Understanding and Managing LSA Protection in Windows 11
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing LSA Protection in Windows 11
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing LSA Protection in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing LSA Protection in Windows 11

The Local Security Authority (LSA) is a core component of Windows operating systems, responsible for managing security policies, user authentication, and access control. It acts as a central authority, enforcing security measures and safeguarding sensitive system information. LSA protection, a security feature integrated within Windows 11, further enhances this security by shielding the LSA process from unauthorized access and manipulation.
The Importance of LSA Protection
LSA protection plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and security of a Windows 11 system. It safeguards the LSA process from malicious attacks that could compromise system security. These attacks could include:
- Exploiting vulnerabilities: Malicious actors may attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in the LSA process to gain unauthorized access or elevate privileges.
- Injecting malicious code: Attackers could inject malicious code into the LSA process, potentially allowing them to control the system or steal sensitive data.
- Modifying security policies: Unauthorized modifications to security policies could weaken the system’s defenses, making it vulnerable to attacks.
Circumstances Where LSA Protection Might Be Disabled
While LSA protection is generally considered a vital security measure, there are specific scenarios where temporarily disabling it might be necessary. These scenarios typically involve:
- Troubleshooting compatibility issues: Some legacy applications or tools might not function correctly with LSA protection enabled. Disabling it temporarily allows for compatibility testing and troubleshooting.
- Specific security auditing requirements: Certain security auditing tools or procedures might necessitate temporarily disabling LSA protection to gain access to specific system information.
- Specialized security environments: In highly controlled environments with stringent security measures, administrators may choose to disable LSA protection for specific applications or services that are deemed secure.
Disabling LSA Protection: A Cautious Approach
