Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Fast startup, a feature introduced in Windows 8, aims to expedite the boot process by utilizing a hybrid shutdown approach. Instead of completely shutting down the system, it saves the system’s current state to a hibernation file, allowing for a quicker boot-up. While this feature offers a noticeable speed improvement, it can lead to compatibility issues with certain software and hardware, and it may not be the ideal solution for all users.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of fast startup in Windows 11, outlining its advantages and disadvantages, and offering a step-by-step process for disabling it.
Delving into the Mechanics of Fast Startup
When you initiate a shutdown in Windows 11 with fast startup enabled, the system does not completely power down. Instead, it performs a hybrid shutdown, taking the following steps:
- Saving the System State: The operating system saves the current state of the kernel, drivers, and user applications to a hibernation file located on the system drive. This file, typically named "hiberfil.sys," stores the essential data required for a faster restart.
- Powering Down: The system enters a low-power state, effectively shutting down the majority of hardware components.
- Quick Restart: Upon restarting, the system loads the saved state from the hibernation file, bypassing the typical boot process and restoring the system to its previous state. This significantly reduces the time it takes to boot into Windows.
The Advantages of Fast Startup
The primary advantage of fast startup is its ability to significantly reduce the time required to boot into Windows. This translates to a more efficient and responsive user experience, especially for users who frequently restart their computers.
The Drawbacks of Fast Startup
While fast startup offers a noticeable speed boost, it also comes with certain drawbacks that may make it unsuitable for all users:
