Understanding and Managing CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding and Managing CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding and Managing CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding CPU Temperature and Its Importance
- 3.2 Monitoring CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops
- 3.3 Factors Affecting CPU Temperature
- 3.4 Managing CPU Temperature
- 3.5 FAQs
- 3.6 Tips
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding and Managing CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops: A Comprehensive Guide
The central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of your laptop, responsible for handling all the computational tasks. Its performance directly impacts your laptop’s overall speed and responsiveness. However, like any other electronic component, the CPU generates heat during operation. Excessive heat can lead to performance throttling, instability, and even permanent damage. Therefore, monitoring and managing CPU temperature is crucial for maintaining optimal laptop performance and longevity.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding CPU temperature monitoring on Windows 10 laptops, exploring its importance, available tools, and best practices for maintaining a healthy thermal environment.
Understanding CPU Temperature and Its Importance
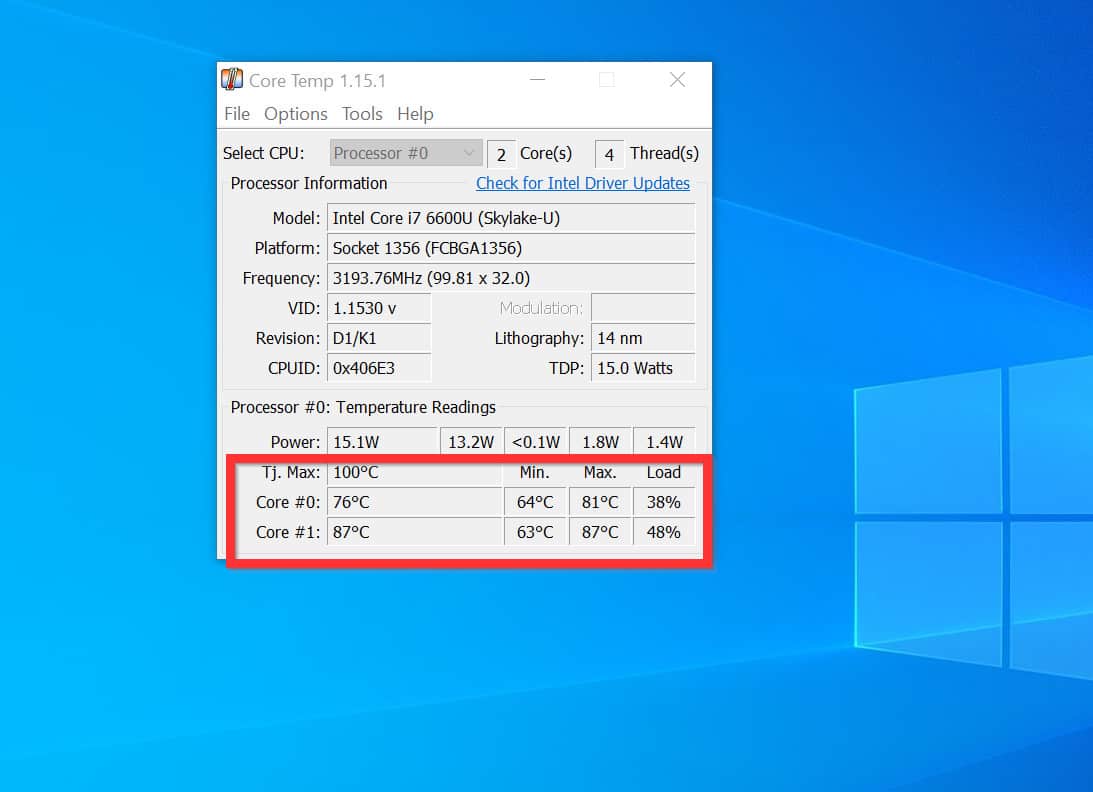
The CPU’s temperature is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F). The ideal operating temperature varies depending on the specific CPU model and its cooling solution. Generally, a CPU temperature below 80°C is considered safe for sustained operation. However, exceeding 90°C can lead to performance throttling, where the CPU automatically reduces its speed to prevent overheating.
Monitoring CPU temperature offers several benefits:
- Early Detection of Overheating: Identifying potential overheating issues before they escalate into serious problems.
