Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows 10’s Fast Startup feature, also known as "Hybrid Shutdown," is designed to significantly reduce boot times, making the user experience smoother and more efficient. However, while this feature is generally beneficial, there are specific scenarios where disabling it might be advantageous. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Fast Startup, exploring its functionalities, potential drawbacks, and how to manage it effectively.
The Essence of Fast Startup:
Fast Startup leverages a hybrid approach, combining aspects of both a traditional shutdown and a hibernation state. When you initiate a shutdown, Windows 10 does not completely power down but instead saves the current system state to a hibernation file. Upon the next boot, Windows 10 loads this saved state, skipping the lengthy process of loading drivers and applications, resulting in a noticeably faster startup.
Benefits of Fast Startup:
- Reduced Boot Times: This is the primary advantage of Fast Startup. By loading the system from a saved state, boot times are significantly reduced, enhancing user productivity and overall system responsiveness.
- Improved User Experience: Faster boot times translate to a smoother and more enjoyable user experience, minimizing the time spent waiting for the system to become operational.
- Energy Efficiency: While not as energy-efficient as a complete shutdown, Fast Startup consumes less power compared to a traditional hibernation, contributing to overall energy savings.
Potential Drawbacks of Fast Startup:
- Compatibility Issues: Some applications or drivers may not be fully compatible with Fast Startup, leading to unexpected behavior or errors during the boot process.
- Data Integrity Concerns: In rare instances, Fast Startup can potentially lead to data corruption or inconsistencies if the system encounters an unexpected shutdown or power failure during the hibernation process.
- Limited Troubleshooting Capabilities: Disabling Fast Startup can be beneficial during troubleshooting, as it allows for a clean boot, potentially isolating issues related to specific drivers or applications.
