Understanding and Managing CPU Temperatures in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing CPU Temperatures in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing CPU Temperatures in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing CPU Temperatures in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of your computer, responsible for executing all the instructions that make your system function. Like any other electronic component, the CPU generates heat during operation. While a certain amount of heat is normal, excessive temperatures can lead to performance degradation, system instability, and even hardware damage. Therefore, monitoring CPU temperature is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your computer.
The Importance of CPU Temperature Monitoring
Monitoring CPU temperature allows users to:
- Identify Potential Overheating Issues: Elevated CPU temperatures can be a sign of various problems, including inadequate cooling, faulty components, or even malware activity. Early detection of such issues can prevent further damage and ensure smooth system operation.
- Optimize System Performance: When the CPU operates at excessively high temperatures, it may throttle its performance to prevent overheating. This can result in sluggish system responsiveness and slow application loading times. Monitoring CPU temperature allows users to identify and address performance bottlenecks caused by overheating.
- Extend Hardware Lifespan: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to premature wear and tear on the CPU and other components. By monitoring CPU temperature and taking appropriate measures to maintain optimal operating conditions, users can significantly extend the lifespan of their hardware.
How to Monitor CPU Temperature in Windows 10
Windows 10 offers various methods for monitoring CPU temperature, ranging from built-in tools to third-party applications.
1. Using the Task Manager:
- Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Navigate to the Performance tab.
- Click on CPU to view the current CPU usage and temperature.
2. Utilizing the Command Prompt:
- Open the Command Prompt by typing cmd in the search bar and selecting the Command Prompt app.
- Execute the command wmic sensors get Temperature.
- This will display the temperature readings of various sensors, including the CPU.
3. Employing Third-Party Monitoring Software:
Several dedicated software programs offer comprehensive system monitoring capabilities, including CPU temperature readings. Some popular options include:
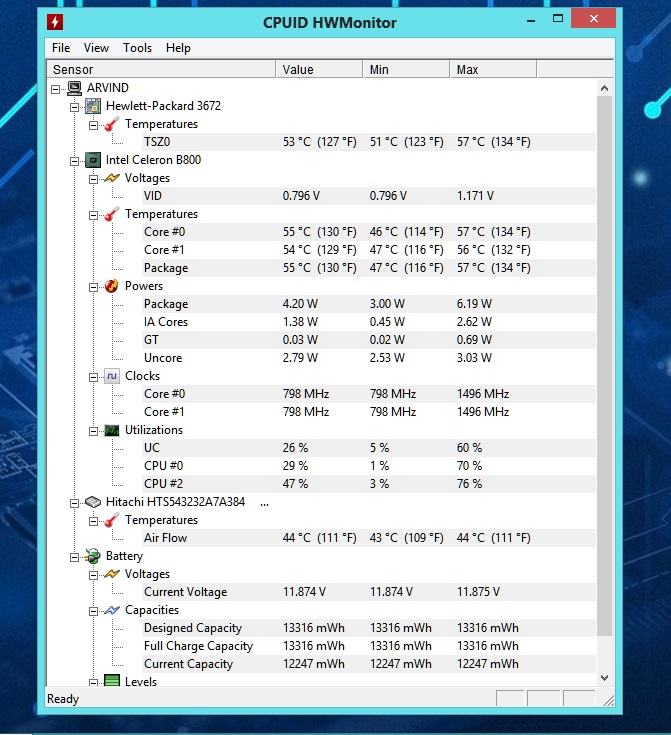
- HWMonitor: Provides detailed hardware information, including CPU temperature, fan speeds, and voltage readings.
- CPU-Z: Offers detailed information about your CPU, including its core temperature, clock speeds, and other specifications.
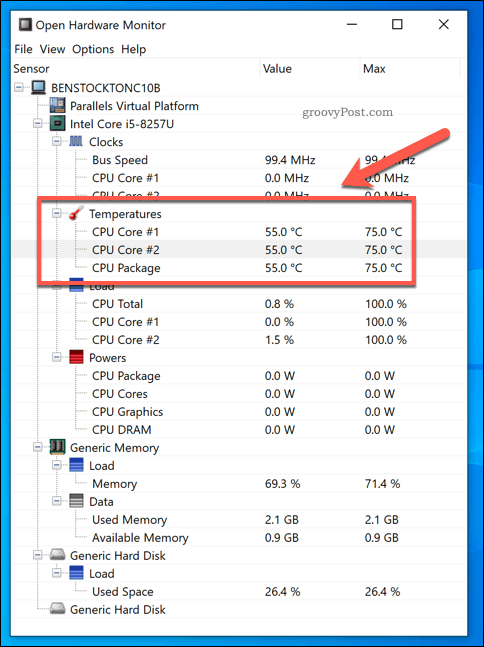
- Open Hardware Monitor: A free, open-source tool that provides real-time hardware monitoring data, including CPU temperature, fan speeds, and voltage readings.
