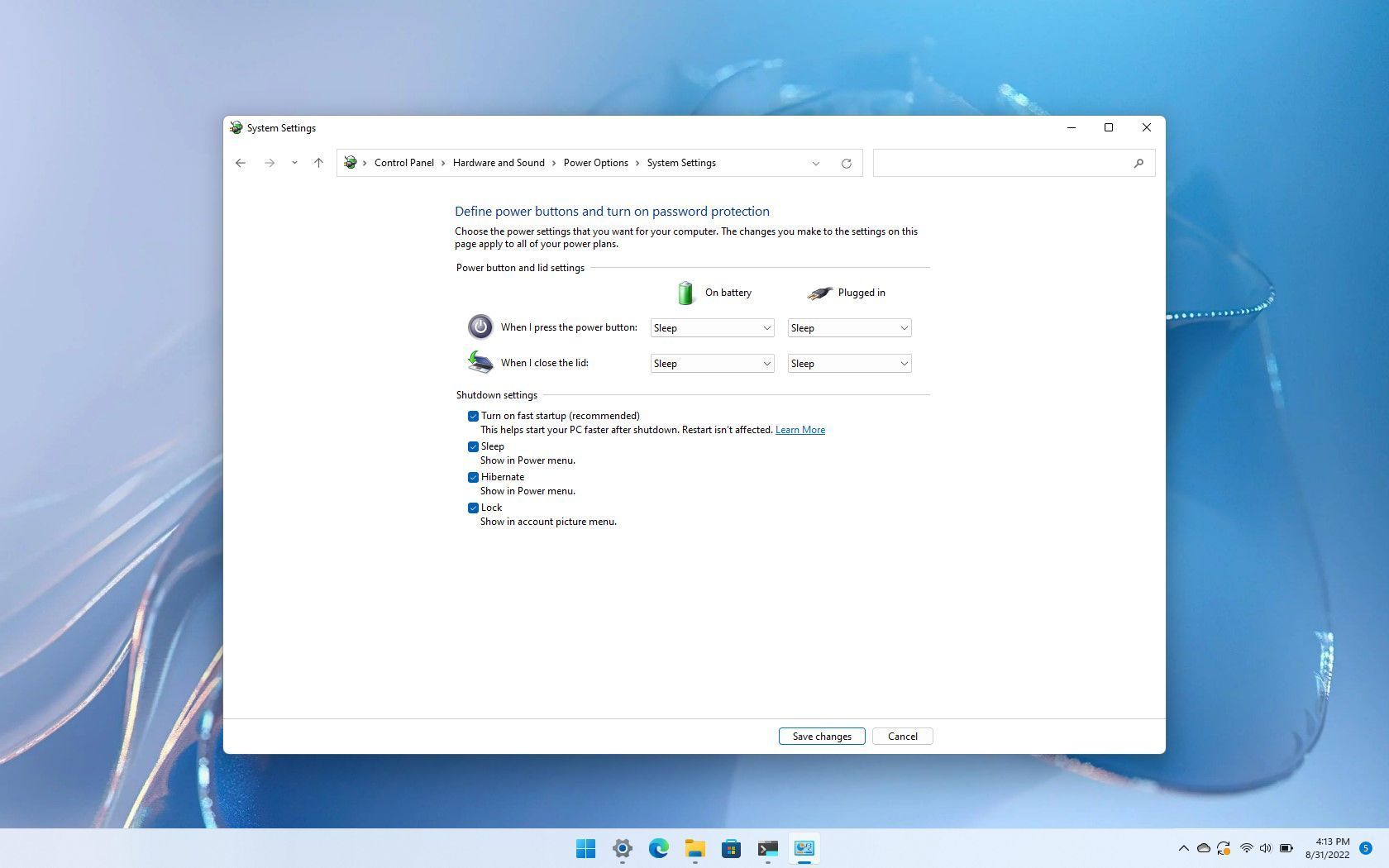
Steps to Disable Fast Startup
Disabling Fast Startup is a straightforward process that can be accomplished through the Windows Control Panel. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Open the Control Panel: Access the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar or by navigating to the "Control Panel" option in the Settings app.
- Navigate to Power Options: Locate the "Power Options" section within the Control Panel. This can typically be found under the "System and Security" category.
- Choose "Choose what the power buttons do": Within the Power Options window, select the option labeled "Choose what the power buttons do."
