Safeguarding Your Digital Life: Understanding Backup Options in Windows 11
Related Articles: Safeguarding Your Digital Life: Understanding Backup Options in Windows 11
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Safeguarding Your Digital Life: Understanding Backup Options in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Safeguarding Your Digital Life: Understanding Backup Options in Windows 11
Windows 11, like its predecessors, offers a robust set of tools to safeguard user data. While the operating system itself does not inherently possess a singular "backup" function, it provides a comprehensive suite of options for creating and maintaining data copies, ensuring resilience against potential data loss scenarios.
This article delves into the various methods available within Windows 11 for creating backups, exploring their functionalities and limitations. It aims to provide a clear understanding of how to leverage these tools effectively to protect valuable data, files, and system configurations.
The Importance of Data Preservation
In today’s digital age, data holds immense value. From personal photos and documents to critical work files and financial records, the loss of digital information can have significant consequences. Hardware failures, accidental deletions, malware infections, and even natural disasters can all threaten the integrity of stored data.
Therefore, implementing a reliable backup strategy becomes paramount. Backups serve as a safety net, providing a means to restore lost or corrupted data, minimizing disruption and potential financial losses.
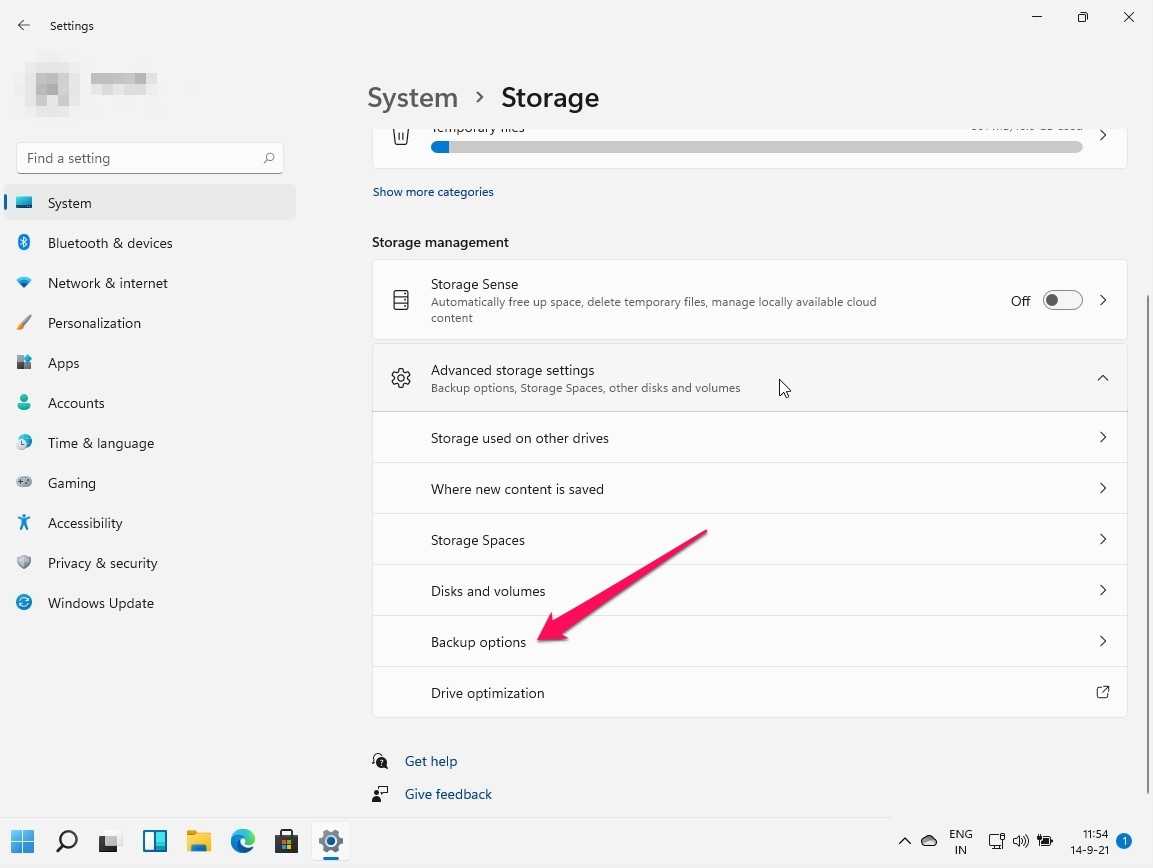
Windows 11 Backup Options: A Comprehensive Overview
Windows 11 offers a variety of tools and methods for creating backups, each tailored to different needs and scenarios:
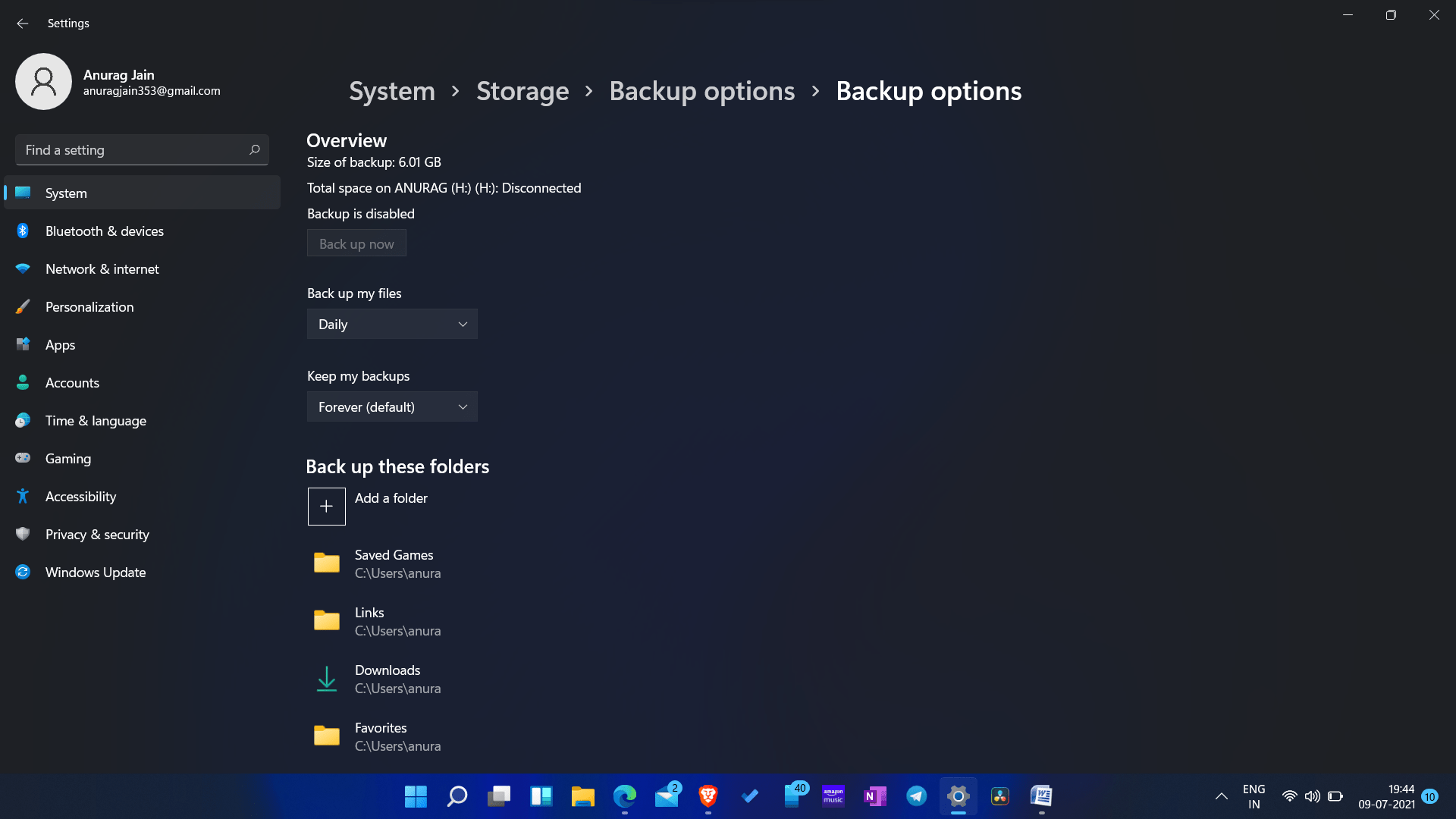
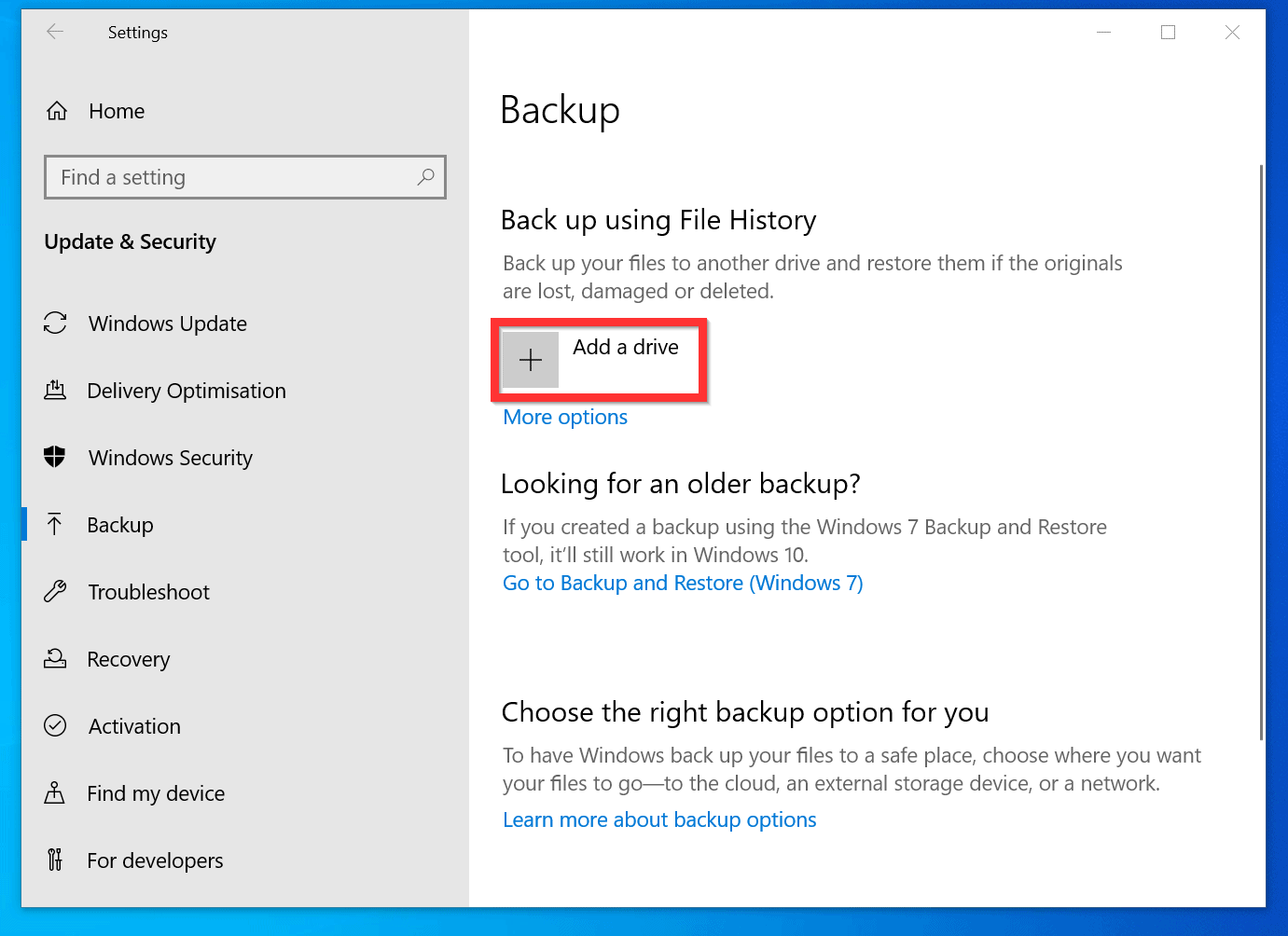
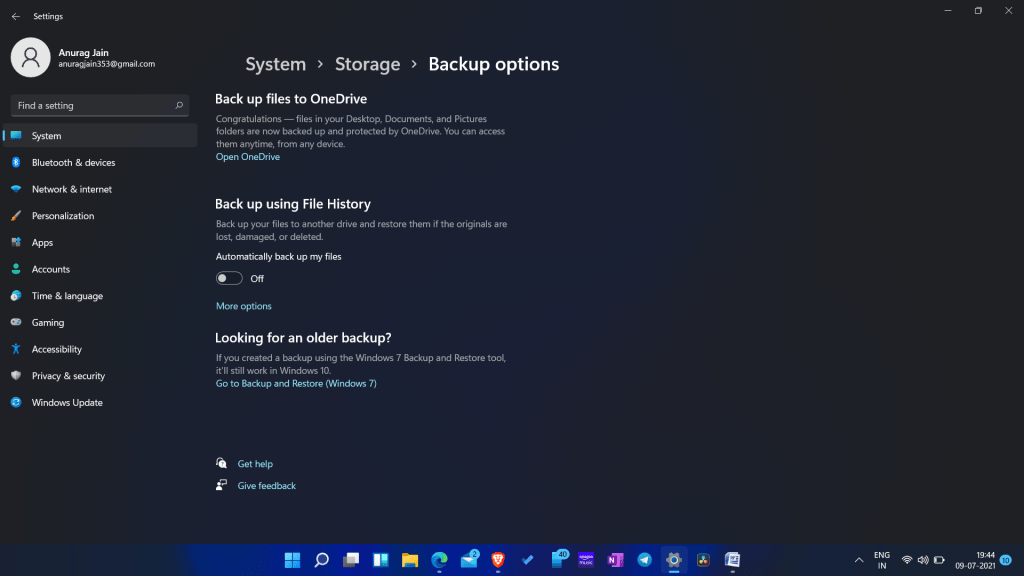
1. File History:
- Functionality: File History is a built-in feature that automatically creates regular backups of files stored in specific locations, including Documents, Pictures, Music, Videos, and Desktop folders.
-
Benefits:
- Simplicity: File History operates seamlessly in the background, requiring minimal user intervention.
- Versioning: It maintains multiple versions of files, allowing users to revert to previous states if necessary.