- Performance Optimization: Understanding the thermal behavior of your CPU allows for adjustments to power settings, fan speeds, and other factors to optimize performance.
- Proactive Maintenance: Identifying and addressing potential cooling issues, such as dust buildup, can prolong the lifespan of your laptop.
- Troubleshooting Performance Issues: Abnormal CPU temperatures can indicate hardware malfunctions, software conflicts, or other issues that require investigation.
Monitoring CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops
Windows 10 offers several built-in tools and third-party applications for monitoring CPU temperature. These tools provide real-time temperature readings, historical data, and alerts when temperatures reach critical levels.
1. Windows Task Manager:
The Task Manager is a built-in tool that provides basic CPU temperature information. To access it, press Ctrl+Shift+Esc or right-click the taskbar and select Task Manager.
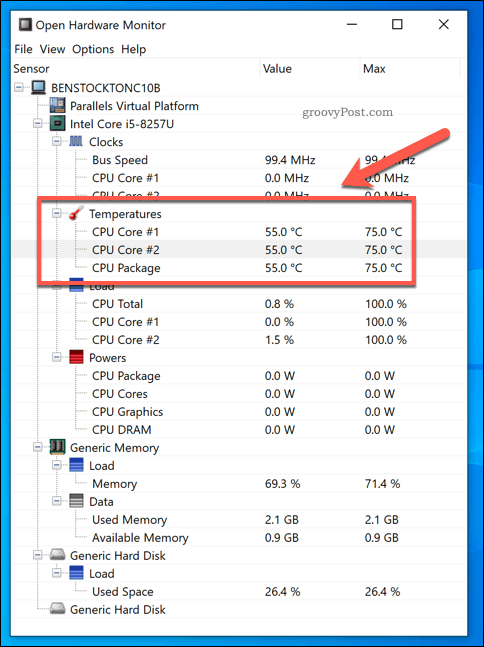
- Performance Tab: Click on the "Performance" tab, and select "CPU" from the left-hand menu. This displays the CPU usage and temperature in real-time. However, the temperature readings might not be as accurate as dedicated monitoring tools.
2. Command Prompt:
The Command Prompt offers a more technical approach to monitoring CPU temperature. Open the Command Prompt by searching for it in the Start menu.
- "wmic sensors get Temperature" command: This command displays the temperature readings of various sensors in your system, including the CPU.
3. Third-Party Monitoring Software:
Several dedicated software applications offer more comprehensive CPU temperature monitoring capabilities, including:
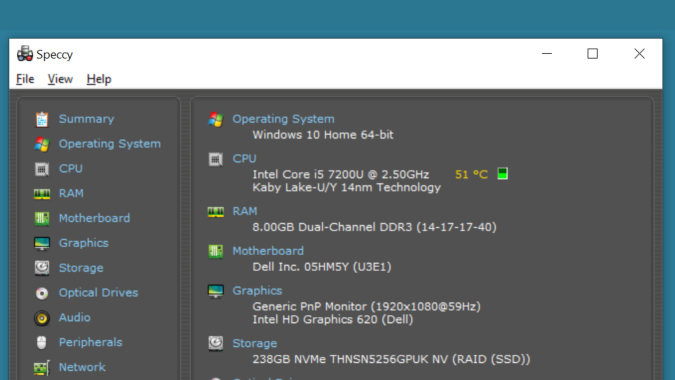
- HWMonitor: A free tool that provides detailed information about hardware components, including CPU temperature, fan speeds, and voltage readings.
- Open Hardware Monitor: Another free and open-source tool that offers similar features to HWMonitor.
- SpeedFan: A popular application for controlling fan speeds and monitoring temperatures.
- MSI Afterburner: A widely used tool for overclocking and monitoring GPUs, also providing CPU temperature readings.
4. BIOS Settings:
Some laptop models allow for CPU temperature monitoring through the BIOS settings. Access the BIOS by pressing a specific key during startup, usually F2, F10, or Del. Look for options related to "Hardware Monitoring" or "System Health" to access temperature readings.
Factors Affecting CPU Temperature
Several factors can influence CPU temperature, including:
- CPU Load: The more demanding the tasks, the higher the CPU load and consequently, the higher the temperature.
- Ambient Temperature: High room temperatures can increase the CPU’s internal temperature.