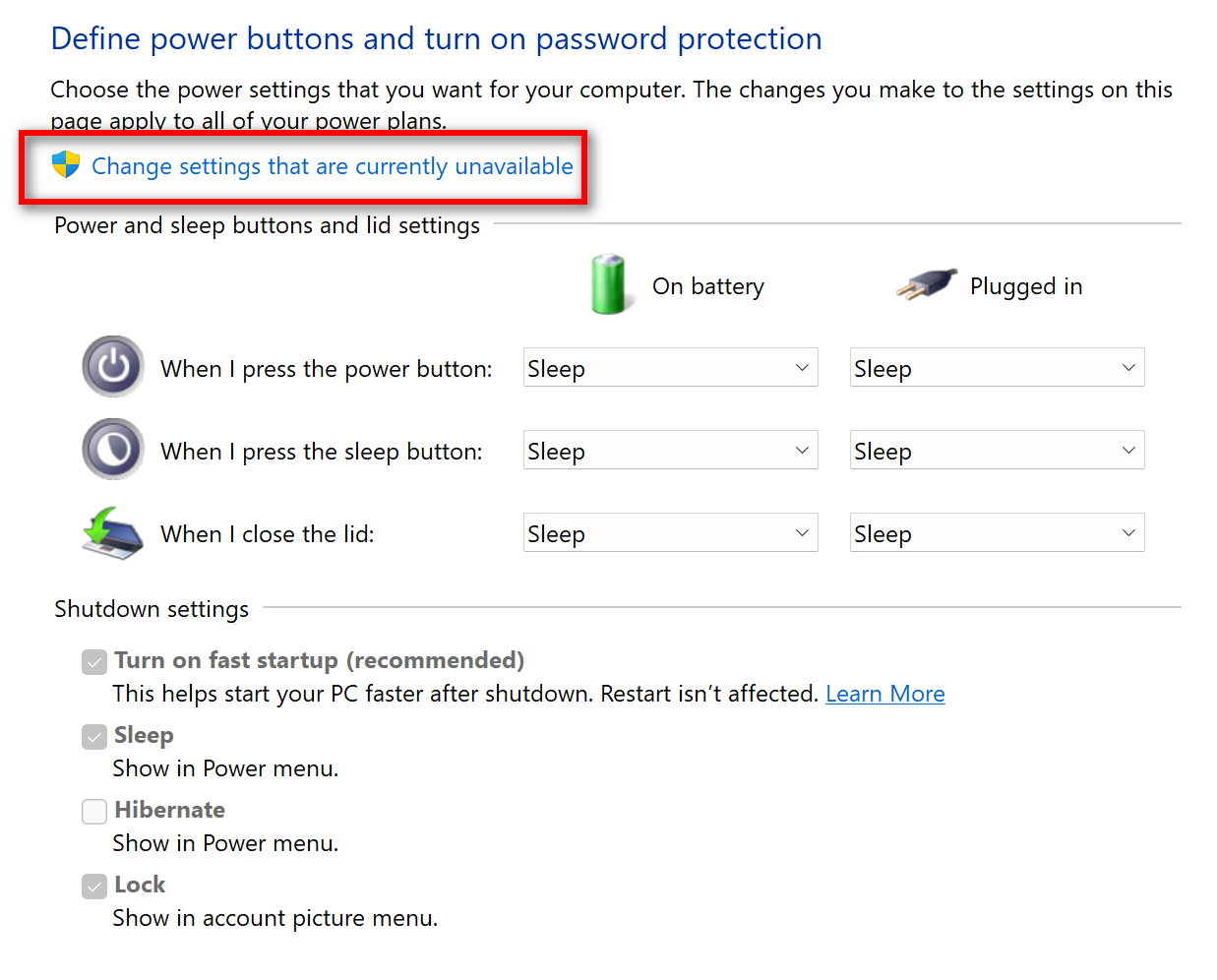
- Click "Change settings that are currently unavailable": This will unlock additional settings, including the option to disable Fast Startup.
- Uncheck "Turn on fast startup (recommended)": Locate the checkbox labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" and uncheck it.
- Save Changes: Click the "Save Changes" button to apply the modifications and disable Fast Startup.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Will disabling Fast Startup significantly impact boot times?
A: Disabling Fast Startup will generally result in slightly longer boot times compared to when it is enabled. However, the difference is usually minimal, especially on modern systems with solid-state drives (SSDs).
Q: Can I re-enable Fast Startup after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can easily re-enable Fast Startup by following the same steps outlined above and checking the "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" checkbox.
Q: Is there a way to check if Fast Startup is currently enabled?
A: You can verify the status of Fast Startup by navigating to the same "Power Options" settings in the Control Panel. The checkbox labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" will be checked if the feature is enabled and unchecked if it is disabled.
Tips for Managing Fast Startup
- Experiment with both states: Consider testing your system with Fast Startup both enabled and disabled to determine the optimal setting for your specific needs and hardware configuration.
- Monitor boot times: Pay attention to boot times after enabling or disabling Fast Startup. This will help you gauge the impact of the feature on your system’s performance.
- Keep a clean system: Regularly clean your system of unnecessary files and applications to improve overall performance, including boot times.
Conclusion
While Fast Startup is generally a beneficial feature that enhances the boot experience, certain scenarios may necessitate its disabling. Troubleshooting system issues, performing updates, accessing advanced boot options, utilizing legacy hardware, and enhancing system security are just a few situations where disabling Fast Startup can be advantageous. The process of disabling Fast Startup is straightforward and can be reversed at any time. By understanding the nuances of this feature and its potential impact, users can make informed decisions about its use and ensure optimal system performance.


![How to Enable or Turn On Fast Startup on Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aO2eIvIHUlU/maxresdefault.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing Windows 11’s Fast Startup Feature. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!