Understanding and Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10
Related Articles: Understanding and Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding and Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding and Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10
- 3.1 The Mechanics of Hibernation
- 3.2 The Trade-offs of Hibernation
- 3.3 Benefits of Disabling Hibernation
- 3.4 Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10
- 3.5 FAQs on Disabling Hibernation
- 3.6 Tips for Disabling Hibernation
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding and Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10
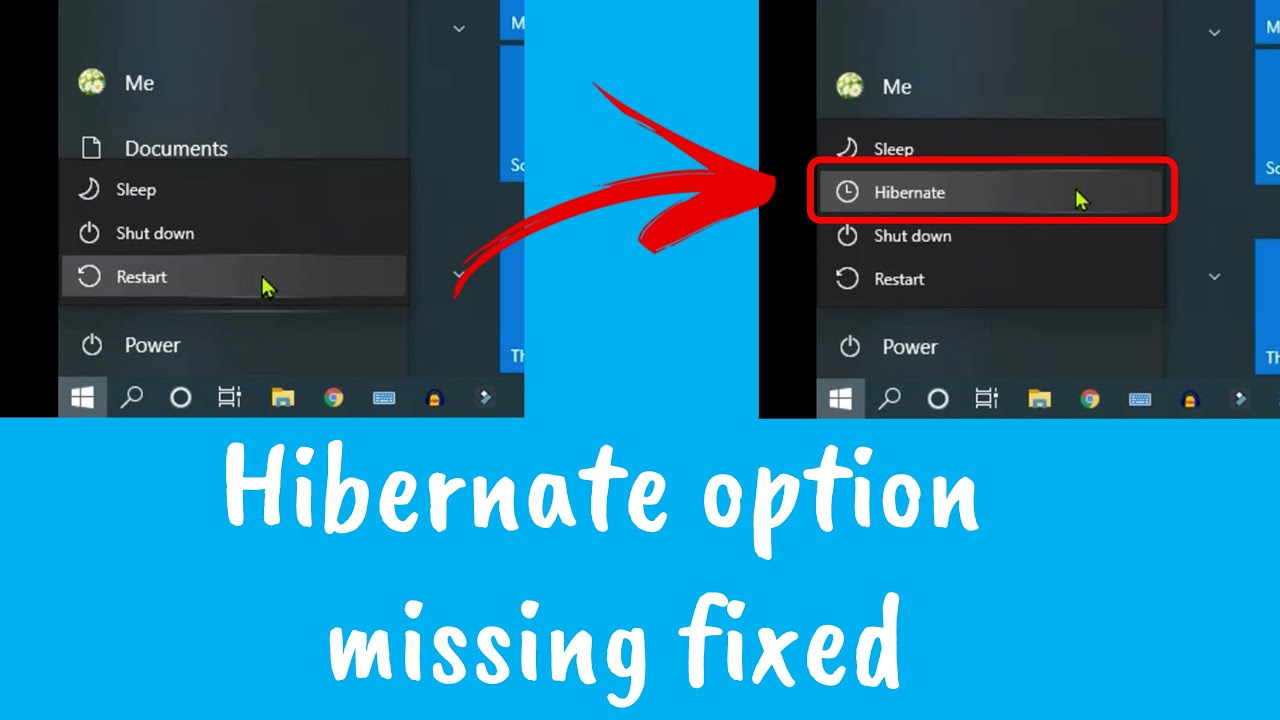
Hibernation, a power-saving feature in Windows 10, allows users to enter a state where the operating system and all open applications are saved to disk, enabling a quick resumption of work when the computer is powered back on. While this feature offers convenience, it can also consume significant disk space and introduce potential issues. Understanding the intricacies of hibernation and the benefits of disabling it can empower users to optimize their system’s performance and storage efficiency.
The Mechanics of Hibernation
When a computer enters hibernation mode, it performs the following actions:
-
Data Preservation: The entire system’s state, including all open applications, documents, and settings, is written to a dedicated hibernation file on the hard drive. This file, typically named
hiberfil.sys, serves as a snapshot of the system’s memory at the time of hibernation. - Power Down: The computer’s power consumption is reduced to a minimal level, effectively shutting down all components except for the hard drive and the motherboard’s minimal power management circuitry.
- Quick Resumption: Upon restarting, the computer reads the hibernation file, restoring the system’s state to the moment of hibernation. This allows for a rapid return to work, eliminating the need to boot the operating system from scratch.
The Trade-offs of Hibernation
While hibernation offers a seemingly convenient way to save energy and quickly resume work, it comes with certain drawbacks:
-
Disk Space Consumption: The hibernation file,
hiberfil.sys, can occupy a significant amount of disk space, potentially exceeding the size of the system’s RAM. This can become problematic for users with limited storage capacity, especially on devices with smaller hard drives. - Potential for Corruption: While rare, the hibernation file can become corrupted, leading to system instability or an inability to resume from hibernation.
- Security Concerns: The hibernation file contains sensitive data about the user’s system and activities, potentially exposing it to unauthorized access if the device is compromised.
Benefits of Disabling Hibernation
Given the potential downsides, disabling hibernation can be beneficial for users who prioritize storage efficiency, system performance, and security:
-
Increased Disk Space: Disabling hibernation eliminates the
hiberfil.sysfile, freeing up valuable disk space. This can be particularly advantageous for users with limited storage capacity or who frequently install large applications and files. - Enhanced System Performance: By eliminating the need to write and read the hibernation file, disabling hibernation can improve system performance, especially during boot-up and shutdown processes.
