The Compatibility of Windows 11 with 7th Generation Intel Processors: A Detailed Analysis
Related Articles: The Compatibility of Windows 11 with 7th Generation Intel Processors: A Detailed Analysis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Compatibility of Windows 11 with 7th Generation Intel Processors: A Detailed Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Compatibility of Windows 11 with 7th Generation Intel Processors: A Detailed Analysis
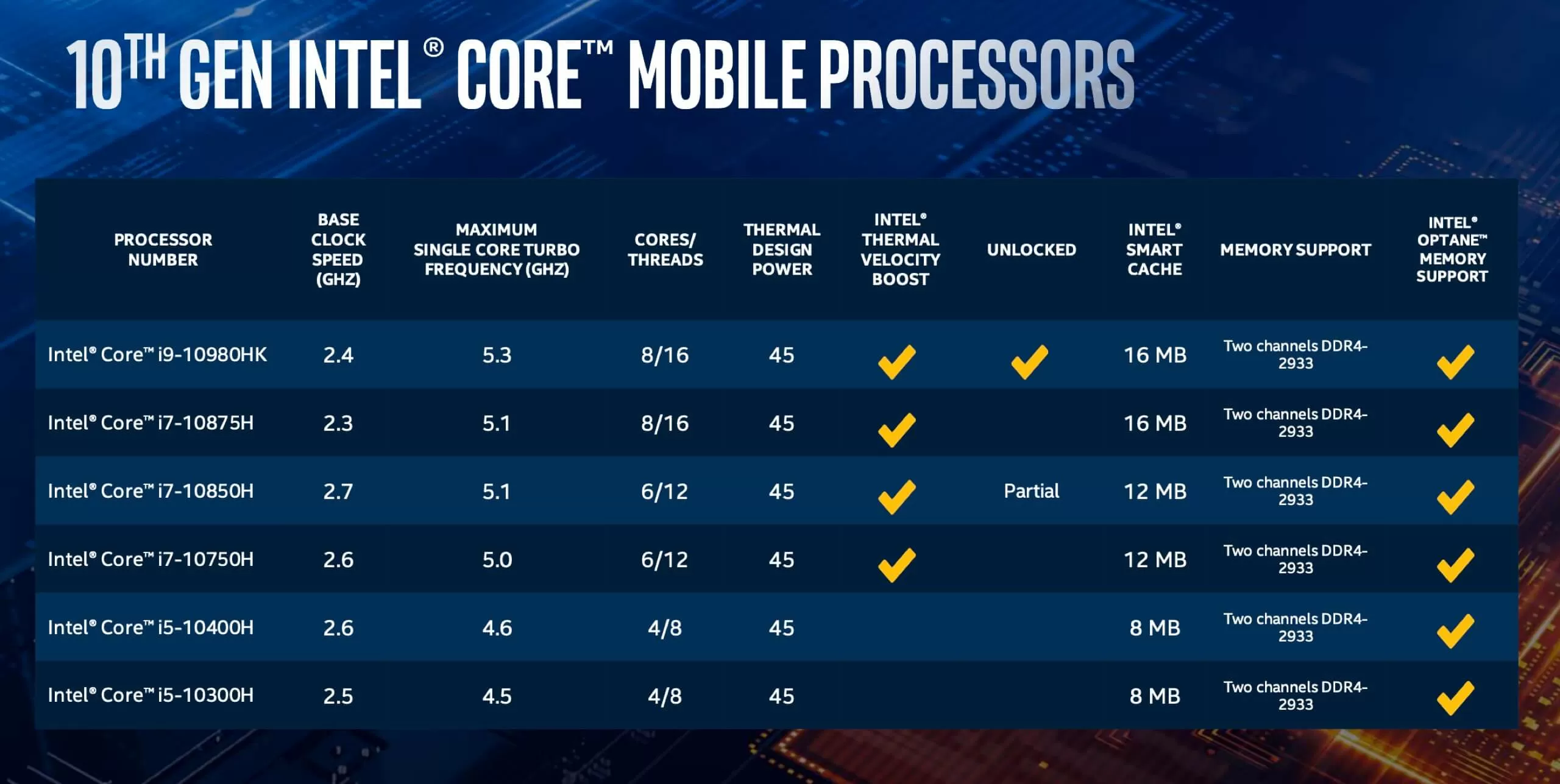
The launch of Windows 11 brought with it a wave of excitement and anticipation, but also a dose of uncertainty regarding its compatibility with older hardware. One of the key questions that arose was whether the new operating system would support 7th generation Intel processors, commonly found in systems built around 2016 and 2017. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of this compatibility issue, addressing the complexities involved and offering valuable insights for users considering an upgrade to Windows 11.
