Strengthening Windows 11 Security: A Deep Dive into Local Security Authority Protection
Related Articles: Strengthening Windows 11 Security: A Deep Dive into Local Security Authority Protection
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Strengthening Windows 11 Security: A Deep Dive into Local Security Authority Protection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Strengthening Windows 11 Security: A Deep Dive into Local Security Authority Protection
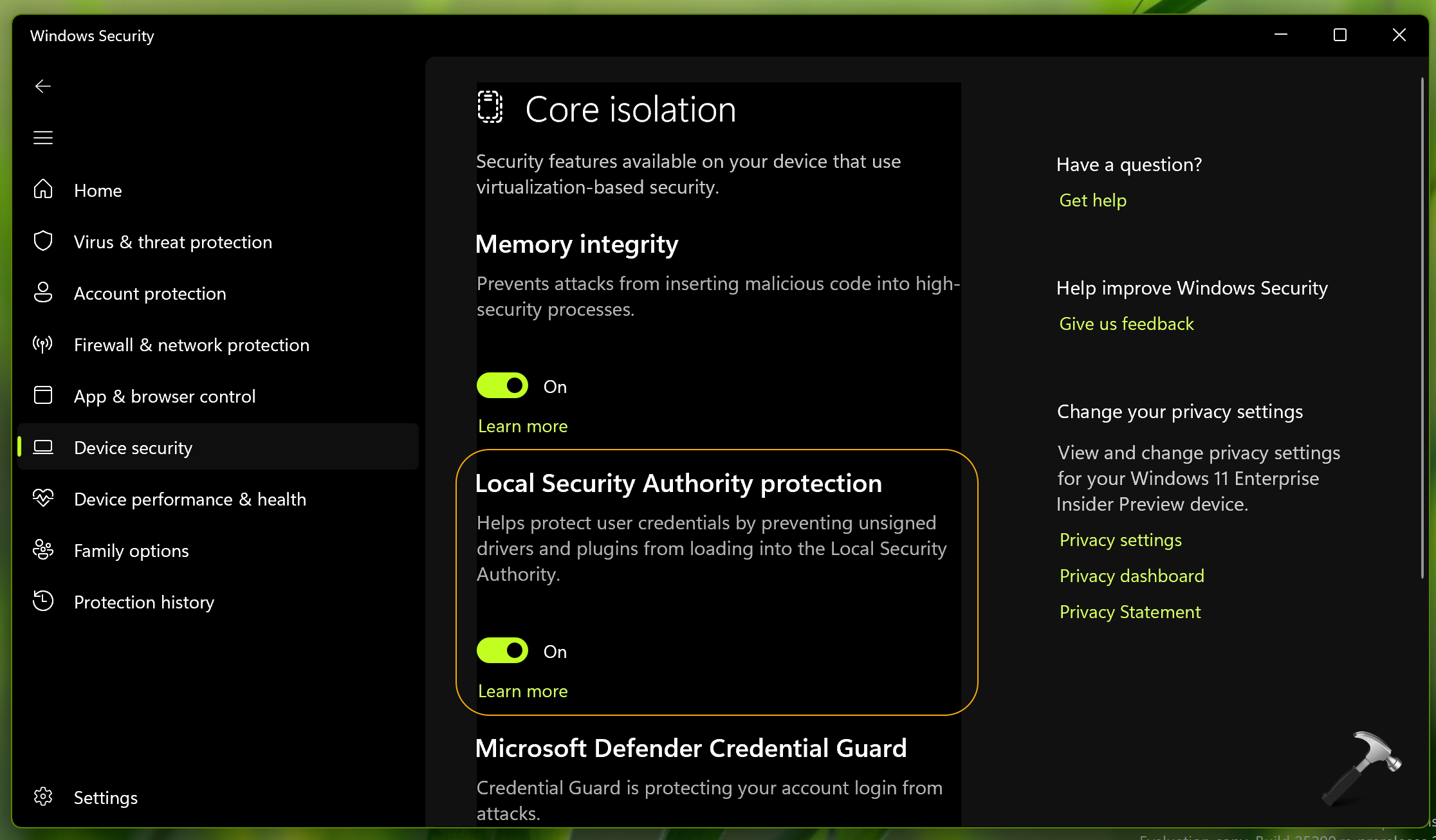
In the digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount. Windows 11, Microsoft’s latest operating system, incorporates robust security features, including the Local Security Authority (LSA) protection. This feature acts as a critical defense mechanism against malicious actors attempting to compromise the integrity of the system’s core functionalities.