Disabling Fast Startup: A Necessary Step in Certain Situations:
While Fast Startup is generally beneficial, there are specific scenarios where disabling it might be necessary:
- Troubleshooting System Issues: Disabling Fast Startup can be crucial during troubleshooting, particularly when encountering issues related to boot processes, driver conflicts, or application compatibility. A clean boot, achieved by disabling Fast Startup, provides a controlled environment to identify and resolve these issues.
- Ensuring Data Integrity: If data integrity is a critical concern, disabling Fast Startup can mitigate potential risks associated with unexpected shutdowns or power failures during the hibernation process.
- Preparing for System Upgrades or Reinstalls: Disabling Fast Startup is recommended before performing system upgrades or reinstalls. It allows for a clean slate and ensures that the new operating system is installed without interference from the previous system’s saved state.
- Specific Application Requirements: Certain applications or software might require a clean boot or a complete shutdown to function correctly. In such cases, disabling Fast Startup is essential.
Understanding the Importance of a Clean Boot:
A clean boot refers to starting Windows with only essential services and drivers loaded. This process is often employed for troubleshooting purposes, as it helps isolate issues related to specific drivers or applications. Disabling Fast Startup is a crucial step in achieving a clean boot, as it prevents the system from loading the saved state, ensuring a fresh start.
How to Disable Fast Startup:
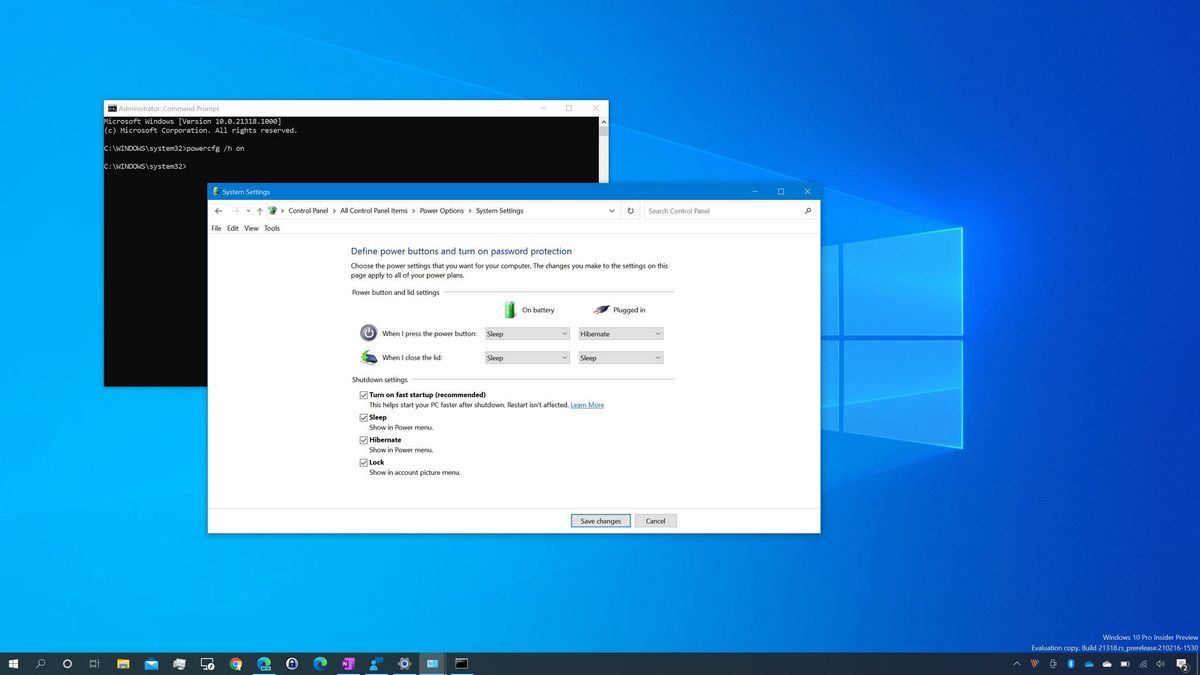
Disabling Fast Startup is a straightforward process that can be accomplished through the Windows Control Panel:
- Open the Control Panel: Navigate to the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
- Select Power Options: Locate and click on the "Power Options" section.
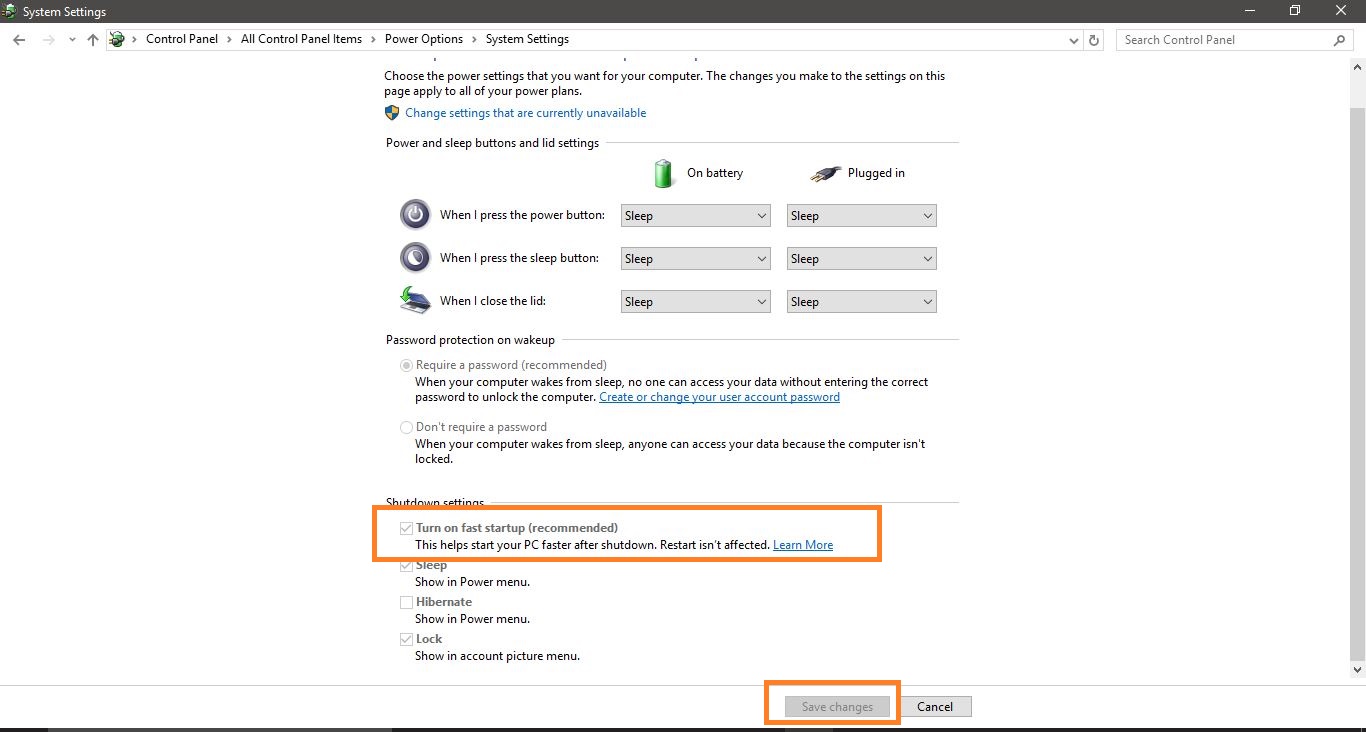
- Choose "Choose what the power buttons do": In the left-hand pane, click on the option "Choose what the power buttons do."