- Cooling Solution: The efficiency of the cooling system, including the fan and heat sink, directly impacts the CPU’s temperature.
- Dust Accumulation: Dust buildup on the fan and heat sink can hinder airflow and lead to overheating.
- Software Conflicts: Certain software programs might be resource-intensive and generate excessive heat.
- Overclocking: Increasing the CPU’s clock speed can lead to higher temperatures.
Managing CPU Temperature
Managing CPU temperature involves taking proactive measures to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance.
1. Optimizing Power Settings:
Windows 10 offers various power plans that influence the CPU’s performance and energy consumption.
- Balanced Plan: Provides a good balance between performance and energy efficiency.
- High Performance Plan: Maximizes performance but consumes more power and generates more heat.
- Power Saver Plan: Prioritizes energy efficiency, reducing CPU speed and potentially lowering temperatures.
2. Adjusting Fan Speed:
Most laptops have automatic fan control, but you can adjust fan speeds manually in some cases.
- BIOS Settings: Some BIOS settings allow for manual fan speed control.
- Third-Party Software: Applications like SpeedFan offer advanced fan speed control options.
3. Cleaning the Cooling System:
Dust buildup can significantly hinder airflow and increase CPU temperature.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the fan and heat sink regularly using compressed air or a soft brush.
- Professional Cleaning: Consider professional cleaning if you are unsure about the process.
4. Managing Software:
Limit the number of running applications, especially resource-intensive programs, to reduce CPU load and temperature.
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Terminate background processes and applications that are not in use.
- Monitor Resource Usage: Use the Task Manager to identify and close resource-hungry applications.
5. Optimizing Windows Settings:
Windows 10 offers various settings that can impact CPU performance and temperature.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Disable services that you don’t need to reduce CPU load.
- Adjust Visual Effects: Reduce visual effects in Windows to minimize CPU usage.
- Disable Background Apps: Disable background apps that are not essential.
6. Using a Laptop Cooler:
A laptop cooler can provide additional airflow and help lower CPU temperature.
- External Cooling Pad: A cooling pad with a fan can improve airflow and reduce heat.
- Laptop Stand: Raising the laptop can improve airflow underneath.
FAQs
Q: What is a normal CPU temperature for a laptop?
A: A normal CPU temperature for a laptop generally ranges between 40°C and 80°C under load. However, the ideal temperature varies depending on the specific CPU model and its cooling solution.
Q: Is it okay if my CPU temperature reaches 90°C?
A: While a CPU temperature of 90°C might not cause immediate damage, it is considered high and can lead to performance throttling and potential long-term issues.
Q: How do I know if my laptop is overheating?
A: Signs of overheating include:
- Slow performance: The laptop becomes sluggish and unresponsive.
- Frequent crashes: The laptop crashes or freezes unexpectedly.
- High fan noise: The fan runs continuously at high speed.
- Hot to the touch: The laptop’s body, especially around the CPU area, becomes hot.
Q: What can I do if my laptop is overheating?
A: If your laptop is overheating, try the following:
- Clean the cooling system: Remove dust buildup from the fan and heat sink.
- Adjust power settings: Switch to a power saver plan or lower performance settings.
- Close unnecessary applications: Terminate background processes and resource-intensive programs.
- Use a laptop cooler: A cooling pad can provide additional airflow.
- Seek professional help: If the issue persists, consider professional repair or replacement.
Tips
- Monitor CPU temperature regularly: Use monitoring tools to track CPU temperature and identify potential issues early.
- Optimize power settings for your needs: Choose a power plan that balances performance and energy efficiency.
- Clean the cooling system regularly: Prevent dust buildup to ensure optimal airflow.
- Avoid using your laptop on soft surfaces: Soft surfaces can block airflow and cause overheating.
- Keep your laptop in a well-ventilated area: Avoid placing the laptop in enclosed spaces or on surfaces that trap heat.
Conclusion
Monitoring and managing CPU temperature is essential for maintaining optimal laptop performance and longevity. By understanding the factors that affect CPU temperature and implementing appropriate management strategies, you can prevent overheating, optimize performance, and extend the lifespan of your laptop. Regular monitoring, proactive cleaning, and proper power settings are key to ensuring a healthy thermal environment for your CPU and maximizing your laptop’s performance.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing CPU Temperature on Windows 10 Laptops: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!