Understanding the Local Security Authority (LSA)
The LSA is a vital component within Windows responsible for managing security policies, user authentication, and access control. It serves as the central authority for enforcing security measures across the operating system. The LSA’s critical role makes it a prime target for attackers seeking to gain unauthorized access or control over the system.
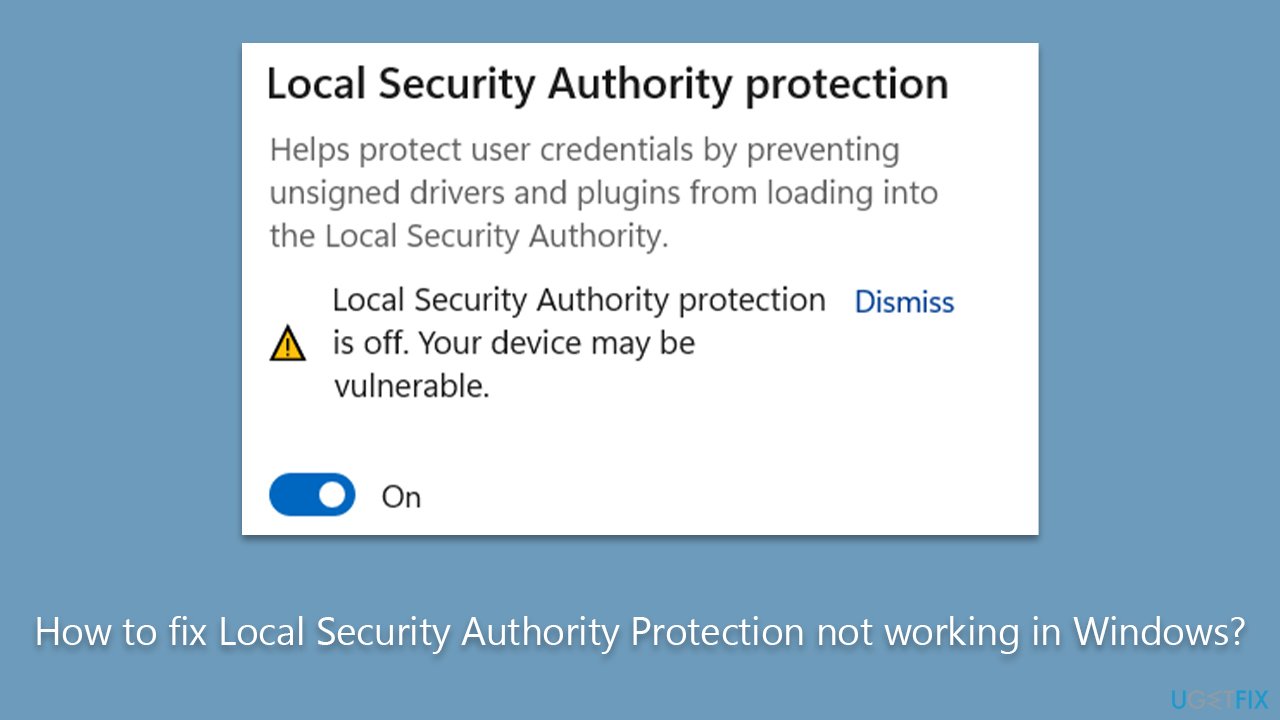
The Significance of LSA Protection
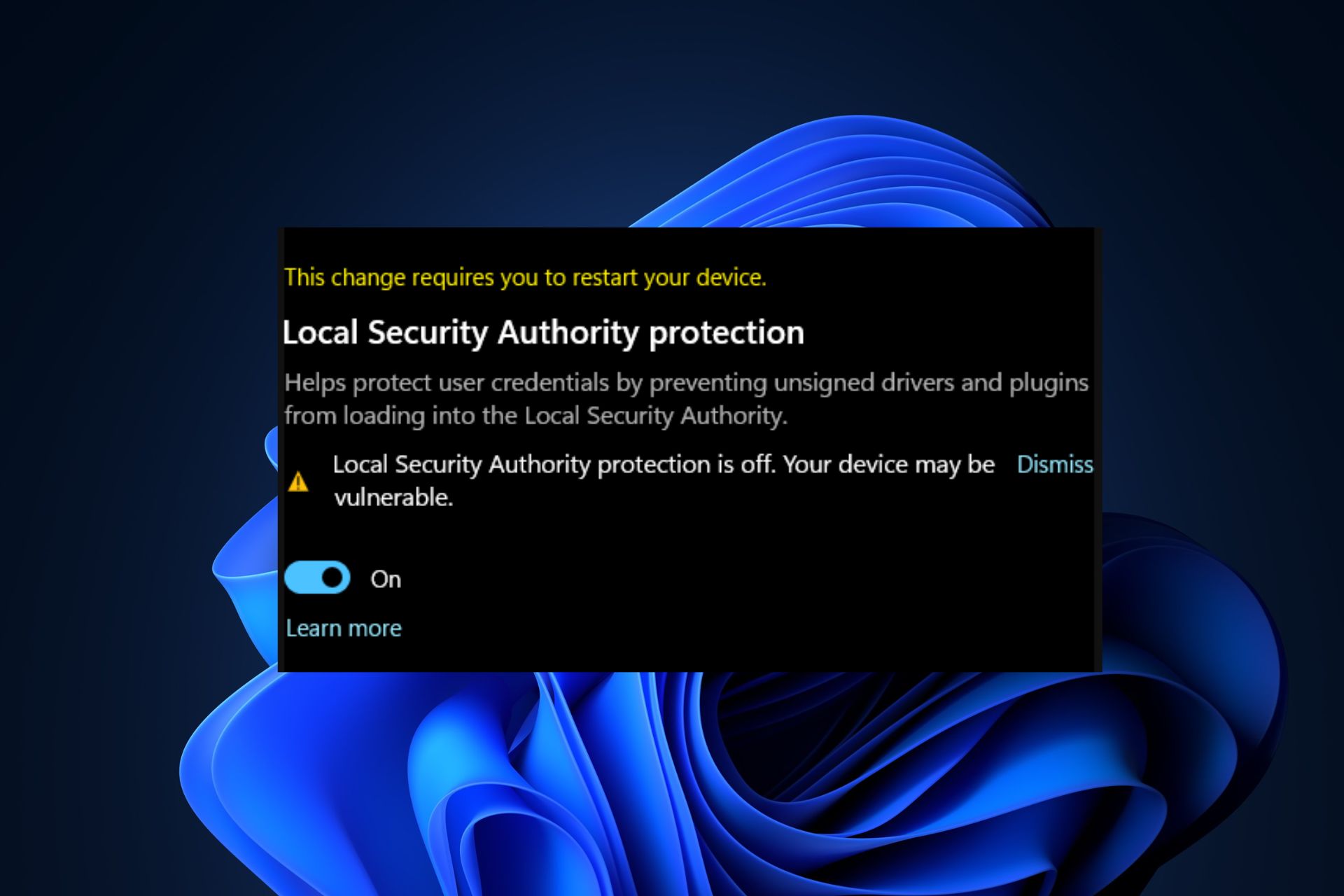
LSA protection is a security feature designed to shield the LSA from unauthorized access and manipulation. It functions as a barrier, preventing malicious programs from altering or exploiting the LSA’s processes, thereby safeguarding the system’s security infrastructure.