- Flexibility: Users can customize backup locations, including external drives, network shares, or cloud storage.
-
Limitations:
- Focus on specific folders: File History primarily backs up user-defined folders.
- Limited system settings: It does not include system settings, applications, or user profiles.
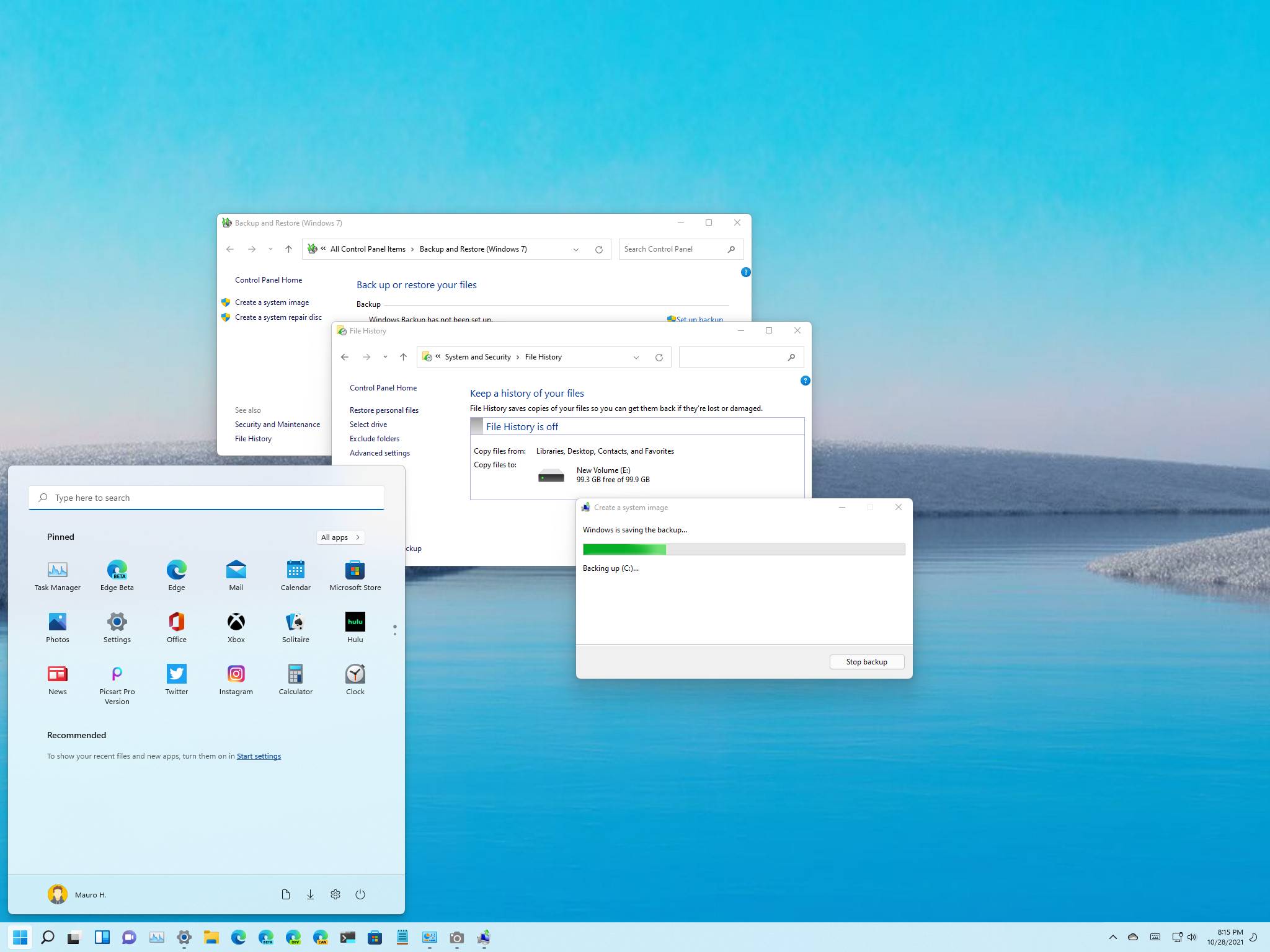
2. System Image Backup:
- Functionality: System Image Backup creates a complete snapshot of the entire system drive, including operating system files, installed applications, and user data.
-
Benefits:
- Comprehensive protection: System Image Backup provides a complete backup of the entire system, ensuring a full restoration in case of a catastrophic failure.
