Optimizing Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhanced Boot Times in 2025
Related Articles: Optimizing Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhanced Boot Times in 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Optimizing Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhanced Boot Times in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Optimizing Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhanced Boot Times in 2025

The advent of Windows 11 ushered in a new era of user experience, boasting streamlined performance and an intuitive interface. However, even with these advancements, the speed at which a computer boots up remains a crucial factor in user satisfaction. While Windows 11 inherently offers a faster boot experience compared to its predecessors, there are further steps users can take to optimize their system’s startup speed, maximizing efficiency and minimizing wait times.
This comprehensive guide explores various methods for accelerating the boot process in Windows 11, focusing on practical strategies and their impact. We will delve into the intricacies of the operating system’s boot process, examine common culprits that hinder speed, and present effective solutions for achieving a noticeably faster startup.
Understanding the Windows 11 Boot Process
The boot process in Windows 11 is a complex sequence of events that occur when the system powers on. It involves the following stages:
- Power-On Self-Test (POST): This initial stage checks the hardware components, ensuring they function correctly.
- BIOS/UEFI Boot: The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) loads the boot loader, which locates the operating system.
- Windows Boot Manager: The boot manager selects the desired operating system to start.
- Kernel Loading: The Windows kernel, the core of the operating system, is loaded into memory.
- Driver Loading: Drivers for various hardware components are loaded, enabling communication between the operating system and devices.
- User Login: The login screen appears, allowing the user to authenticate and access their account.
- Startup Applications: Pre-configured applications and services are launched, preparing the system for use.
Factors Impacting Boot Speed
Several factors can contribute to a slow boot time in Windows 11:
- Startup Applications: Excessive applications configured to launch at startup consume valuable system resources, delaying the boot process.
- Hardware Configuration: Outdated or incompatible hardware components, such as slow hard drives or insufficient RAM, can hinder boot speed.
- Disk Fragmentation: Over time, files on the hard drive become fragmented, slowing down access and impacting boot times.
- System Files: Corrupted or outdated system files can lead to delays during the boot process.
- Background Processes: Unnecessary background processes running during startup can contribute to slower boot times.
- Malware Infection: Malware can hinder system performance, including boot speed.
- Windows Updates: Large updates or updates downloaded during startup can significantly increase boot times.
Strategies for Accelerating Boot Times
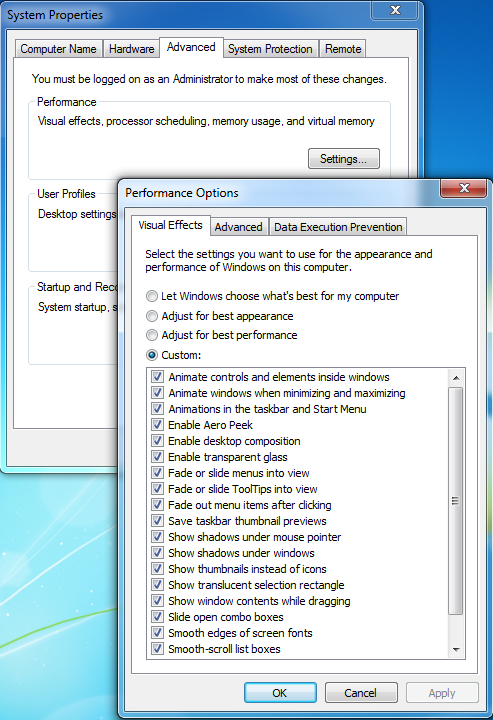
1. Managing Startup Applications:
- Disable Unnecessary Programs: Identify and disable applications that are not essential for daily use from launching at startup. This can be done through the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) by navigating to the Startup tab.
- Use Startup Manager Tools: Third-party tools like Autoruns or CCleaner offer more comprehensive control over startup applications.
2. Optimizing Hardware:
- Upgrade Storage: Replacing a traditional hard drive with a solid-state drive (SSD) offers significantly faster data access speeds, resulting in a noticeable boost to boot times.
- Increase RAM: Insufficient RAM can slow down the system, especially during the boot process. Increasing RAM capacity can improve performance and speed up startup.
3. Defragmenting the Hard Drive:
- Regular Defragmentation: Regularly defragmenting the hard drive ensures files are stored contiguously, improving access speeds and reducing boot times. Windows 11 includes a built-in defragmentation tool accessible through the Control Panel.
