Understanding and Managing User Account Switching in Windows 10
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing User Account Switching in Windows 10
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing User Account Switching in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing User Account Switching in Windows 10
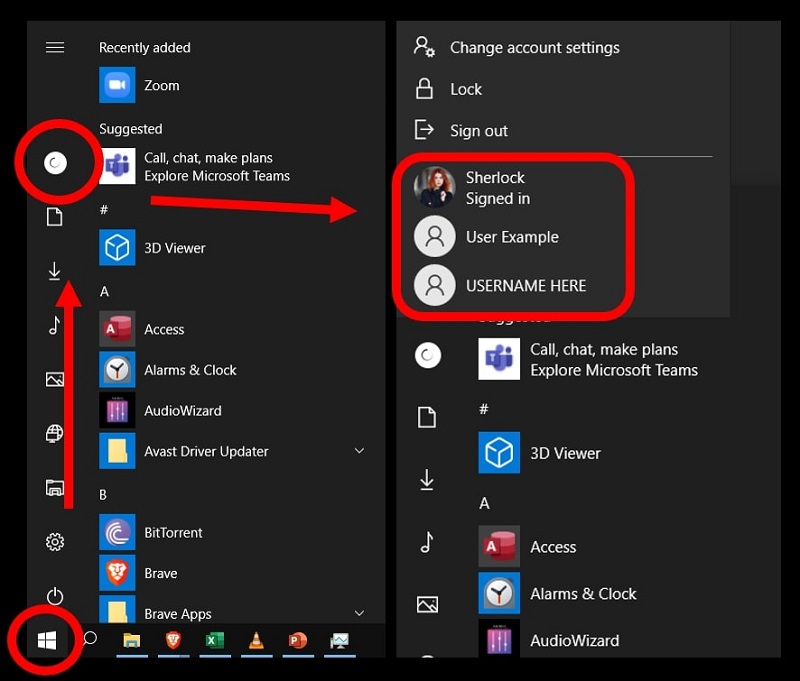
Windows 10, known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive design, offers a convenient feature that allows seamless switching between multiple user accounts. This functionality, often referred to as "Fast User Switching," enables users to effortlessly transition between different profiles without logging out and restarting the system. While this feature enhances productivity and flexibility for multi-user environments, certain scenarios might necessitate its deactivation. This article explores the intricacies of user account switching in Windows 10, delves into the reasons for disabling this feature, and provides a comprehensive guide to effectively manage user account transitions.
The Mechanics of User Account Switching
Windows 10 employs a sophisticated system for managing user accounts, ensuring a secure and personalized experience for each individual. When a user logs in, Windows creates a dedicated session, isolating their files, settings, and applications from other users. This approach maintains data integrity and prevents unintended access to sensitive information.
Fast User Switching, a component of this user account management system, simplifies the process of switching between these distinct user sessions. By enabling this feature, users can effortlessly transition from one account to another without the need to log out and restart the system. This streamlined approach saves time and effort, particularly in environments where multiple users share a single computer.
Why Disable User Account Switching?
While Fast User Switching offers significant convenience, certain scenarios might necessitate its deactivation. These situations often arise due to security concerns, privacy considerations, or specific system configurations.
Security Concerns:
- Unauthorized Access: Disabling Fast User Switching can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access to user accounts. By eliminating the quick switching option, users are required to explicitly log in to each account, thereby enhancing security and preventing unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data.
- Data Protection: In environments where data confidentiality is paramount, disabling Fast User Switching can strengthen data protection measures. By preventing users from switching accounts without explicit authentication, the system minimizes the potential for accidental or malicious data disclosure.
- System Integrity: Disabling Fast User Switching can contribute to system integrity by reducing the likelihood of user profiles interfering with each other. This is particularly relevant in scenarios where multiple users share the same computer and their actions might inadvertently affect other user accounts.
Privacy Considerations:
- Data Isolation: Disabling Fast User Switching can reinforce data isolation between user accounts, ensuring that personal information and settings remain private and inaccessible to other users. By requiring explicit login for each account, the system prevents users from inadvertently accessing sensitive data belonging to other individuals.
- Account Security: Disabling Fast User Switching can enhance account security by preventing unauthorized access to personal information and settings. By requiring explicit authentication for each account, the system safeguards user data from unauthorized access, even if other users are logged in.
System Configuration:
- Resource Allocation: In scenarios where system resources are limited, disabling Fast User Switching can optimize resource allocation and improve overall system performance. By eliminating the overhead associated with multiple user sessions, the system can dedicate more resources to running applications and processes.
- Application Compatibility: Certain applications might not be compatible with Fast User Switching and may experience issues when multiple user sessions are active. Disabling this feature can ensure that these applications function correctly without encountering conflicts or errors.
