RAID 0: Enhancing Storage Performance in Windows 11
Related Articles: RAID 0: Enhancing Storage Performance in Windows 11
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to RAID 0: Enhancing Storage Performance in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: RAID 0: Enhancing Storage Performance in Windows 11
- 2 Introduction
- 3 RAID 0: Enhancing Storage Performance in Windows 11
- 3.1 Understanding RAID 0: A Deeper Dive
- 3.2 Creating a RAID 0 Array in Windows 11: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.3 Managing the RAID 0 Array in Windows 11
- 3.4 FAQs: Understanding RAID 0 in Windows 11
- 3.5 Tips for Optimizing RAID 0 Performance in Windows 11
- 3.6 Conclusion: Navigating the World of RAID 0 in Windows 11
- 4 Closure
RAID 0: Enhancing Storage Performance in Windows 11
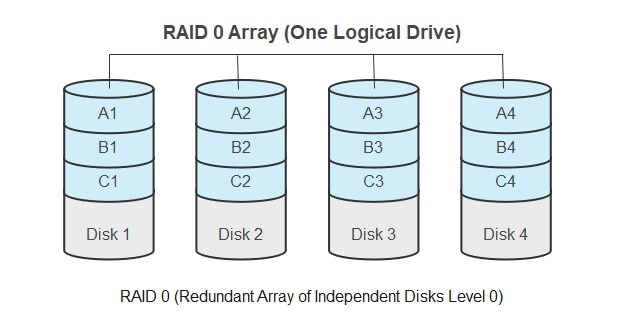
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology designed to improve storage performance and reliability by combining multiple physical disks into a single logical unit. RAID 0, also known as "striping," is a performance-focused RAID level that distributes data across multiple disks, effectively increasing read and write speeds. This article delves into the intricacies of creating and managing RAID 0 configurations within the Windows 11 operating system, highlighting its benefits and potential drawbacks.
Understanding RAID 0: A Deeper Dive
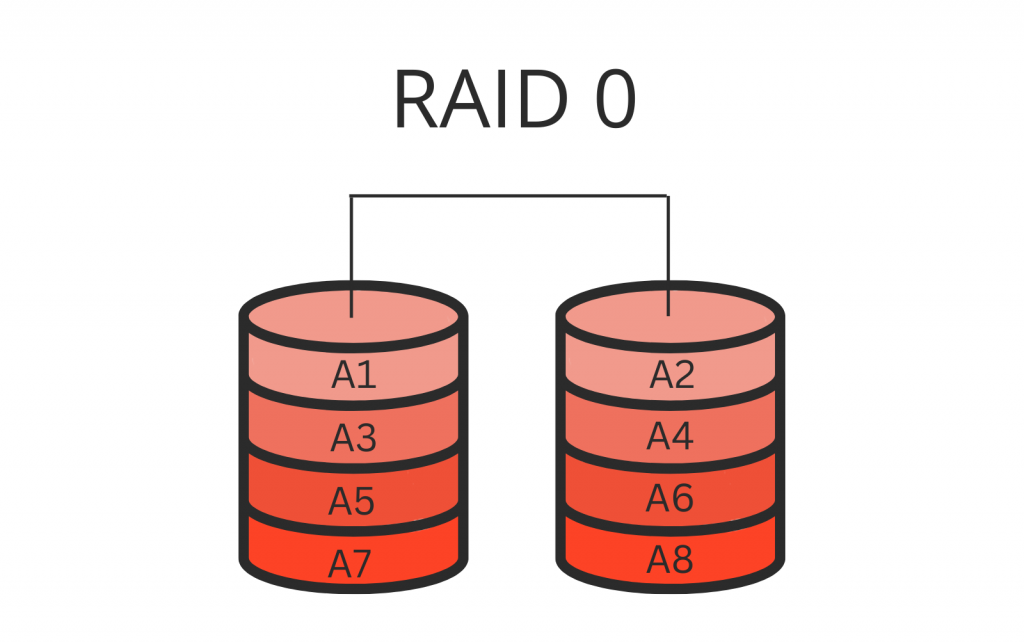
RAID 0 operates by splitting data into smaller blocks, writing these blocks simultaneously across multiple disks. This parallel access significantly accelerates data transfer rates, making it ideal for applications demanding high read and write speeds, such as video editing, gaming, and large database operations.
Illustrative Example:
Imagine a file requiring 10GB of storage. In a traditional single-disk setup, the entire file would be stored on one disk. However, in a RAID 0 configuration with two disks, the file would be split into two 5GB chunks, with each chunk residing on a separate disk. When accessing this file, the system can read or write data from both disks simultaneously, effectively doubling the data transfer rate.
Key Benefits of RAID 0:
- Enhanced Performance: RAID 0 delivers significantly faster read and write speeds compared to a single disk, resulting in a noticeable boost in application responsiveness and overall system performance.
- Increased Storage Capacity: By combining multiple disks, RAID 0 effectively expands the total available storage space, providing a larger storage pool for data and applications.
Important Considerations:
- Data Redundancy: Unlike RAID levels that provide data redundancy, RAID 0 does not offer any protection against data loss. If one disk fails, all data on the RAID 0 array is lost.
- Single Point of Failure: RAID 0 is susceptible to a single point of failure. If any disk in the array fails, the entire system becomes inaccessible, leading to data loss.