Understanding CPU Temperature Readings
CPU temperature readings are typically expressed in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F). The normal operating temperature range for CPUs varies depending on the specific model and workload. Generally, temperatures below 80°C (176°F) are considered safe for most CPUs under normal usage. However, it is crucial to consult your CPU’s specifications for the recommended operating temperature range.
Factors Affecting CPU Temperature
Several factors can influence CPU temperature, including:
- CPU Load: The more demanding the tasks being executed, the higher the CPU utilization and heat generation.
- Ambient Temperature: The temperature of the surrounding environment can directly impact the CPU’s operating temperature.
- Cooling System: The effectiveness of the cooling system, including the heatsink and fan, plays a crucial role in dissipating heat from the CPU.
- Case Ventilation: Proper airflow within the computer case is essential for effective heat dissipation.
- Thermal Paste: The thermal paste applied between the CPU and heatsink acts as a thermal conductor, facilitating heat transfer.
Managing CPU Temperature
If your CPU temperature consistently exceeds the recommended operating range, you can take several steps to manage it:
- Ensure Proper Cooling: Check that the heatsink and fan are properly installed and functioning correctly. Consider replacing the thermal paste if it is old or degraded.
- Improve Case Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow within the computer case by removing dust buildup and optimizing fan placement.
- Reduce CPU Load: Close unnecessary applications and minimize resource-intensive processes to reduce CPU utilization and heat generation.
- Adjust Power Settings: Set the power plan to a more balanced or power-saving mode to reduce CPU performance and heat generation.
- Consider Overclocking: While overclocking can increase CPU performance, it also increases heat generation. If you choose to overclock, ensure that your cooling system is sufficient to handle the increased thermal load.
FAQs
1. What is the normal operating temperature for a CPU?
The normal operating temperature for a CPU varies depending on the specific model and workload. Generally, temperatures below 80°C (176°F) are considered safe for most CPUs under normal usage. However, it is crucial to consult your CPU’s specifications for the recommended operating temperature range.
2. How can I tell if my CPU is overheating?
Several signs can indicate that your CPU is overheating, including:
- System crashes or freezes: Excessive heat can cause system instability and crashes.
- Slow performance: Overheating can cause the CPU to throttle its performance, resulting in sluggish system responsiveness and slow application loading times.
- High fan noise: The cooling fan may run at a higher speed to compensate for increased heat generation.
- Error messages: Some error messages, such as "CPU temperature too high," may indicate an overheating problem.
3. What should I do if my CPU is overheating?
If your CPU is overheating, take the following steps:
- Ensure proper cooling: Check that the heatsink and fan are properly installed and functioning correctly. Consider replacing the thermal paste if it is old or degraded.
- Improve case ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow within the computer case by removing dust buildup and optimizing fan placement.
- Reduce CPU load: Close unnecessary applications and minimize resource-intensive processes to reduce CPU utilization and heat generation.
- Adjust power settings: Set the power plan to a more balanced or power-saving mode to reduce CPU performance and heat generation.
4. Can overheating damage my CPU?
Yes, prolonged exposure to excessive heat can damage your CPU. High temperatures can lead to premature wear and tear on the CPU, resulting in reduced performance, system instability, and even complete failure.
5. How often should I monitor my CPU temperature?
It is recommended to monitor your CPU temperature regularly, especially if you are using resource-intensive applications or playing demanding games. You can use a dedicated monitoring tool or the built-in Task Manager to track your CPU temperature.
Tips
- Keep your computer clean: Dust buildup can hinder airflow and increase CPU temperature. Regularly clean your computer case and components to maintain optimal thermal performance.
- Monitor fan speeds: Ensure that the cooling fan is running at an appropriate speed. If the fan is not spinning or is running too slowly, it may need to be replaced.
- Avoid overclocking without proper cooling: Overclocking can increase CPU performance but also generates more heat. Ensure that your cooling system is sufficient to handle the increased thermal load before overclocking.
- Consider liquid cooling: Liquid cooling systems offer more efficient heat dissipation than air cooling, especially for high-performance CPUs.
Conclusion
Monitoring CPU temperature is essential for ensuring optimal performance, stability, and longevity of your computer. By understanding the factors affecting CPU temperature and taking appropriate measures to manage it, users can prevent overheating issues and ensure that their system runs smoothly and efficiently. Regular monitoring and proactive maintenance can help extend the lifespan of your hardware and prevent costly repairs or replacements.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing CPU Temperatures in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!