- Improved Security: Disabling hibernation removes a potential entry point for malicious actors who might exploit vulnerabilities in the hibernation file to gain unauthorized access to the system.
Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10
Disabling hibernation in Windows 10 is a straightforward process that can be achieved through the command prompt or the Power Options menu.
Method 1: Using the Command Prompt
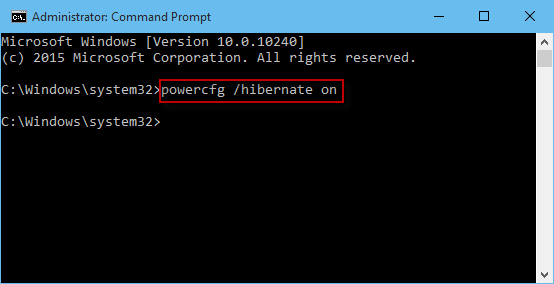
- Open the Command Prompt: Search for "cmd" in the Windows search bar and run it as administrator.
-
Disable Hibernation: Type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /hibernate off -
Verify: To confirm that hibernation is disabled, type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /hibernateIf hibernation is disabled, the output will display "Hibernation is disabled."
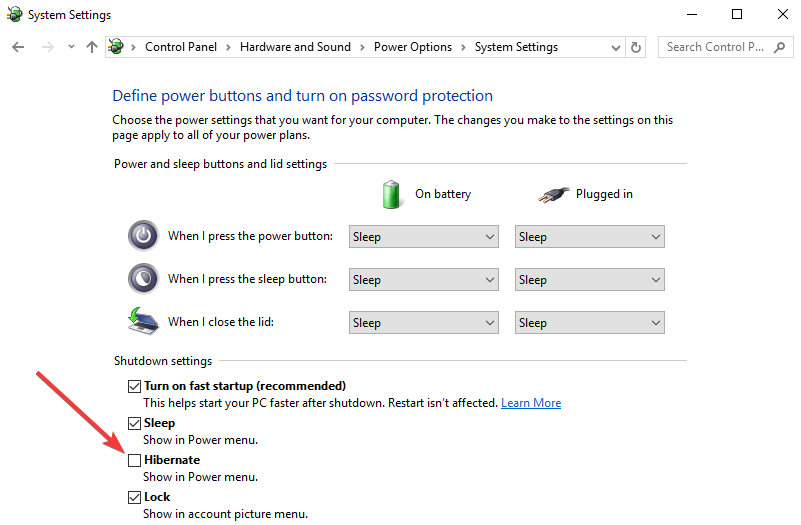
Method 2: Using Power Options
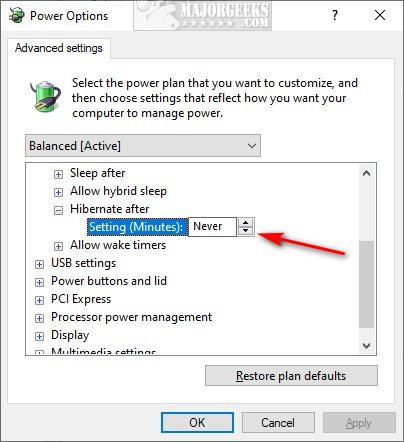
- Open Power Options: Search for "power options" in the Windows search bar and select the result.
- Choose a Power Plan: Select the power plan currently in use (usually Balanced or High Performance).
- Change Plan Settings: Click on "Change plan settings" next to the selected plan.
- Advanced Power Settings: Click on "Change advanced power settings."
- Disable Hibernation: Expand the "Sleep" section, then "Hibernate after," and set the value to "Never."
FAQs on Disabling Hibernation
Q: What happens to my unsaved work if I disable hibernation?
A: Disabling hibernation does not affect unsaved work. Any unsaved data will be lost upon shutting down the computer, just as it would with a normal shutdown.
Q: Will disabling hibernation affect my system’s battery life?
A: Disabling hibernation will not have a significant impact on battery life. The primary purpose of hibernation is to quickly resume work, not to conserve battery power.
Q: Can I re-enable hibernation if I change my mind?
A: Yes, hibernation can be re-enabled by following the same steps as disabling it, but using the powercfg /hibernate on command in the Command Prompt or setting the "Hibernate after" value to a specific time in the Power Options menu.
Q: Should I disable hibernation on all Windows 10 devices?
A: The decision to disable hibernation depends on individual needs and preferences. For users with limited storage space or those who prioritize system performance and security, disabling hibernation can be beneficial. However, if quick resumption is a key requirement, hibernation may be a valuable feature to retain.
Tips for Disabling Hibernation
- Backup Important Data: Before disabling hibernation, ensure that all important data is backed up to prevent accidental loss.
- Monitor Disk Space: Regularly monitor disk space usage to ensure that disabling hibernation has freed up sufficient storage.
- Consider Alternatives: Explore alternative power-saving options, such as sleep mode, which consumes less disk space and offers a faster resume time than hibernation.
Conclusion
Disabling hibernation in Windows 10 can be a valuable step towards optimizing system performance, maximizing storage efficiency, and enhancing security. By carefully considering the benefits and drawbacks of hibernation, users can make an informed decision that aligns with their individual needs and preferences. While hibernation may offer convenience, the potential for disk space consumption, corruption, and security vulnerabilities can be mitigated by disabling the feature and exploring alternative power-saving options.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Disabling Hibernation in Windows 10. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!