Disabling Fast User Switching in Windows 10: A Step-by-Step Guide
Disabling Fast User Switching in Windows 10 is a straightforward process that involves modifying system settings. The following steps outline the process for deactivating this feature:
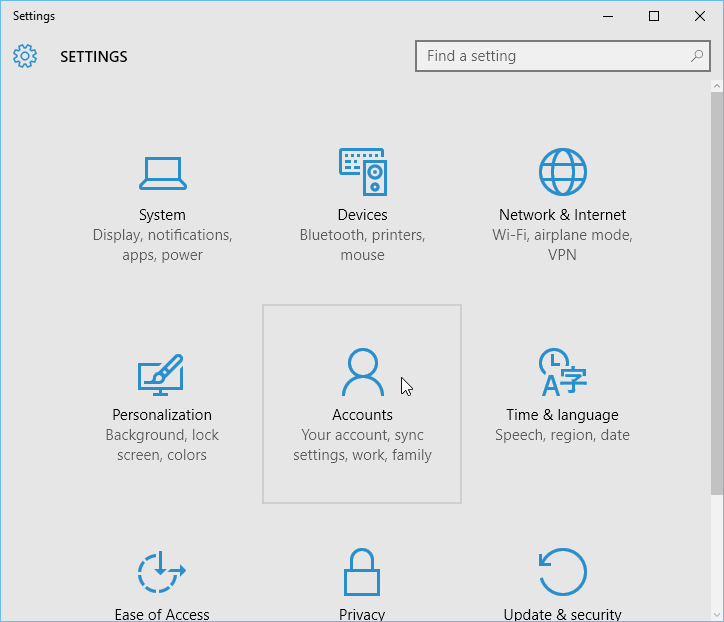
- Open Settings: Access the Windows Settings app by pressing the Windows key + I on your keyboard.
- Navigate to Accounts: In the Settings window, click on "Accounts."
- Select Sign-in Options: Within the Accounts settings, click on "Sign-in Options" in the left-hand pane.
- Disable Fast User Switching: Locate the "Fast User Switching" option and toggle the switch to the "Off" position.
- Confirm Changes: The system will prompt you to confirm the changes. Click "Sign out now" to apply the changes and restart the system.
Once you have completed these steps, Fast User Switching will be disabled, and users will be required to explicitly log in to each account.
Managing User Account Switching: A Comprehensive Approach
While disabling Fast User Switching can enhance security and privacy, it might not be the ideal solution for all scenarios. A more nuanced approach involves managing user account switching based on specific needs and preferences. Windows 10 offers several options for customizing user account management:
- Setting Account Types: Windows 10 allows users to define different account types, such as Administrator, Standard, and Guest. Each account type has specific privileges and access rights, enabling users to tailor account permissions based on individual requirements.
- Password Protection: Enabling password protection for user accounts adds an extra layer of security, preventing unauthorized access even if Fast User Switching is enabled. This ensures that only authorized individuals can access specific user accounts.
- Guest Accounts: Windows 10 offers a dedicated Guest account that provides limited access to the system. This account is ideal for temporary users who require basic functionality without accessing personal data or settings.
- Family Settings: For families with children, Windows 10 provides Family Settings, allowing parents to control and monitor their children’s online activity and access to specific applications and websites.
FAQs Regarding User Account Switching
Q: Can I disable Fast User Switching for specific users while keeping it enabled for others?
A: Windows 10 does not offer granular control over Fast User Switching on a per-user basis. Disabling this feature affects all users on the system.
Q: Will disabling Fast User Switching affect system performance?
A: Disabling Fast User Switching might have a minimal impact on system performance, as it eliminates the overhead associated with maintaining multiple user sessions. However, the performance difference is generally negligible.
Q: Is it possible to re-enable Fast User Switching after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable Fast User Switching by following the same steps mentioned earlier, toggling the switch to the "On" position.
Q: Can I disable Fast User Switching using the Registry Editor?
A: While it is possible to modify the Registry to disable Fast User Switching, this is not recommended for novice users. Modifying the Registry can lead to system instability if not done correctly.
Tips for Managing User Account Switching
- Regularly Review Account Settings: It is essential to periodically review user account settings and ensure that they align with current security and privacy requirements.
- Implement Strong Passwords: Encourage users to set strong passwords for their accounts, using a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: If available, enable two-factor authentication for user accounts, adding an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a secondary authentication factor, such as a code sent to their mobile device.
- Use Guest Accounts for Temporary Users: Encourage the use of Guest accounts for temporary users who need access to the system without accessing personal data or settings.
- Keep Software Up-to-Date: Regularly update operating system and software applications to ensure that you have the latest security patches and bug fixes.
Conclusion
Disabling Fast User Switching in Windows 10 can enhance security and privacy, particularly in scenarios where data confidentiality and unauthorized access are major concerns. However, this decision should be made on a case-by-case basis, considering the specific requirements and preferences of the user environment. By understanding the nuances of user account switching and employing appropriate management strategies, users can ensure a secure and personalized computing experience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing User Account Switching in Windows 10. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!