- Compatibility Issues: Fast startup can lead to compatibility issues with certain software and hardware, especially older applications or devices that are not designed to work with this feature. This can manifest as unexpected errors, program crashes, or system instability.
- Limited System Control: Fast startup utilizes a hybrid shutdown approach, which means the system does not completely shut down. This can lead to issues with hardware that relies on a complete power cycle, such as external hard drives or certain peripherals.
- Potential Data Corruption: In rare cases, fast startup can lead to data corruption if the hibernation file is corrupted or incomplete. This can result in data loss or system instability.
- Increased Power Consumption: Fast startup keeps the system in a low-power state instead of completely shutting down, potentially increasing power consumption.
When to Consider Disabling Fast Startup
Disabling fast startup may be beneficial in the following scenarios:
- Troubleshooting Compatibility Issues: If you are experiencing compatibility issues with certain software or hardware, disabling fast startup can help identify and resolve these problems.
- Using Hardware That Requires a Complete Shutdown: If you use hardware that requires a complete power cycle, such as external hard drives or certain peripherals, disabling fast startup ensures a proper shutdown and prevents potential issues.
- Minimizing Power Consumption: If you are concerned about power consumption, disabling fast startup ensures that the system completely shuts down, reducing power consumption.
- Addressing Data Corruption Concerns: If you have concerns about potential data corruption due to fast startup, disabling it can minimize this risk.
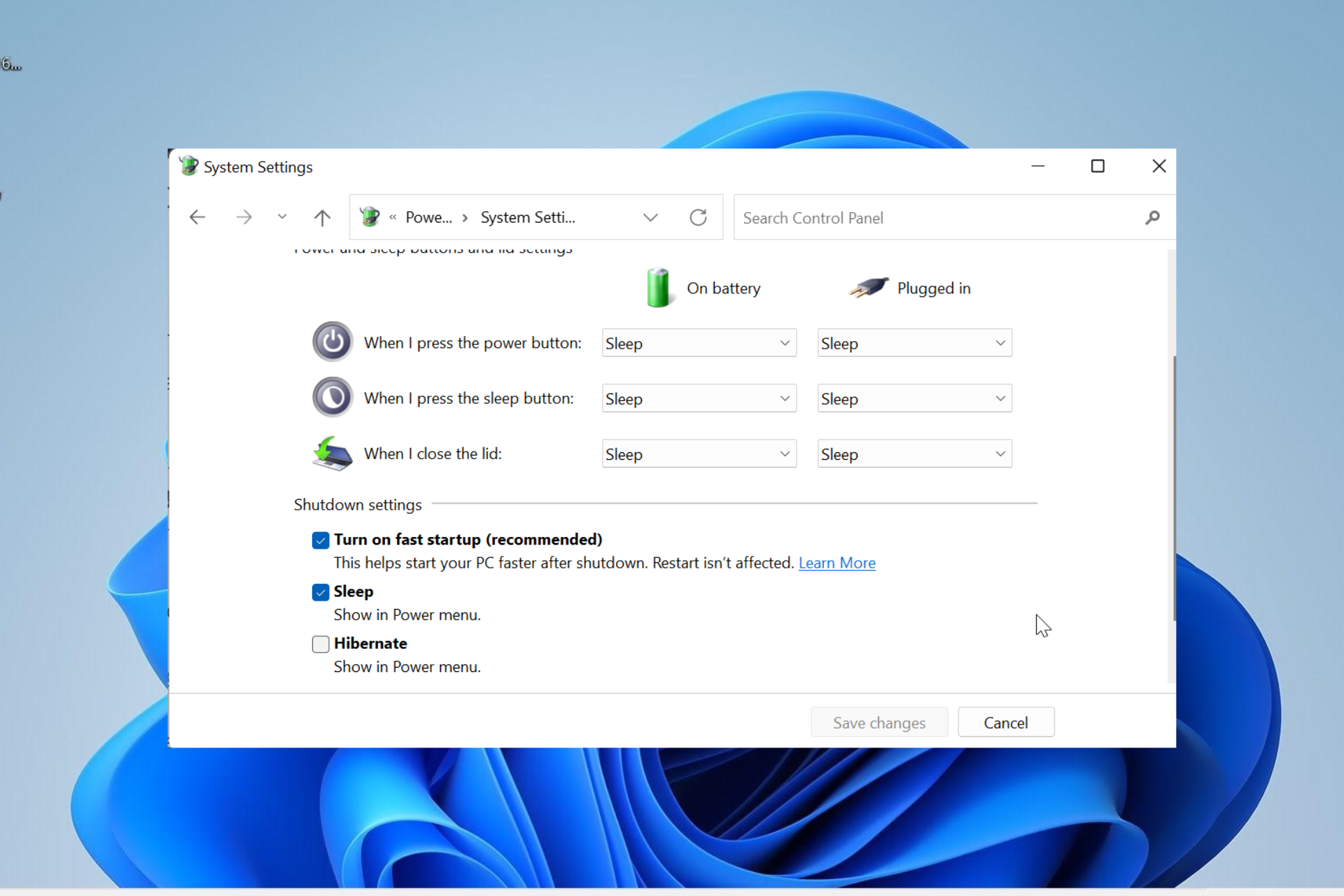
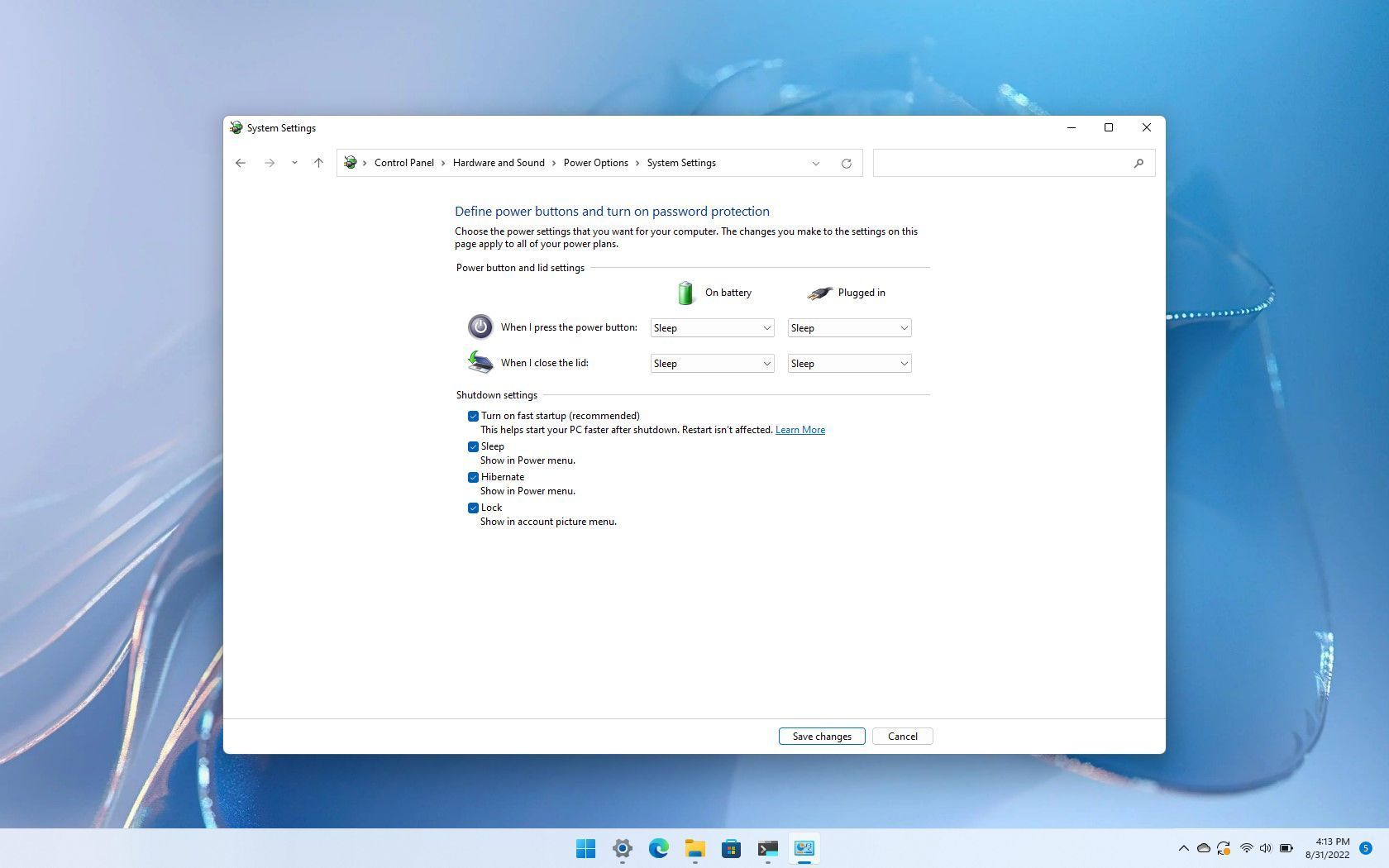
Step-by-Step Guide to Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11
- Open Control Panel: Navigate to the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar or by pressing the Windows key + R and typing "control" followed by Enter.