- System recovery: It enables users to restore the entire system to a previous state, including all settings and applications.
-
Limitations:
- Time-consuming: Creating a system image backup can be time-consuming, depending on the size of the system drive.
- Storage requirements: System images require significant storage space, often necessitating external drives.
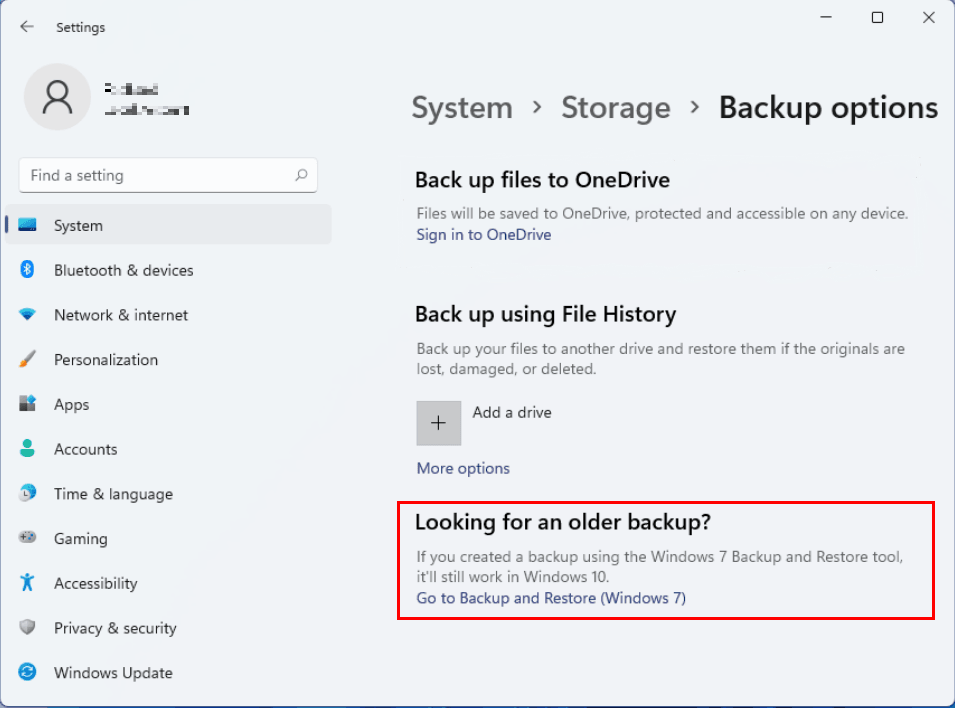
3. Backup and Restore (Windows 7 Feature):
- Functionality: This feature, inherited from Windows 7, allows users to create backups of specific files and folders, as well as system settings.
-
Benefits:
- Selective backups: Users can choose specific files and folders to include in the backup.
- System settings: It allows backing up system settings, including user accounts and network configurations.