Disabling LSA protection should be undertaken with extreme caution, as it weakens the system’s security posture. It is recommended to only disable it when absolutely necessary and for the shortest possible duration.
Important Considerations:
- Risk assessment: Carefully assess the potential risks associated with disabling LSA protection. Consider the environment, the applications involved, and the potential consequences of a security breach.
- Limited duration: Only disable LSA protection for the minimum time required to accomplish the task. Re-enable it as soon as possible to restore the system’s security.
- Alternative solutions: Explore alternative solutions before resorting to disabling LSA protection. For example, consider using a compatibility mode for legacy applications or investigating alternative security auditing methods.
- Security best practices: Implement strong security practices, such as regular security updates, robust passwords, and multi-factor authentication, to mitigate the risks associated with disabling LSA protection.
Disabling LSA Protection: A Step-by-Step Guide
Disabling LSA protection is not a straightforward process and requires advanced system administration skills. It is crucial to understand the implications and risks involved before proceeding. This guide outlines the general steps, but it is essential to consult relevant documentation and seek expert advice if needed.
1. Understanding the Risks:
- Increased vulnerability: Disabling LSA protection exposes the system to a higher risk of security breaches.
- Potential data loss: A security breach could lead to data loss, system compromise, or unauthorized access.
- Reversibility: While disabling LSA protection is possible, restoring it may not always be straightforward.
2. Backing Up Critical Data:
- Create a full system backup before making any changes to the system’s security settings. This backup can be used to restore the system to its previous state if necessary.
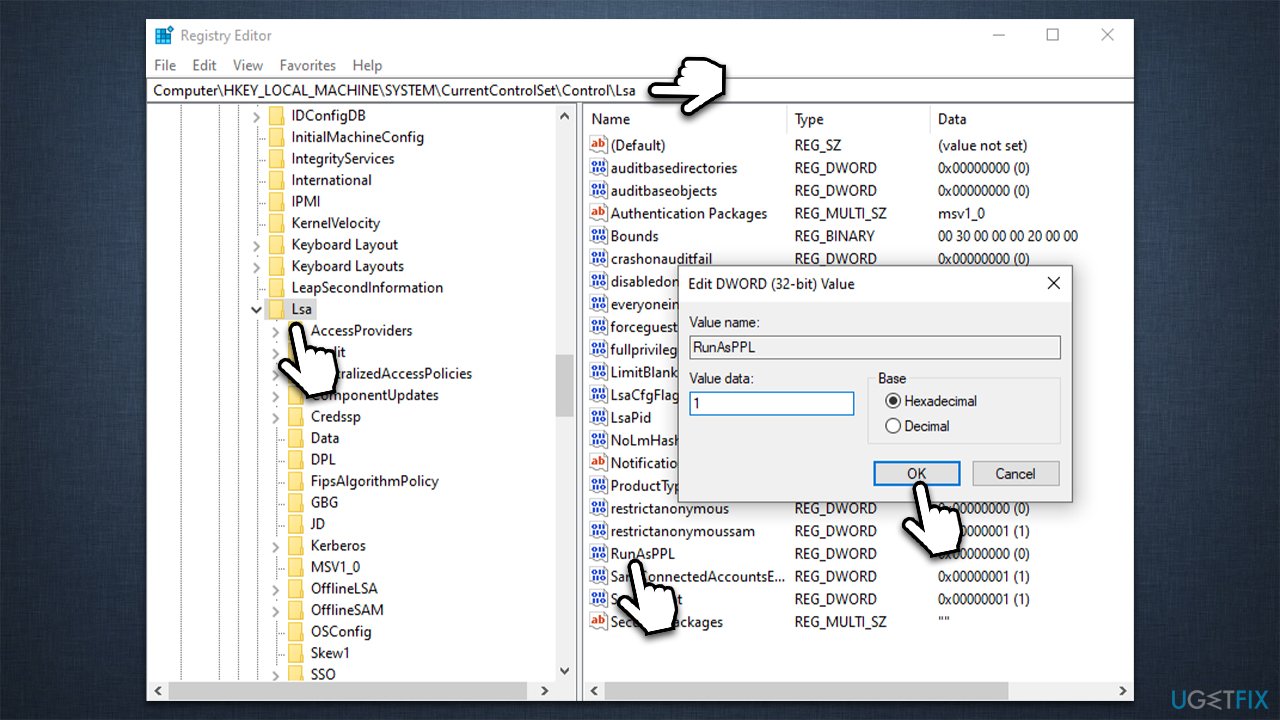
3. Using the Registry Editor (regedit):
- Open the Registry Editor (regedit) by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
- Navigate to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlLsa
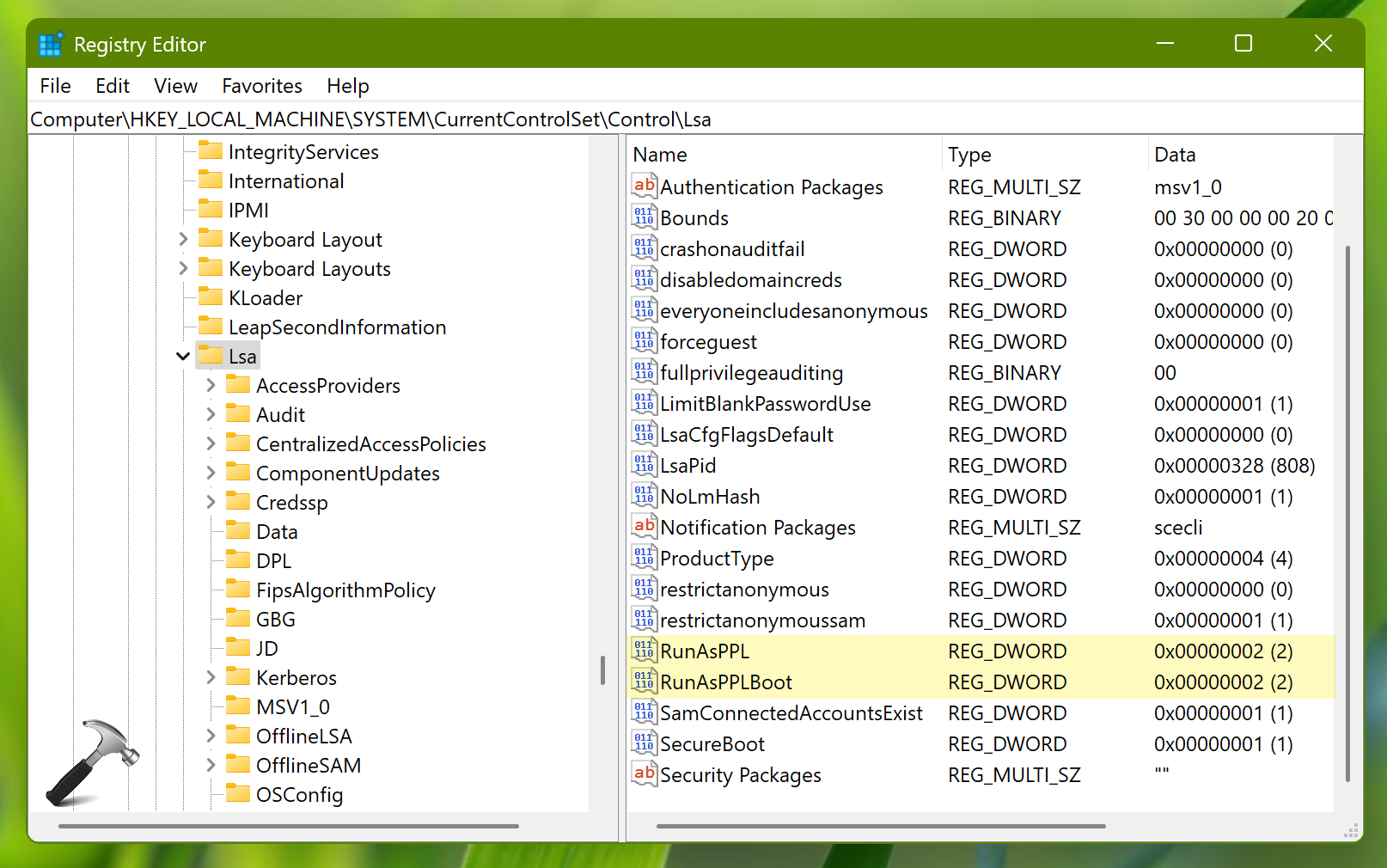
- Locate the
LsaProtectedProcessvalue. - Double-click the
LsaProtectedProcessvalue and change its data type toREG_DWORD. - Set the value to
0to disable LSA protection. - Close the Registry Editor and restart the computer.