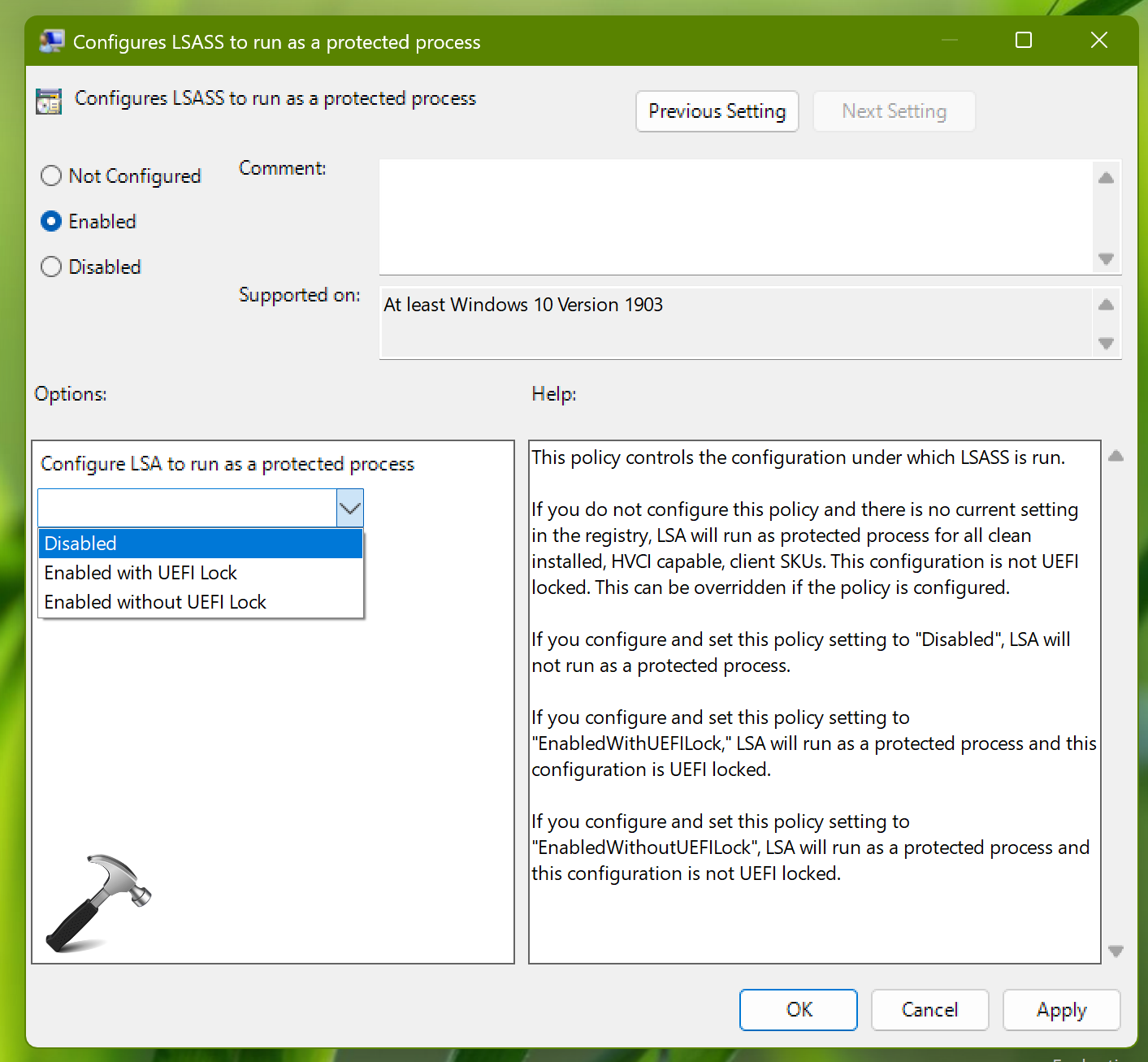
How LSA Protection Works
LSA protection in Windows 11 employs a multi-layered approach to enhance security:
- Process Isolation: The LSA is isolated from other processes, limiting potential attack vectors. This isolation restricts unauthorized access to the LSA’s critical functions.
