The Built-in Power of Compression: Exploring Windows 10’s File Archiving Capabilities
Related Articles: The Built-in Power of Compression: Exploring Windows 10’s File Archiving Capabilities
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Built-in Power of Compression: Exploring Windows 10’s File Archiving Capabilities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Built-in Power of Compression: Exploring Windows 10’s File Archiving Capabilities

Windows 10, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s flagship operating system, offers a range of features designed to enhance user experience and streamline everyday tasks. Among these features is the native ability to handle compressed files, a crucial aspect of efficient file management and data transfer.
While Windows 10 does not explicitly include a dedicated program labeled "Zip," it seamlessly integrates file compression functionality directly into its core file explorer. This integration allows users to create, extract, and manage compressed files effortlessly, eliminating the need for external applications.
Understanding File Compression
File compression is a process that reduces the size of a file by removing redundant data. This reduction in size offers several advantages:
- Reduced storage space: Compressed files occupy less storage space on hard drives, allowing users to store more data within the same physical capacity.
- Faster data transfer: Smaller files transfer more quickly over the internet or local networks, saving time and bandwidth.
- Enhanced data security: Compression can be used to encrypt files, adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Windows 10’s Built-in Compression Capabilities
Windows 10 leverages the ZIP file format, a widely adopted standard for file compression. This format is supported by most operating systems and applications, ensuring compatibility and ease of sharing.
Creating Compressed Files:
To create a compressed file in Windows 10, users can follow these simple steps:
- Select the files or folders: Right-click on the files or folders you want to compress.
- Choose "Add to archive": From the context menu, select the "Add to archive" option.
- Configure archive settings: A dialogue box will appear, allowing users to customize settings like archive name, compression level, and password protection.
- Create the archive: Click the "OK" button to create the compressed ZIP file.
Extracting Compressed Files:
Extracting compressed files is equally straightforward:
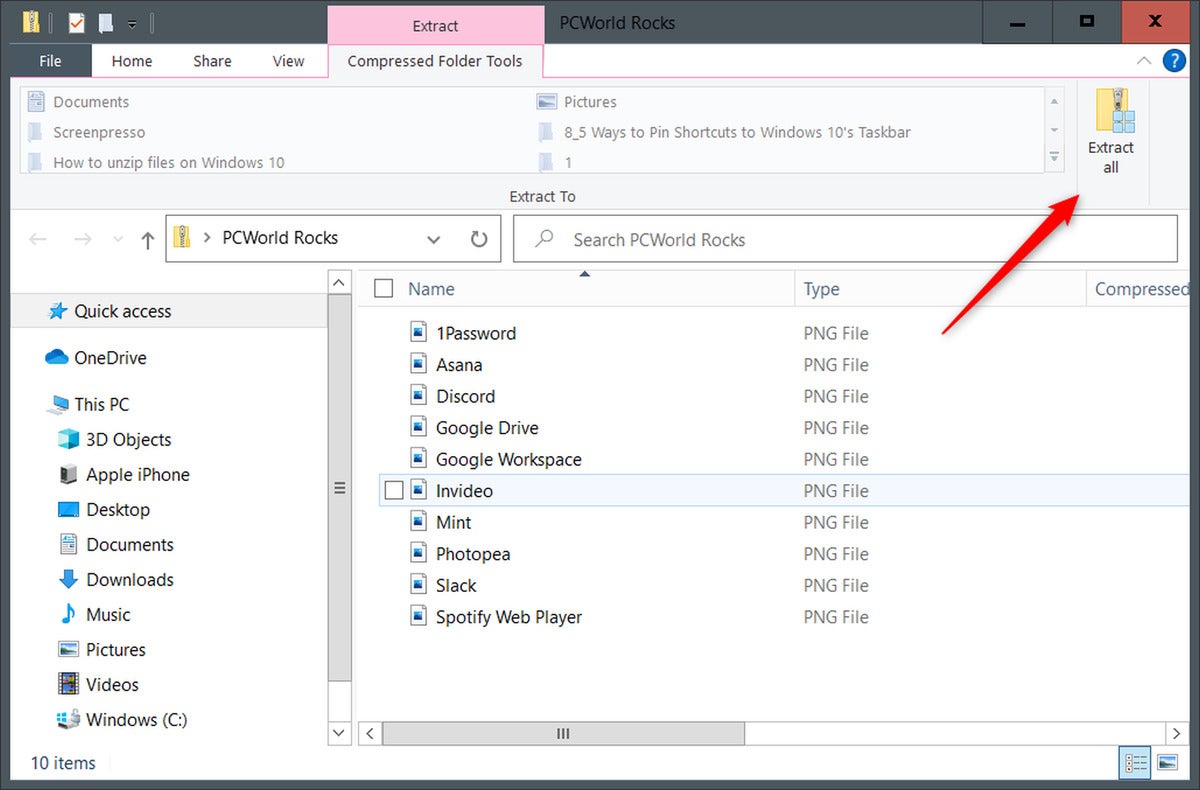
- Right-click the ZIP file: Locate the ZIP file and right-click on it.
