Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature
Windows 10’s Fast Startup feature is designed to expedite the boot process, offering a faster and more efficient user experience. However, there are scenarios where disabling this feature can be beneficial, particularly for users who prioritize data integrity, system stability, or require access to specific functionalities during the boot process. This article delves into the intricacies of Fast Startup, outlining its workings, benefits, drawbacks, and potential reasons for disabling it.
The Mechanics of Fast Startup
Fast Startup, also known as Hybrid Boot, leverages a combination of traditional hibernation and cold boot methods. When enabled, the operating system saves a "hibernation image" of the current system state to the hard drive upon shutdown. This image includes the kernel, device drivers, and user applications that were running at the time of shutdown. Upon startup, Windows 10 loads this image into memory, skipping the lengthy process of loading the entire operating system from scratch. This significantly reduces the boot time.
Benefits of Fast Startup
The primary advantage of Fast Startup is its ability to drastically shorten the time it takes for Windows 10 to boot up. This can be particularly noticeable on older or less powerful hardware. Additionally, Fast Startup can contribute to a smoother user experience by minimizing the time spent waiting for the system to become fully operational.
Drawbacks of Fast Startup
While Fast Startup offers significant speed improvements, it also comes with certain drawbacks.
-
Data Integrity: Due to the hibernation image, the system may not properly shut down all applications and processes. This can potentially lead to data corruption, especially if applications were actively writing data to files at the time of shutdown.
-
System Stability: The hibernation image can sometimes become corrupted, leading to system instability or boot errors. This can necessitate a complete system restart, potentially losing unsaved data.
-
Limited Access: Fast Startup prevents access to certain system functionalities during the boot process. This includes accessing the BIOS, using diagnostic tools, or performing specific system maintenance tasks.
-
Power Consumption: Although negligible, Fast Startup can consume a small amount of power even when the computer is shut down. This is due to the system maintaining the hibernation image on the hard drive.
Situations Where Disabling Fast Startup is Recommended
While Fast Startup is generally beneficial, there are specific scenarios where disabling it is recommended.
-
Data Integrity: For users who work with sensitive data, such as financial records or scientific research, disabling Fast Startup can minimize the risk of data corruption.
-
System Stability: If experiencing frequent system crashes or boot errors, disabling Fast Startup might help identify and resolve underlying issues.
-
System Maintenance: Users who regularly perform system maintenance tasks, such as disk cleanup, defragmentation, or antivirus scans, might need to disable Fast Startup to ensure proper execution of these tasks.
-
Troubleshooting: Disabling Fast Startup can be helpful during troubleshooting processes, as it allows access to diagnostic tools and system information that might be unavailable during a Fast Startup boot.
-
BIOS Access: If needing to access the BIOS settings, disabling Fast Startup is necessary as it prevents the system from directly booting into the operating system.
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10 is a straightforward process.
-
Open the Control Panel: Access the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
-
Navigate to Power Options: Click on "Power Options" under "System and Security."
-
Select Choose what the power buttons do: On the left-hand side of the window, click on "Choose what the power buttons do."