- Integrity Level Control: The LSA operates at a high integrity level, restricting interactions with processes at lower integrity levels. This prevents malicious programs from influencing the LSA’s operations.
- Code Signing Verification: The LSA’s code is digitally signed, ensuring its authenticity and integrity. This verification process prevents malicious code injection or modification.
- Memory Protection: The LSA’s memory is protected from unauthorized access and manipulation, preventing attackers from directly accessing or altering sensitive data.
Benefits of Enabling LSA Protection
Enabling LSA protection in Windows 11 offers significant security benefits:
- Enhanced System Integrity: By safeguarding the LSA, LSA protection ensures the integrity of the system’s security policies and access control mechanisms, preventing unauthorized modifications or compromises.
- Protection Against Malware and Exploits: The isolation and integrity checks provided by LSA protection make it difficult for malware and exploits to target and manipulate the LSA, reducing the risk of successful attacks.
- Reduced Attack Surface: LSA protection limits the attack surface by restricting access to the LSA, making it a less attractive target for malicious actors.
- Improved User Authentication: LSA protection safeguards user authentication processes, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data and resources.
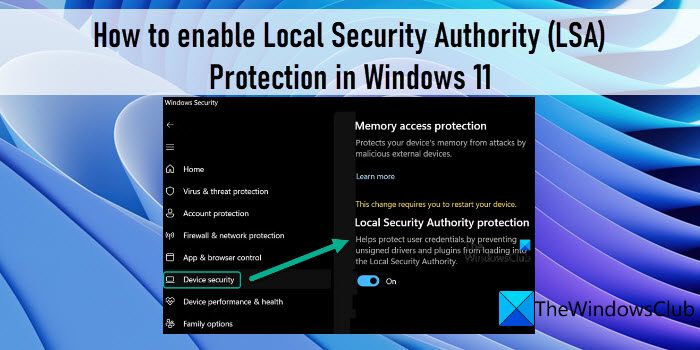
Enabling LSA Protection in Windows 11
LSA protection is typically enabled by default in Windows 11. However, it’s essential to verify its status and ensure it’s functioning correctly:
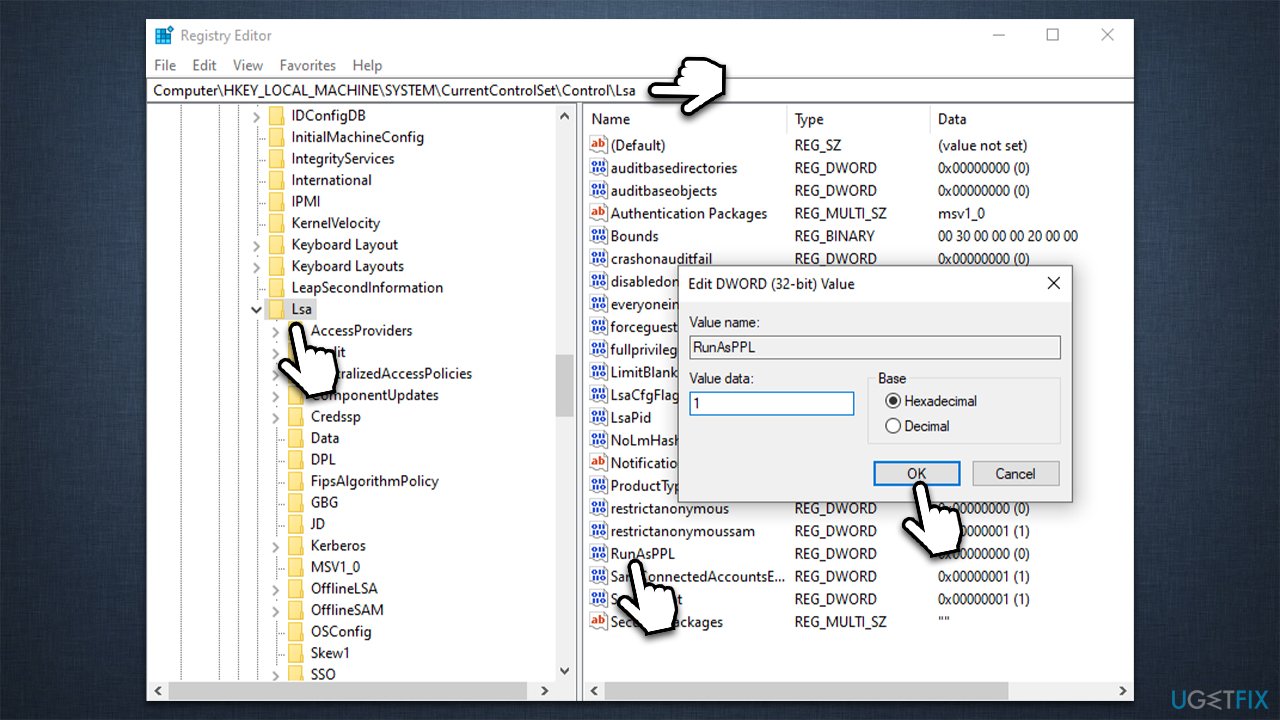
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor: Press Windows key + R, type gpedit.msc, and press Enter.
- Navigate to the Security Options: Expand Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options.
-
Verify LSA Protection Settings: Look for the following settings and ensure they are enabled:
- "Network security: LAN Manager authentication level" should be set to "Send LM & NTLM – use NTLMv2 if negotiated".
- "Network security: Restrict NTLM: Server" should be set to "Enabled".
- "Network security: Restrict NTLM: Workstation" should be set to "Enabled".
- "Network security: Do not store LAN Manager hash value on the SAM" should be set to "Enabled".
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is LSA protection always enabled in Windows 11?
A: While LSA protection is generally enabled by default in Windows 11, it’s crucial to verify its status and ensure it’s configured correctly.