-
Limitations:
- Outdated interface: The Backup and Restore interface is considered outdated compared to newer features.
- Limited functionality: It lacks features like versioning and automatic scheduling.
4. Third-Party Backup Solutions:
- Functionality: Numerous third-party backup applications offer advanced features and customization options beyond the built-in Windows tools.
-
Benefits:
- Comprehensive features: Third-party solutions often provide more granular control, scheduling options, and advanced backup strategies.
- Cloud integration: Many applications offer cloud storage integration, ensuring offsite backups.
-
Limitations:
- Cost: Some third-party applications are paid software.
- Complexity: Advanced features might require a steeper learning curve for users.
5. Cloud Storage Services:
- Functionality: Cloud storage services like OneDrive, Google Drive, and Dropbox allow users to synchronize files across multiple devices and create backups in the cloud.
-
Benefits:
- Accessibility: Files are accessible from any device with an internet connection.
- Automatic synchronization: Changes made to files are automatically synchronized with the cloud.
-
Limitations:
- Data ownership: Users rely on the cloud provider for data security and privacy.
- Internet dependency: Access to backed-up data requires an active internet connection.
Choosing the Right Backup Strategy
Selecting the most suitable backup strategy depends on individual needs and priorities. Consider the following factors:
- Data Importance: The criticality of the data being backed up dictates the level of redundancy required.
- Frequency of Backups: Regular backups minimize data loss in case of unforeseen events.
- Storage Capacity: The size of the data to be backed up determines the necessary storage space.
- Budget: Third-party backup solutions and cloud storage services may incur additional costs.
Best Practices for Effective Backups
To ensure robust data protection, follow these best practices:
- Regular Backups: Schedule regular backups at least once a day, especially for critical data.
- Multiple Backup Locations: Use a combination of local and offsite backups to protect against physical damage or theft.
- Test Backup Recovery: Regularly test the backup recovery process to ensure it functions correctly.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt backups to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Versioning and Retention: Retain multiple versions of backups to allow for restoration to previous states.
Conclusion
Windows 11 provides a comprehensive suite of tools and options for creating backups, offering varying levels of functionality and complexity. By understanding these options and implementing a robust backup strategy, users can effectively safeguard their valuable data, minimizing the impact of potential data loss events. Regular backups, combined with best practices, ensure data resilience and peace of mind, allowing users to focus on their digital endeavors without fear of data loss.
FAQs
1. What is the best backup method for Windows 11?
The best method depends on individual needs and priorities. For basic file backups, File History is a simple and effective option. For comprehensive system protection, System Image Backup is recommended. Third-party solutions and cloud storage services offer advanced features and flexibility.
2. How often should I back up my data?
The frequency of backups depends on the criticality of the data. For essential files and system configurations, daily backups are recommended. For less critical data, weekly or monthly backups may suffice.
3. What are the best free backup tools for Windows 11?
Several free backup tools are available, including:
- Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows Free Edition: Offers system image backups and file-level backups.
- AOMEI Backupper Standard: Provides system image backups, file backups, and disk cloning.
- Macrium Reflect Free: Provides system image backups and disk cloning.
4. Can I use cloud storage as a primary backup solution?
Cloud storage can serve as a primary backup solution, but it’s recommended to use a combination of local and offsite backups for redundancy. Cloud storage relies on the internet for access, and data ownership lies with the cloud provider.
5. How do I recover data from a backup in Windows 11?
The recovery process varies depending on the backup method used. File History backups can be restored from the File History settings. System Image backups can be restored using the Recovery Options in Windows 11. Third-party backup tools provide their own recovery methods.
Tips
- Automate Backups: Schedule regular backups to ensure they are performed consistently.
- Use External Storage: Store backups on external drives or cloud services to protect against data loss from hardware failures.
- Label Backups: Clearly label backups with dates and descriptions for easy identification.
- Keep Backups Secure: Store backups in a secure location and encrypt sensitive data.
- Regularly Test Backups: Periodically test the backup recovery process to ensure it functions correctly.
Conclusion
Data protection is essential in the digital age. Windows 11 offers a range of backup tools to safeguard user data, providing options for different needs and priorities. By understanding these options, implementing best practices, and choosing the most suitable backup strategy, users can effectively protect their valuable digital assets, minimizing the impact of potential data loss events and ensuring peace of mind in the digital world.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Safeguarding Your Digital Life: Understanding Backup Options in Windows 11. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!