- Complexity: Setting up and managing RAID 0 requires a higher level of technical expertise compared to other RAID levels.
Creating a RAID 0 Array in Windows 11: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
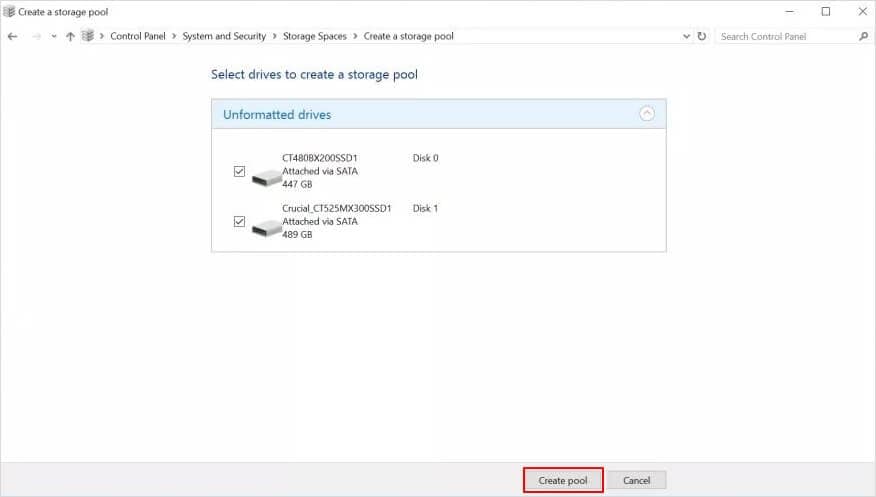
Prepare the Disks: Ensure the disks you intend to use for the RAID 0 array are properly formatted and meet the following criteria:
- Identical Size: The disks should be of equal size to ensure balanced data distribution.
- Performance: Choose disks with high read/write speeds for optimal performance.
- Empty Disks: It is recommended to use empty disks for the RAID 0 array to avoid data loss.
-
Access Disk Management: Navigate to the "Disk Management" tool in Windows 11 by searching for it in the Start Menu or by right-clicking the "This PC" icon and selecting "Manage" followed by "Disk Management."
-
Create the RAID 0 Array:
- Select the Disks: Right-click on the disks you wish to include in the RAID 0 array and choose "New Simple Volume."
- Assign a Drive Letter: Assign a unique drive letter to the newly created volume.
- Format the Volume: Format the volume using the desired file system, such as NTFS.
-
Confirm the RAID 0 Configuration:
- Check the Properties: Right-click on the newly created RAID 0 volume and select "Properties."
- Verify the RAID Level: Navigate to the "Volumes" tab and confirm that the RAID level is set to "RAID 0."
-
Monitor the RAID 0 Array: Regularly monitor the health of the disks in the RAID 0 array using the Disk Management tool or third-party monitoring software.
Managing the RAID 0 Array in Windows 11
- Disk Management: Windows 11’s Disk Management tool provides basic functionality for managing the RAID 0 array, including viewing disk health, formatting, and assigning drive letters.
- Third-Party RAID Management Software: For advanced RAID management capabilities, such as hot swapping, disk rebuild, and performance monitoring, consider using specialized RAID management software from reputable vendors.
FAQs: Understanding RAID 0 in Windows 11
Q: Can I convert an existing RAID 0 array to a different RAID level?
A: Converting a RAID 0 array to another RAID level is not possible without data loss. The data on the RAID 0 array needs to be backed up before attempting any conversion.
Q: What happens if one disk in the RAID 0 array fails?
A: If one disk in the RAID 0 array fails, the entire array becomes inaccessible, and all data on the array is lost.
Q: Is RAID 0 suitable for all users?
A: RAID 0 is not suitable for all users. It is best suited for users who prioritize performance and can tolerate the risk of data loss in case of disk failure.
Q: Can I add more disks to an existing RAID 0 array?
A: Adding disks to an existing RAID 0 array is not possible. The array needs to be recreated from scratch with the desired number of disks.
Q: What are the best practices for managing a RAID 0 array?
A: Best practices for managing a RAID 0 array include:
- Regularly backup data: Implement a robust backup strategy to protect against data loss in case of disk failure.
- Monitor disk health: Use Disk Management or third-party monitoring software to monitor the health of the disks in the array.
- Keep drivers updated: Ensure the RAID controller drivers are up-to-date to maintain optimal performance and stability.
Tips for Optimizing RAID 0 Performance in Windows 11
- Use high-performance disks: Choose disks with high read/write speeds for optimal performance.
- Use a dedicated RAID controller: A dedicated RAID controller can enhance performance and provide additional features.
- Configure the RAID controller: Optimize the RAID controller settings for your specific needs, such as setting the stripe size and cache settings.
- Avoid using fragmented files: Fragmentation can negatively impact RAID 0 performance. Use a defragmentation tool to optimize file placement.
Conclusion: Navigating the World of RAID 0 in Windows 11
RAID 0 offers significant performance gains for users demanding high read and write speeds. However, it is crucial to understand its limitations, particularly the lack of data redundancy and susceptibility to single point of failure. Before implementing RAID 0, carefully assess your needs and consider the potential risks involved. By understanding the principles of RAID 0 and following best practices, users can leverage its performance benefits while mitigating potential data loss risks.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into RAID 0: Enhancing Storage Performance in Windows 11. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!