Q: What are the potential risks if LSA protection is disabled?
A: Disabling LSA protection significantly increases the risk of system compromise. Malicious actors could exploit vulnerabilities in the LSA, gaining unauthorized access and control over the system.
Q: Can LSA protection be bypassed?
A: While LSA protection is a robust security measure, it’s not foolproof. Advanced attackers might still find ways to bypass it through sophisticated techniques. However, LSA protection significantly raises the bar for attackers, making it much more challenging to compromise the system.
Q: How can I further enhance security beyond LSA protection?
A: In addition to LSA protection, consider implementing other security measures, such as:
- Strong Passwords and Multi-factor Authentication: Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your operating system and software up-to-date to patch vulnerabilities.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Protection: Install and regularly update antivirus and anti-malware software to protect against threats.
- Firewall Protection: Enable and configure your firewall to block unauthorized network access.
- User Account Control (UAC): Keep UAC enabled to prevent unauthorized program installations and changes.
Tips for Ensuring Effective LSA Protection
- Verify Configuration: Regularly check the LSA protection settings in the Local Group Policy Editor to ensure they remain enabled.
- Stay Updated: Keep Windows 11 and all software up-to-date to patch any security vulnerabilities.
- Implement Security Best Practices: Follow general security best practices, such as using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, and avoiding suspicious links and attachments.
- Monitor System Logs: Regularly review system logs for any suspicious activity that might indicate a security breach.
Conclusion
LSA protection is a critical security feature in Windows 11, providing a robust defense against malicious actors attempting to compromise the system’s core security mechanisms. By enabling and maintaining LSA protection, users can significantly enhance the security of their Windows 11 systems, protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access. Implementing LSA protection alongside other security measures creates a comprehensive security posture, reducing the risk of successful attacks and safeguarding the integrity of the system.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Strengthening Windows 11 Security: A Deep Dive into Local Security Authority Protection. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!