- Select "Extract All": Choose the "Extract All" option from the context menu.
- Choose destination folder: A dialogue box will appear, allowing users to select the destination folder for the extracted files.
- Extract the files: Click the "Extract" button to extract the contents of the ZIP file.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Compression Options
While the basic compression functionality is readily accessible, Windows 10 also offers advanced options for users with specific needs:
- Compression levels: Users can select from different compression levels, balancing file size reduction with processing time. Higher compression levels result in smaller files but take longer to compress and extract.
- Password protection: Users can add passwords to their ZIP files, restricting access to authorized individuals.
- Self-extracting archives: Windows 10 allows users to create self-extracting archives (EXE files) that automatically extract their contents when executed.
- Splitting large archives: For very large files, users can split the archive into multiple smaller files, making it easier to transfer and manage.
The Importance of Compression in Modern Computing
File compression plays a vital role in modern computing, offering numerous benefits for users and organizations alike.
- Efficient data storage: Compression allows users to store more data within the same storage space, reducing the need for expensive upgrades and maximizing storage capacity.
- Faster data transfer: Compressed files transfer more quickly, enabling faster downloads, uploads, and file sharing. This is particularly important for users working with large files, such as videos, images, and software installations.
- Enhanced data security: Compression can be used to encrypt files, adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. This is crucial for sensitive data like financial records, personal documents, and confidential business information.
- Streamlined collaboration: Compression facilitates efficient collaboration by allowing users to share large files quickly and easily. This is particularly important for teams working on projects that involve the exchange of large datasets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I compress files without using the "Add to archive" option?
A: Yes, you can compress files using the "Send to" option in the context menu. Select the files you want to compress, right-click, choose "Send to," and then select "Compressed (zipped) folder."
Q: Can I change the compression level of an existing ZIP file?
A: Unfortunately, Windows 10 does not provide a built-in option to modify the compression level of an existing ZIP file. You would need to use a third-party compression tool to achieve this.
Q: What are the limitations of Windows 10’s built-in compression?
A: While Windows 10’s built-in compression is generally efficient, it may not be as powerful as dedicated compression software. For example, it may not achieve the same level of compression for certain file types, such as images or videos.
Tips for Effective File Compression
- Choose the right compression level: Select a compression level that balances file size reduction with processing time. Higher compression levels are generally more effective for data-rich files like images and videos, while lower levels are suitable for text-based files.
- Use password protection: Protect sensitive data by adding passwords to your ZIP files.
- Consider splitting large archives: Splitting large archives into smaller files makes them easier to transfer and manage.
- Explore third-party compression tools: For advanced compression needs, consider using dedicated compression software that offers more features and options.
Conclusion
Windows 10 seamlessly integrates file compression functionality into its core file explorer, empowering users to create, extract, and manage compressed files effortlessly. This built-in capability offers numerous benefits, including reduced storage space, faster data transfer, and enhanced data security. While Windows 10’s compression features are generally efficient, users with specific needs or who require advanced compression options may want to explore third-party compression tools. Regardless of the approach, understanding and utilizing file compression is essential for efficient file management and data handling in the modern digital landscape.



![9 best file compression tools for Windows 10 [2020 Guide]](https://cdn.windowsreport.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/winzip-windows-10-compression-tool.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Built-in Power of Compression: Exploring Windows 10’s File Archiving Capabilities. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!