- Use Third-Party Tools: Third-party defragmentation tools, such as Defraggler, offer advanced features and can optimize hard drives for faster performance.
4. Maintaining System Files:
- Run System File Checker (SFC): The SFC tool scans for and repairs corrupted system files, ensuring a smooth boot process. It can be accessed through the Command Prompt (cmd) by typing "sfc /scannow."
- Use Disk Cleanup: Regularly cleaning up unnecessary files and temporary data using the Disk Cleanup tool can free up disk space and improve system performance, including boot times.
5. Minimizing Background Processes:
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Identify and disable services that are not essential for system operation. This can be done through the Services app (services.msc) in the Control Panel.
- Use Task Manager: Monitor background processes and terminate any unnecessary ones consuming system resources.
6. Addressing Malware Infections:
- Run Antivirus Scans: Regularly scan the system for malware using a reputable antivirus program.
- Use Malware Removal Tools: If a malware infection is detected, use specialized malware removal tools to eliminate the threat and restore system performance.
7. Managing Windows Updates:
- Schedule Updates: Schedule updates to occur outside of peak usage hours to avoid delays during startup.
- Prioritize Updates: Prioritize critical updates over optional updates to ensure the most important security patches are installed promptly.
8. Enabling Fast Startup (Hybrid Shutdown):
- Enable Fast Startup: Windows 11’s Fast Startup feature speeds up boot times by storing a system image in memory, allowing for a faster resumption of the operating system.
- Understand Potential Drawbacks: Fast Startup can cause some applications to open slower or experience compatibility issues.
9. Using Boot Optimization Tools:
- Third-Party Tools: Various third-party tools, such as TuneUp Utilities or Advanced SystemCare, offer comprehensive system optimization features, including boot speed enhancement.
- Consider Potential Risks: Exercise caution when using third-party tools, as some may contain malware or potentially compromise system stability.
10. Optimizing BIOS/UEFI Settings:
- Enable UEFI Boot: UEFI boot is generally faster than legacy BIOS boot.
- Disable Legacy Boot Options: Disabling legacy boot options can streamline the boot process.
- Adjust Boot Order: Ensure the boot order is optimized, with the primary boot drive listed first.
FAQs Regarding Boot Speed Optimization
Q: Is it safe to disable startup applications?
A: Disabling startup applications is generally safe, but it is crucial to identify and disable only those that are not essential for system operation. Disabling critical applications may lead to system instability or functionality issues.
Q: How often should I defragment my hard drive?
A: For traditional hard drives, defragmentation is recommended every few weeks or months, depending on usage patterns. However, SSDs do not require defragmentation as they do not suffer from fragmentation.
Q: Can I disable all background processes?
A: Disabling all background processes is not recommended, as some are essential for system operation and functionality. However, disabling unnecessary processes can improve boot speed and overall performance.
Q: Is it necessary to use third-party tools for boot speed optimization?
A: While third-party tools can offer additional optimization features, many of the methods described in this guide can be achieved through built-in Windows tools.
Tips for Maintaining Boot Speed:
- Regularly monitor startup applications: Review and adjust startup applications periodically to ensure only essential programs are launching at startup.
- Keep the system clean: Regularly clean up temporary files, unnecessary downloads, and outdated programs to free up disk space and improve performance.
- Schedule regular maintenance tasks: Automate defragmentation, disk cleanup, and system file checks to maintain optimal system performance.
- Update drivers: Ensure all hardware drivers are up-to-date to optimize system compatibility and performance.
- Avoid excessive multitasking: Minimize the number of applications running simultaneously to reduce system load and improve boot speed.
- Use a lightweight antivirus program: Select an antivirus program that has minimal impact on system resources to avoid slowing down the boot process.
Conclusion
Optimizing boot speed in Windows 11 is a multi-faceted process that involves understanding the boot process, identifying factors that impact speed, and implementing appropriate strategies. By employing the methods outlined in this guide, users can significantly reduce boot times, enhancing their overall computing experience. From managing startup applications to optimizing hardware, the key is to strike a balance between performance and functionality, ensuring a smooth and efficient boot process without compromising system stability. Remember, a well-maintained and optimized Windows 11 system will not only boot faster but also perform more efficiently across various tasks.




![Optimize Windows 11 For Gaming: How to Guide [ 6 Ways ]](https://www.buildsometech.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Optimize-Windows-11-For-Gaming-How-to-Guide.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Optimizing Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhanced Boot Times in 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!