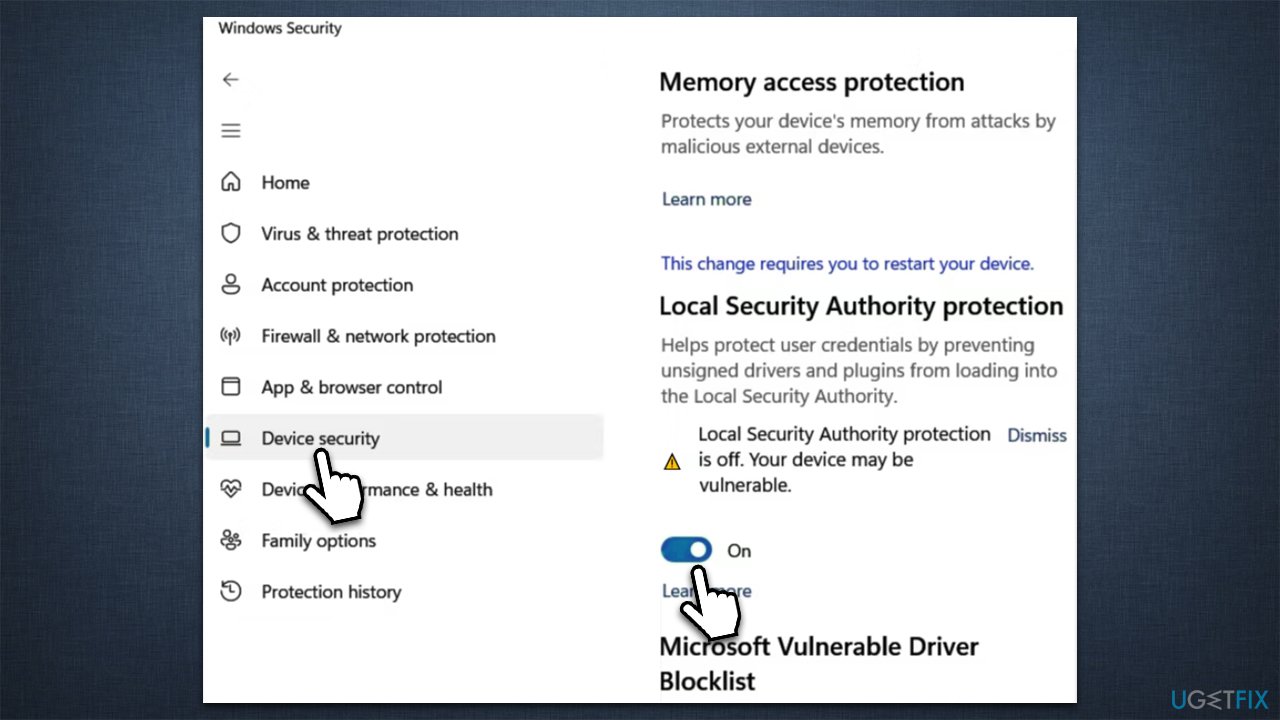
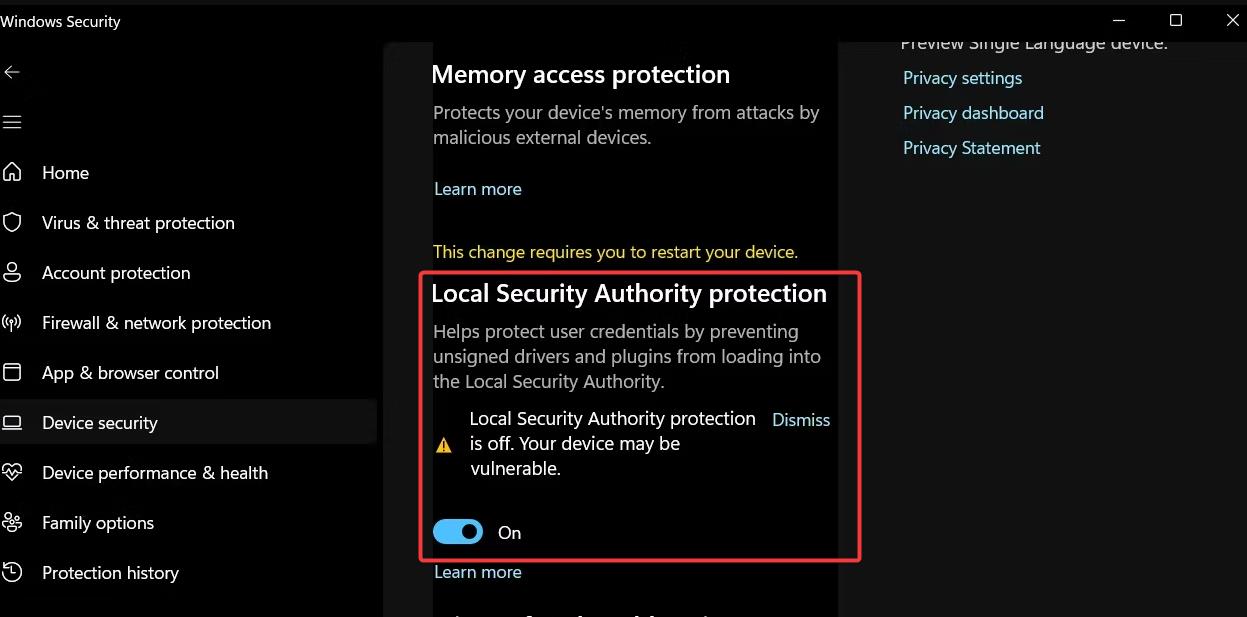
4. Verifying the Changes:
- After restarting, verify that LSA protection is disabled by checking the
LsaProtectedProcessvalue in the registry. - If the value is set to
0, LSA protection is disabled.
5. Re-enabling LSA Protection:
- To re-enable LSA protection, follow the same steps as above, but set the
LsaProtectedProcessvalue back to1.
Important Note:
- This guide provides a general overview of the process. The specific steps and settings may vary depending on the version of Windows 11 and the system configuration.
- Always consult the official Microsoft documentation and seek expert advice before making any changes to system security settings.
FAQs about LSA Protection in Windows 11
1. What are the potential risks of disabling LSA protection?
Disabling LSA protection significantly increases the system’s vulnerability to security threats. It exposes the LSA process to potential exploitation, malicious code injection, and unauthorized modifications to security policies, leading to data loss, system compromise, or unauthorized access.
2. Why might someone need to disable LSA protection?
Disabling LSA protection is generally not recommended and should only be done in specific scenarios, such as troubleshooting compatibility issues with legacy applications or conducting specific security auditing tasks.
3. How long should LSA protection be disabled?
LSA protection should be disabled only for the shortest possible duration necessary to accomplish the required task. Re-enable it as soon as possible to restore the system’s security posture.
4. Can I use third-party tools to disable LSA protection?
While some third-party tools might offer features to modify security settings, it is strongly advised to avoid using them for disabling LSA protection. Such tools may introduce vulnerabilities or compromise the system’s security.
5. What are some alternative solutions to disabling LSA protection?
Instead of disabling LSA protection, consider exploring alternative solutions, such as using compatibility modes for legacy applications, investigating alternative security auditing methods, or consulting with security experts to identify appropriate workarounds.
Tips for Managing LSA Protection in Windows 11
- Keep your system updated: Regularly install security updates and patches to address known vulnerabilities and strengthen system security.
- Use strong passwords: Employ complex and unique passwords for all user accounts.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication for critical accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Monitor system activity: Use security monitoring tools to detect suspicious activity and promptly address any security incidents.
- Consult security experts: Seek advice from security professionals for guidance on managing security settings and mitigating potential risks.
Conclusion
LSA protection is a critical security feature in Windows 11, safeguarding the system from various security threats. While disabling it might be necessary in specific situations, it should be undertaken with extreme caution and only for the shortest possible duration. Prioritize security best practices, such as regular updates, strong passwords, and multi-factor authentication, to mitigate the risks associated with disabling LSA protection. Always consult relevant documentation and seek expert advice before making any changes to system security settings.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing LSA Protection in Windows 11. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!