Understanding the Minimum System Requirements:
Microsoft, in its official documentation, outlines a set of minimum hardware requirements for Windows 11, including a processor requirement. The initial release specified that systems must have a processor with at least four cores, a clock speed of 1 GHz or higher, and support for Secure Boot and TPM 2.0. These requirements, however, were not explicitly tied to specific processor generations.
The Initial Exclusion of 7th Generation Intel Processors:
Following the initial release of Windows 11, it became apparent that while the minimum requirements were met by 7th generation Intel processors, they were not officially supported. This led to widespread confusion and frustration among users who found themselves unable to upgrade their systems. The exclusion stemmed from Microsoft’s decision to focus on enhancing security and performance, and it believed that older processors, including 7th generation Intel, lacked the necessary security features and capabilities to meet its standards.
The Subsequent Change in Policy:
In response to the backlash and concerns raised by users and manufacturers alike, Microsoft revised its stance on compatibility. Recognizing the limitations of its initial approach, the company acknowledged that 7th generation Intel processors, while not originally included in the supported list, could indeed run Windows 11 effectively. This change was implemented through a combination of updates and policy revisions, making it possible for users with compatible systems to install Windows 11.
The Importance of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot:
Despite the revised policy, it is crucial to understand that not all systems with 7th generation Intel processors are automatically compatible with Windows 11. The key determining factor remains the presence of two critical security features: TPM 2.0 (Trusted Platform Module) and Secure Boot.
- TPM 2.0: A hardware component that provides a secure environment for storing cryptographic keys and performing security operations.
- Secure Boot: A firmware feature that ensures the operating system and boot process are free from malicious tampering.
These features, while not mandatory for older Windows versions, are considered essential for the enhanced security framework of Windows 11. Therefore, even if your system has a 7th generation Intel processor, it might still be ineligible for Windows 11 if it lacks TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot.
Determining Compatibility and Potential Workarounds:
To ascertain whether your system with a 7th generation Intel processor is compatible with Windows 11, you can utilize the following methods:
-
Microsoft’s PC Health Check App: This free tool, available from the Microsoft website, will analyze your system’s hardware and determine its compatibility with Windows 11. It will specifically check for the presence of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot.
-
BIOS Settings: Access your system’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and navigate to the security settings. Look for options related to TPM and Secure Boot. Ensure they are enabled. If your system does not support these features, you might be unable to upgrade to Windows 11.
-
Manual Verification: You can manually check your system’s specifications to confirm the presence of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot. However, this method requires a more advanced understanding of hardware and system configuration.
Tips for Ensuring Compatibility:
-
Update Your BIOS: Ensure your system’s BIOS is up to date. Newer BIOS versions may provide improved support for Windows 11 and enable TPM 2.0 or Secure Boot if previously unavailable.
-
Check for TPM 2.0 Module: If your system lacks a dedicated TPM 2.0 chip, you might be able to utilize a firmware-based TPM solution. However, this might require further investigation and specific instructions from your system manufacturer.
-
Contact Your System Manufacturer: For assistance with compatibility issues, reach out to your system’s manufacturer. They may have specific guidance or workarounds for enabling TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot on your particular model.
FAQs on Windows 11 Compatibility with 7th Generation Intel Processors:
-
Q: Will all systems with 7th generation Intel processors be able to upgrade to Windows 11?
- A: No. While Microsoft has relaxed its initial stance, the presence of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot remains crucial for compatibility. Systems lacking these features will not be able to upgrade.
-
Q: Is it possible to upgrade to Windows 11 without TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot?
- A: While there are workarounds and unofficial methods, Microsoft strongly discourages upgrading without these security features. Doing so might compromise the security of your system and expose it to vulnerabilities.
-
Q: What are the benefits of using Windows 11 on a system with a 7th generation Intel processor?
- A: Windows 11 offers various benefits, including enhanced security, improved performance, a modern user interface, and access to the latest features and apps. However, these benefits may not be fully realized on older systems with limited hardware capabilities.
-
Q: Should I upgrade to Windows 11 if my system has a 7th generation Intel processor?
- A: The decision to upgrade depends on your individual needs and priorities. If you value the security enhancements and new features of Windows 11, and your system meets the compatibility requirements, then upgrading might be beneficial. However, if your system is nearing the end of its lifecycle or you are not comfortable with potential performance limitations, it might be more prudent to stick with your current operating system.
Conclusion:
The compatibility of Windows 11 with 7th generation Intel processors is a complex issue that has undergone significant changes since the initial release. While Microsoft initially excluded these processors, it later revised its stance, acknowledging their capability to run Windows 11 effectively. However, the presence of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot remains paramount for ensuring compatibility and maintaining the security integrity of the operating system. Users considering an upgrade to Windows 11 on systems with 7th generation Intel processors should carefully evaluate their system’s specifications, explore potential workarounds, and weigh the benefits against the potential limitations before making a decision.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Compatibility of Windows 11 with 7th Generation Intel Processors: A Detailed Analysis. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!