Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11
Related Articles: Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11
Windows 11, like its predecessor Windows 10, incorporates a feature known as "Fast Startup" designed to expedite the boot process. This feature, while seemingly beneficial, can sometimes present challenges for users, especially those involved in system troubleshooting or data recovery. Disabling Fast Startup allows for a more traditional boot sequence, providing greater control and access during critical system operations.
The Mechanics of Fast Startup
Fast Startup, also referred to as "Hybrid Shutdown," combines elements of both a full shutdown and a hibernation state. Upon selecting "Shut Down," the system does not completely power off. Instead, it saves the current system state to a hibernation file, known as "hiberfil.sys," and then enters a low-power state. This pre-loaded state enables a quicker boot-up, as the system can quickly restore the saved state rather than loading everything from scratch.
Why Disable Fast Startup?
While Fast Startup offers a faster boot experience, it can introduce certain limitations and complexities:
- Troubleshooting Challenges: Disabling Fast Startup is often necessary when troubleshooting system errors or performing data recovery. In a traditional boot sequence, the system undergoes a complete power cycle, ensuring a clean start. Fast Startup, however, maintains the system state, potentially hindering troubleshooting efforts.
- Data Recovery Complications: During data recovery processes, especially those involving deleted files or system crashes, disabling Fast Startup is crucial. This allows for a more thorough examination of the system’s state, potentially increasing the chances of successful data retrieval.
- Compatibility Issues: Some applications or hardware configurations may not fully support Fast Startup. Disabling this feature can resolve compatibility issues and ensure smooth operation.
- Enhanced Security: While less common, disabling Fast Startup can potentially enhance system security by preventing the persistence of sensitive data in the hibernation file.
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11 is a straightforward process:
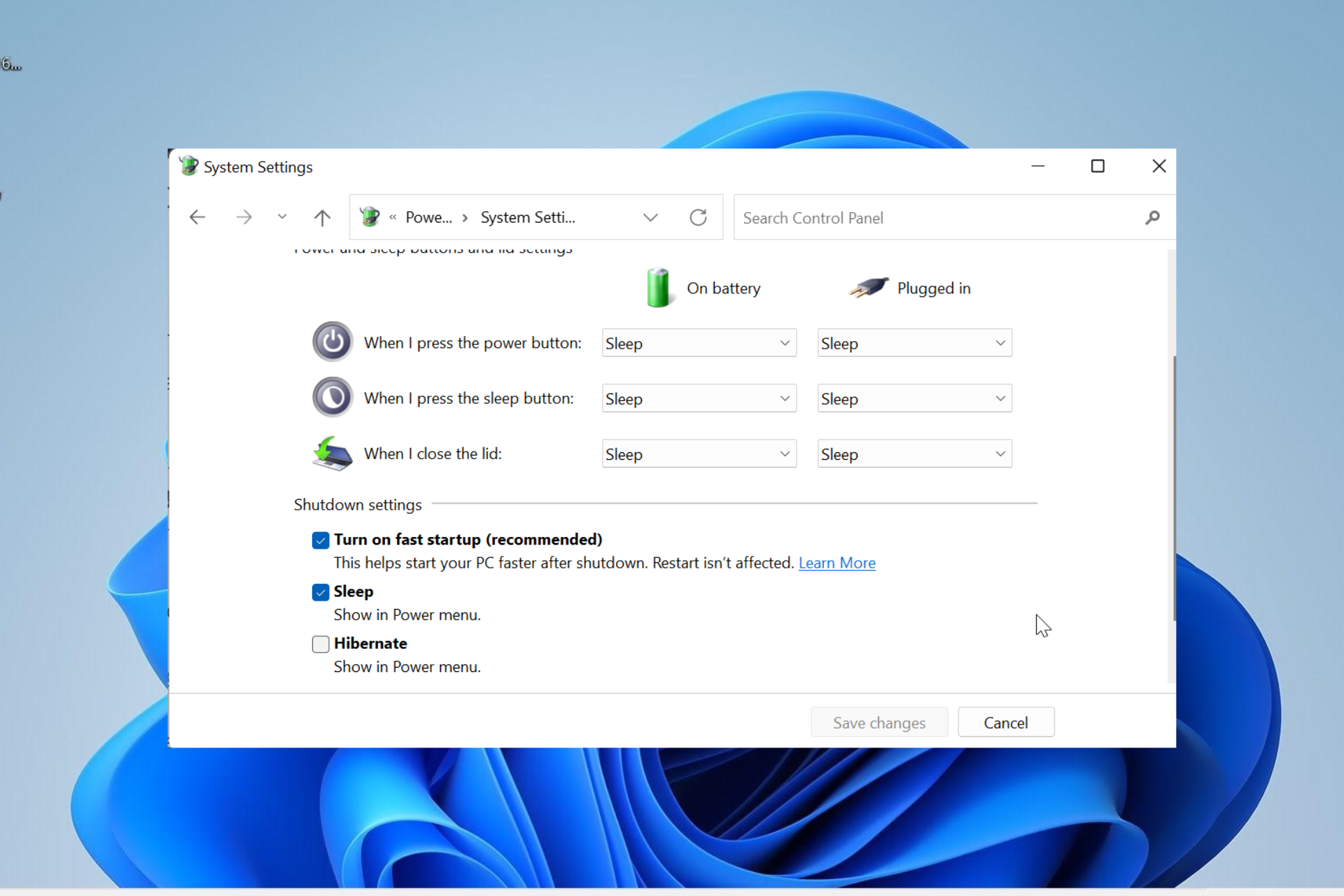
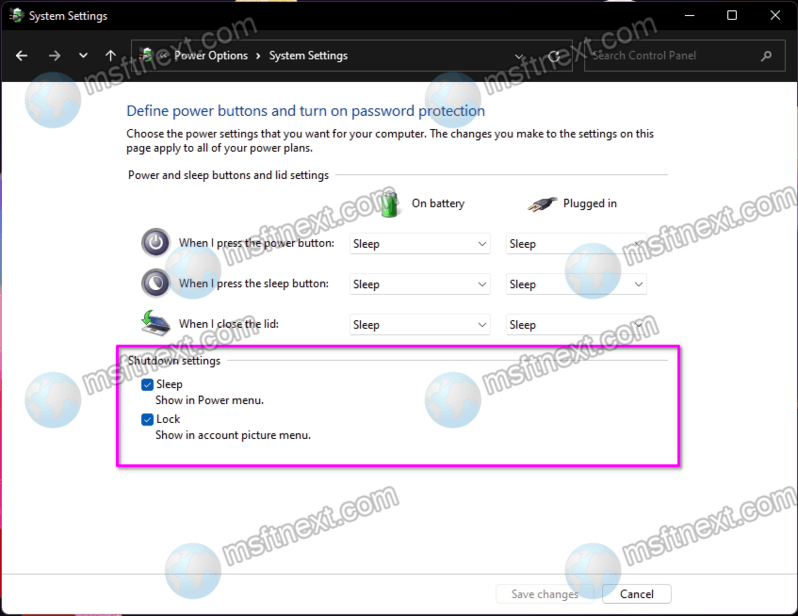
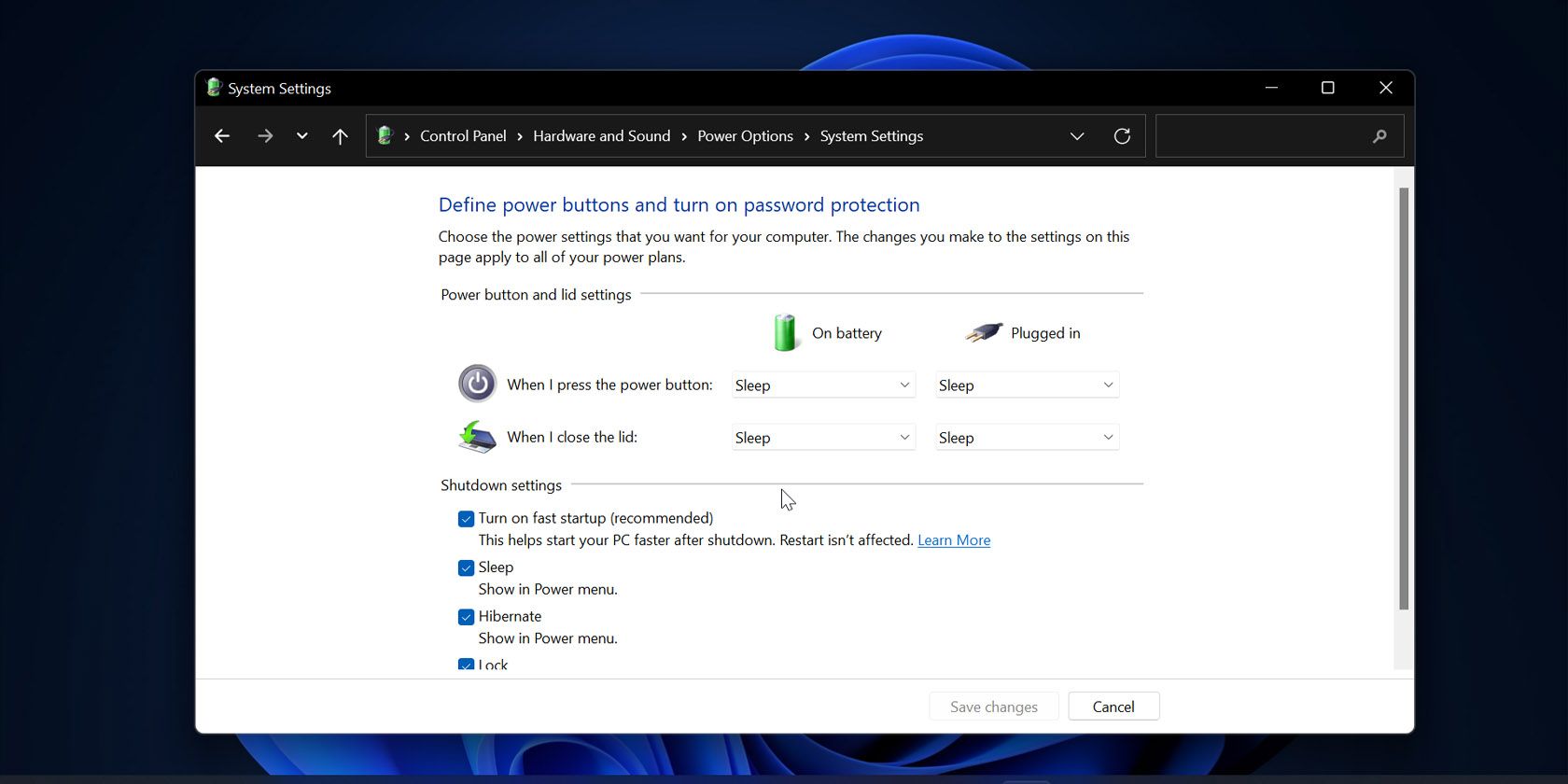
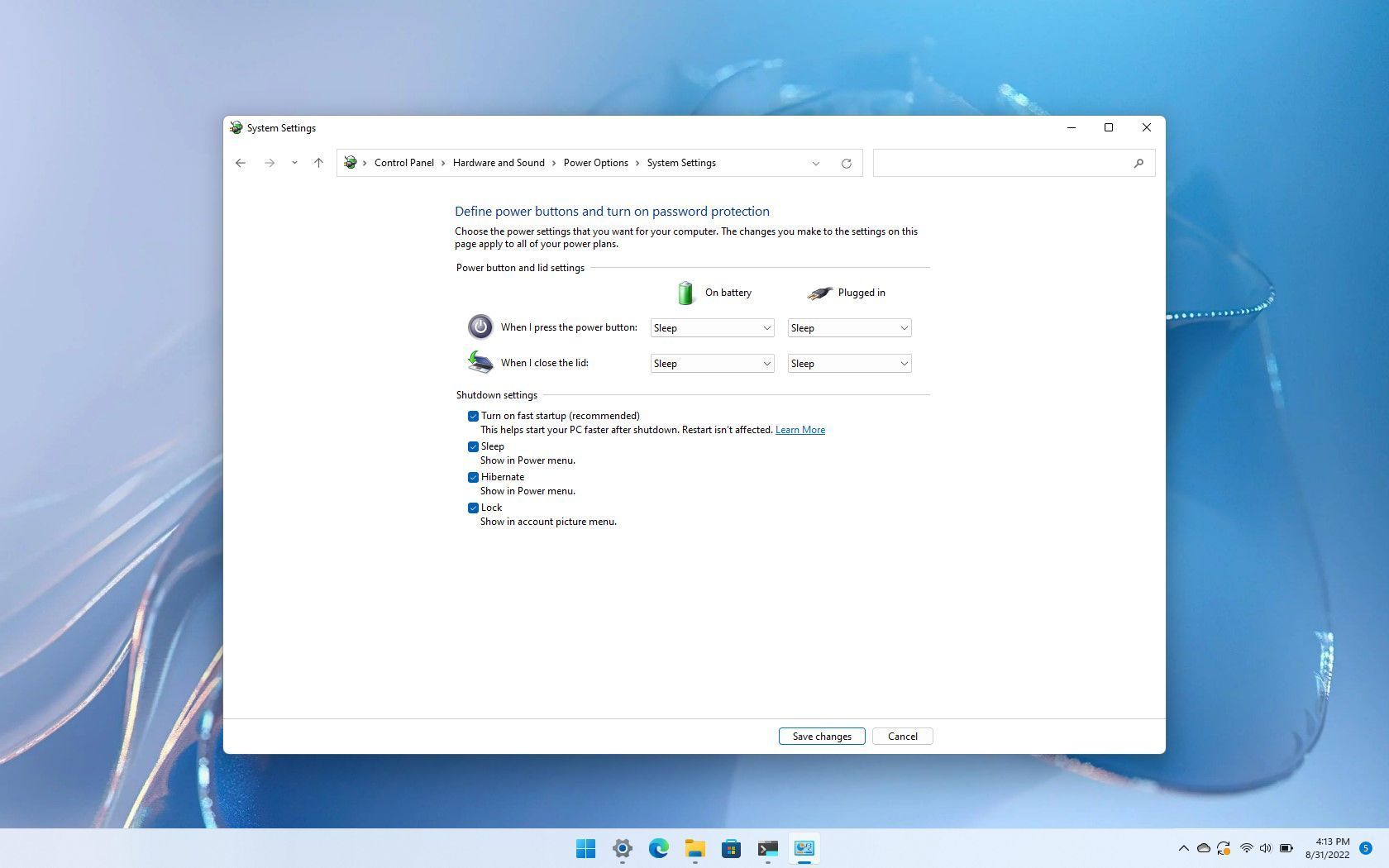
- Access Power Options: Open the "Control Panel" by searching for it in the Windows search bar. Navigate to "Hardware and Sound" and then "Power Options."