- Select "Power Options": Within the Control Panel, locate and click on "Power Options."
- Choose "Choose what the power buttons do": In the left-hand pane of the Power Options window, click on "Choose what the power buttons do."
- Click "Change settings that are currently unavailable": At the bottom of the window, click on the link "Change settings that are currently unavailable."
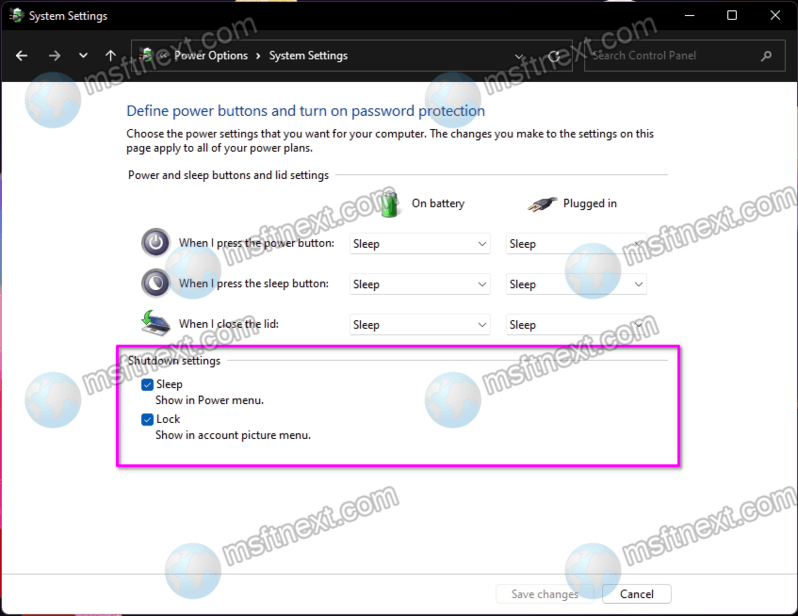
- Uncheck "Turn on fast startup (recommended)": Locate the "Shutdown settings" section and uncheck the box next to "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
- Save Changes: Click on "Save Changes" to apply the modifications and disable fast startup.
FAQs on Disabling Fast Startup
Q: Will disabling fast startup slow down my computer’s boot time?
A: Disabling fast startup will slightly increase the boot time as the system will have to go through the complete boot process. However, the difference in boot time will generally be minimal, especially on modern computers with fast hardware.
Q: Can I enable fast startup again after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable fast startup by following the same steps outlined above and checking the "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" box.
Q: Is it necessary to restart my computer after disabling fast startup?
A: It is recommended to restart your computer after disabling fast startup to ensure the changes take effect properly.
Q: Can I disable fast startup using the Command Prompt?
A: Yes, you can disable fast startup using the Command Prompt by executing the following command:
powercfg /h offQ: Can I disable fast startup through the BIOS settings?
A: No, fast startup is a feature managed by the operating system and cannot be disabled through the BIOS settings.
Tips for Disabling Fast Startup
- Backup Your Data: Before making any changes to system settings, it is always recommended to back up your important data to prevent accidental data loss.
- Monitor System Performance: After disabling fast startup, monitor your system’s performance and ensure there are no unexpected issues or errors.
- Consider Using Other Optimization Techniques: If you are concerned about system performance, explore other optimization techniques such as using an SSD for your system drive, cleaning up your hard drive, or disabling unnecessary startup programs.
Conclusion
Disabling fast startup in Windows 11 can be beneficial in certain situations, particularly when dealing with compatibility issues, hardware limitations, or concerns about data corruption. While it may slightly increase the boot time, the potential benefits outweigh the minor inconvenience for some users. By carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages of fast startup, users can make an informed decision about whether or not to disable it based on their individual needs and preferences.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!