- Access Advanced Settings: Click on the "Change settings that are currently unavailable" link.
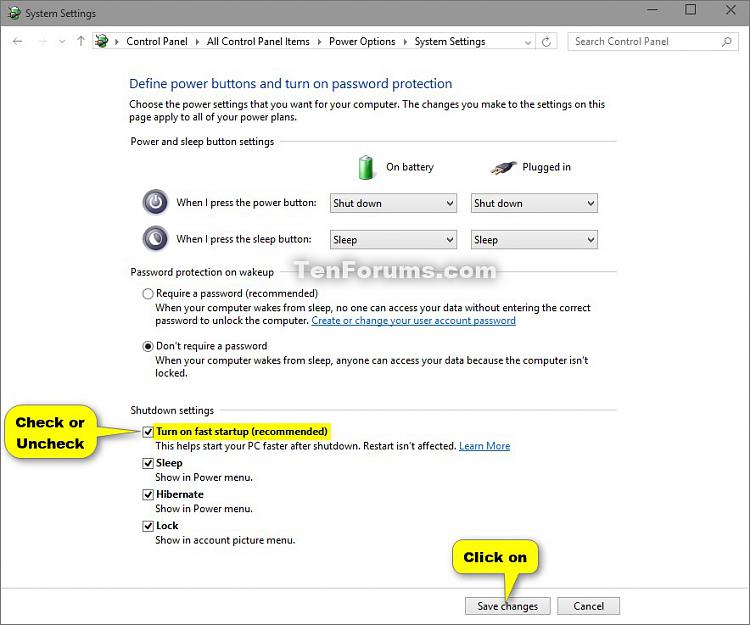
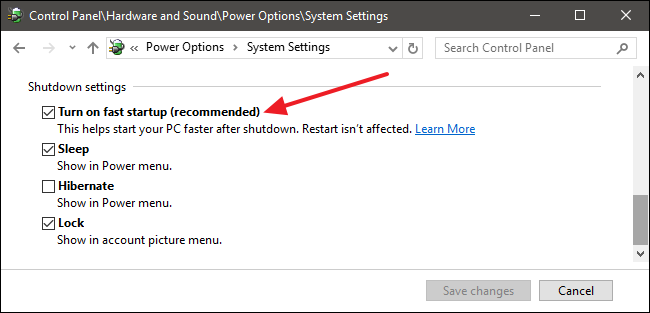
- Uncheck "Turn on fast startup": Locate the "Shutdown settings" section and uncheck the box labeled "Turn on fast startup."
- Save Changes: Click on the "Save Changes" button to confirm the modification.
FAQs Regarding Fast Startup:
Q: What are the potential risks associated with disabling Fast Startup?
A: Disabling Fast Startup is generally safe and does not pose any significant risks. However, it might slightly increase boot times, as the system will need to go through the full loading process.
Q: Can I enable Fast Startup again after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can easily re-enable Fast Startup by following the same steps mentioned above, checking the "Turn on fast startup" box.
Q: Is Fast Startup suitable for all Windows 10 users?
A: While Fast Startup is generally beneficial, it might not be ideal for everyone. Users who frequently perform system troubleshooting, upgrade their system, or require a clean boot for specific applications might benefit from disabling it.
Tips for Managing Fast Startup:
- Monitor Boot Times: Pay attention to your system’s boot times. If you notice significant delays, disabling Fast Startup might be worth considering.
- Consider System Upgrades: If you are planning a system upgrade or reinstall, it is recommended to disable Fast Startup beforehand.
- Perform Regular System Maintenance: Regular system maintenance, such as cleaning up temporary files and defragmenting the hard drive, can improve overall system performance and reduce boot times.
Conclusion:
Windows 10’s Fast Startup feature is a valuable tool for enhancing system performance and user experience. However, it is crucial to understand the potential drawbacks and to disable it when necessary. By carefully evaluating the benefits and drawbacks, users can effectively manage Fast Startup to optimize their system’s performance and ensure optimal data integrity and troubleshooting capabilities.


![[Full Guide] How To Enable Windows Fast Startup](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/03/Windows-10-Fast-Startup-usage-guide.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing Windows 10’s Fast Startup Feature: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!