-
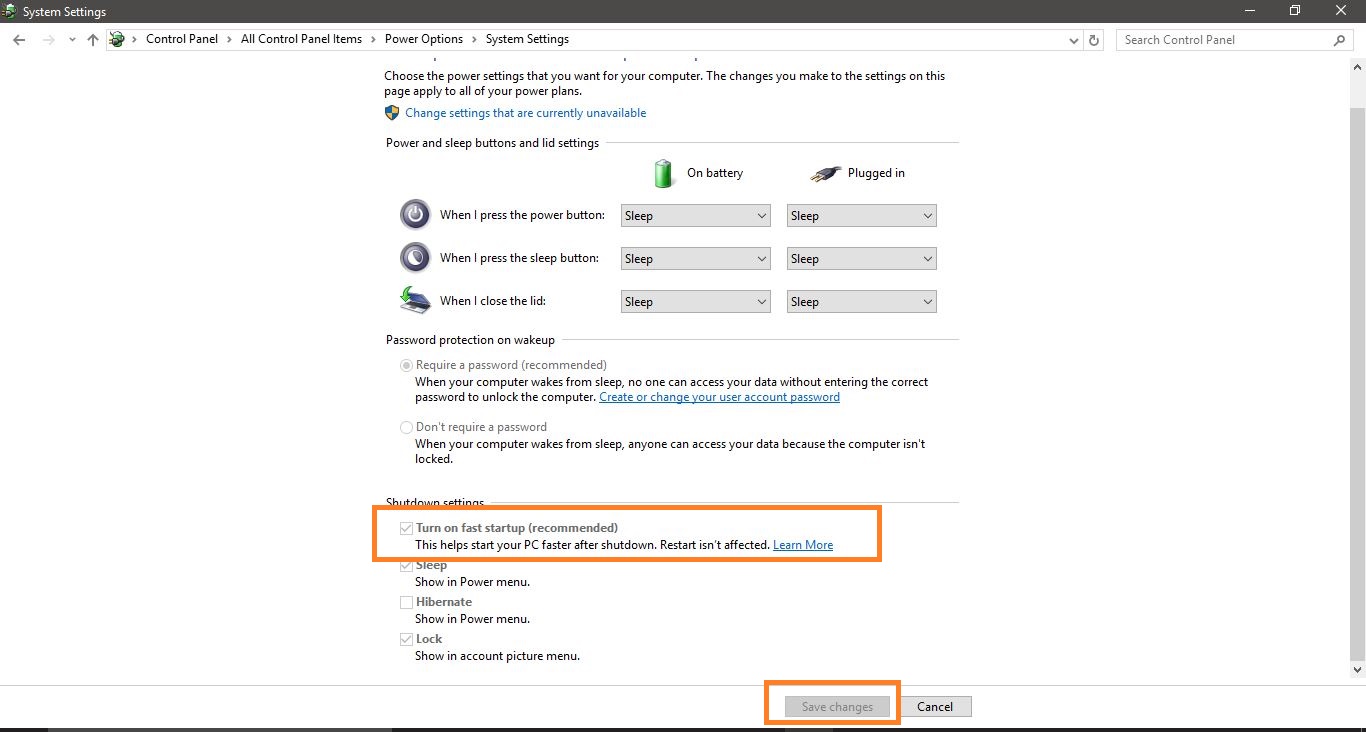
Change settings that are currently unavailable: Click on the link "Change settings that are currently unavailable" at the top of the window.
-
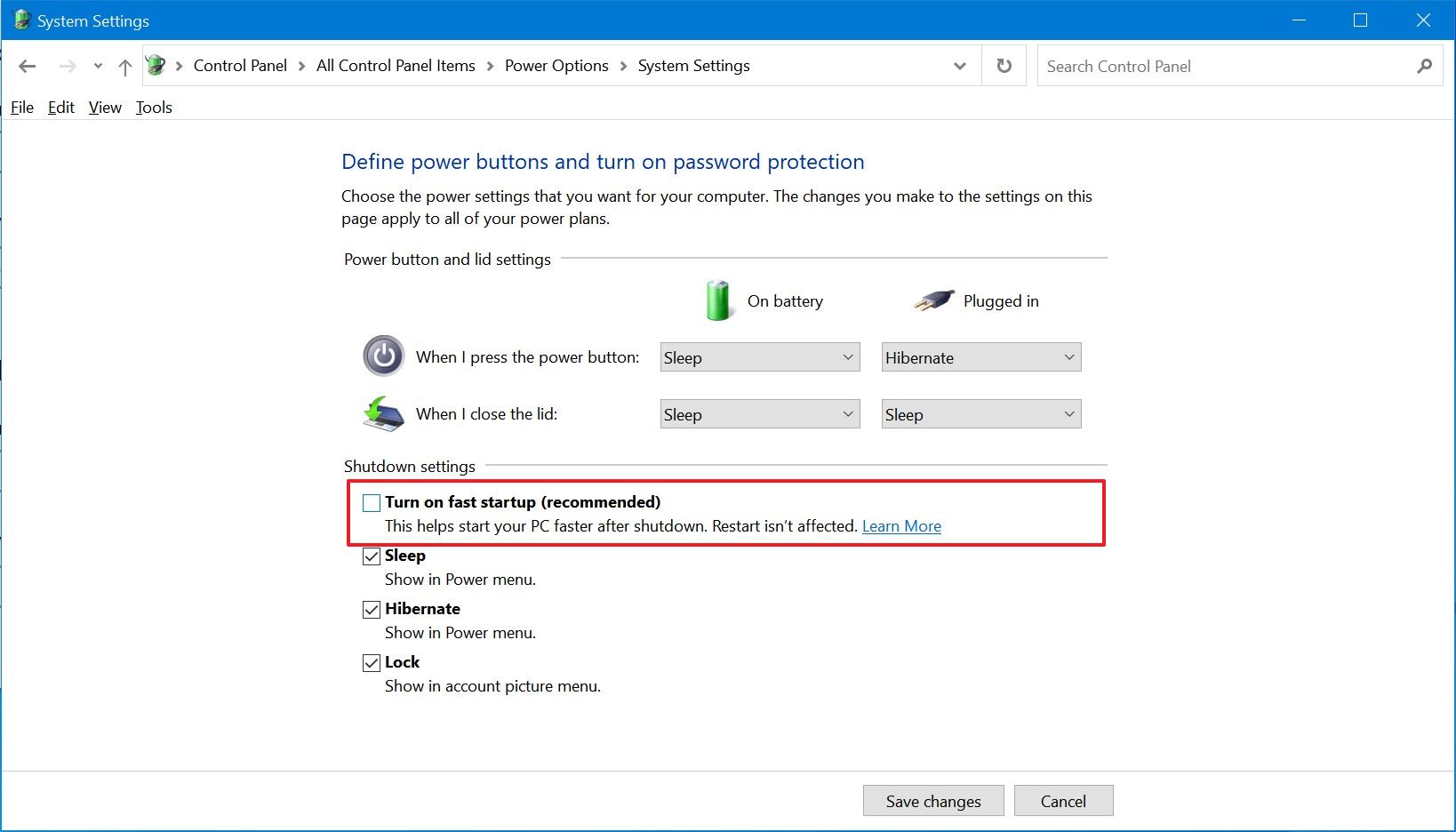
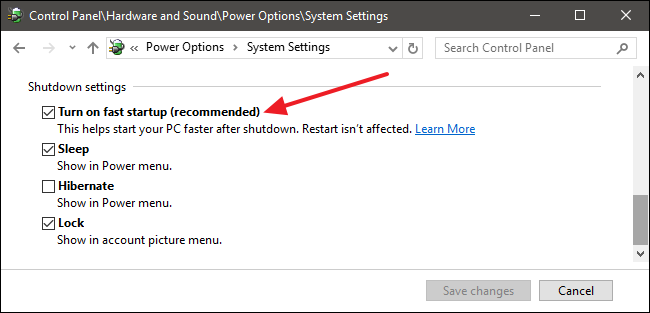
Uncheck Fast Startup: Under "Shutdown settings," uncheck the box labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
-
Save Changes: Click on "Save Changes" to apply the changes and disable Fast Startup.
FAQs about Disabling Fast Startup
Q: Is it safe to disable Fast Startup?
A: Yes, disabling Fast Startup is safe and does not harm your system. It simply reverts the boot process to a traditional cold boot, which is considered more secure in terms of data integrity.
Q: Will disabling Fast Startup slow down my computer?
A: Disabling Fast Startup will increase the boot time, but the difference might be negligible, especially on modern hardware. The overall performance of your system will not be significantly affected.
Q: Can I enable Fast Startup again after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable Fast Startup at any time by following the same steps outlined above and checking the "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" box.
Q: Should I disable Fast Startup if I have a SSD?
A: While SSDs generally boot faster than HDDs, disabling Fast Startup can still be beneficial for the reasons mentioned earlier, such as data integrity and system stability.
Tips for Disabling Fast Startup
-
Back up your data: Before disabling Fast Startup, it is always recommended to back up your important data to avoid potential data loss.
-
Monitor boot time: After disabling Fast Startup, monitor the boot time to see if it has noticeably increased.
-
Consider other performance optimizations: If boot time is a concern, consider other performance optimizations, such as disabling unnecessary startup programs or upgrading your hardware.
Conclusion
While Windows 10’s Fast Startup feature can significantly enhance the boot experience, there are valid reasons to disable it. Users who prioritize data integrity, system stability, or require access to specific functionalities during the boot process should consider disabling Fast Startup. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of this feature, users can make informed decisions about whether to enable or disable it based on their individual needs and preferences. Ultimately, the choice rests on balancing the convenience of a faster boot with the potential risks associated with Fast Startup.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!