- Choose "Choose what the power buttons do": On the left pane of the Power Options window, click on "Choose what the power buttons do."
- Access Advanced Settings: Click on the "Change settings that are currently unavailable" link at the top of the window.
- Disable Fast Startup: In the "Shutdown settings" section, uncheck the box labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
- Save Changes: Click "Save Changes" to apply the modification.
FAQs Regarding Disabling Fast Startup
Q: What are the potential downsides of disabling Fast Startup?
A: Disabling Fast Startup can lead to a slightly longer boot time compared to using the Fast Startup feature. However, the difference is usually negligible and the benefits of disabling it often outweigh this minor inconvenience.
Q: Is it necessary to disable Fast Startup for every user on the computer?
A: Disabling Fast Startup is a system-wide setting. This means that the change will apply to all user accounts on the computer.
Q: Can I re-enable Fast Startup after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable Fast Startup by following the same steps mentioned above and checking the "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" box.
Tips for Disabling Fast Startup
- Create a System Restore Point: Before making any significant system changes, including disabling Fast Startup, it is always advisable to create a system restore point. This allows you to revert to a previous system state if any issues arise.
- Check for Updates: Ensure your Windows 11 system is up to date with the latest updates and patches. This can help minimize potential compatibility issues or bugs related to Fast Startup.
- Monitor System Performance: After disabling Fast Startup, monitor your system’s performance for any noticeable changes in boot times or overall responsiveness.
Conclusion
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11 is a decision that should be made based on individual needs and system usage patterns. While Fast Startup offers a faster boot experience, it can sometimes hinder troubleshooting and data recovery efforts. By understanding the mechanics and potential implications of Fast Startup, users can make informed decisions regarding its activation or deactivation, ultimately optimizing their system’s performance and functionality for their specific requirements.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!