Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility with Intel 7th Generation Processors
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility with Intel 7th Generation Processors
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility with Intel 7th Generation Processors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility with Intel 7th Generation Processors

The release of Windows 11 brought with it a wave of excitement and, for some, a dash of uncertainty. A key concern for many users was whether their existing hardware, particularly older processors, would meet the minimum system requirements. This article delves into the compatibility of Intel 7th generation processors with Windows 11, providing clarity on the issue and exploring its implications.
Understanding Windows 11’s Hardware Requirements
Windows 11, compared to its predecessor, introduced stricter hardware requirements. This was driven by Microsoft’s aim to ensure optimal performance and security for users. These requirements included a focus on processor capabilities, specifically the inclusion of a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 and a compatible CPU.
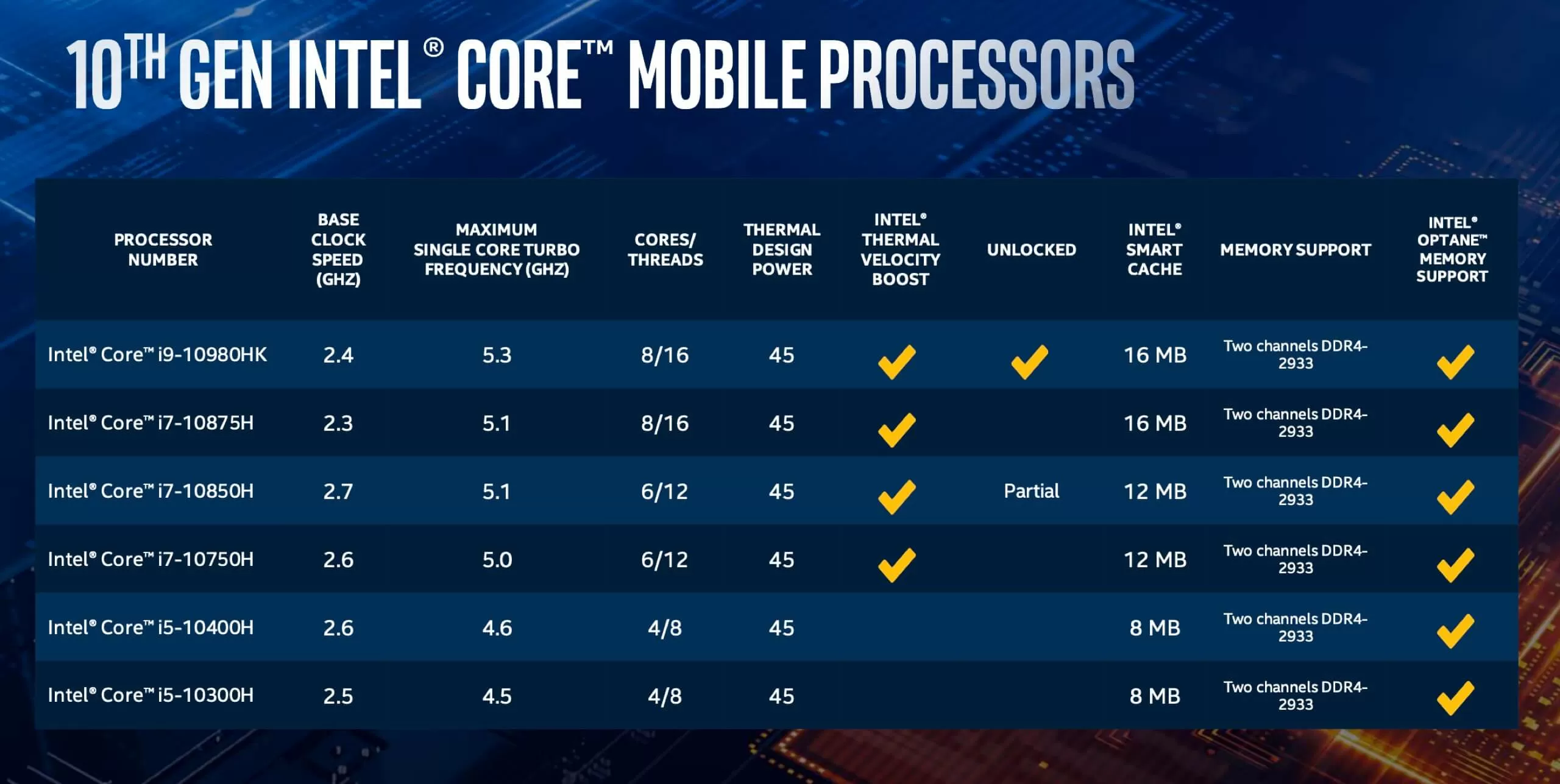
Intel 7th Generation Processors and Windows 11 Compatibility
Intel’s 7th generation processors, commonly referred to as "Kaby Lake," were released in 2016. While these processors generally offer robust performance, their compatibility with Windows 11 is a point of contention. The issue lies in the absence of TPM 2.0 support in many 7th generation processors.
TPM 2.0: A Crucial Component for Windows 11
TPM 2.0 is a security chip embedded within the motherboard, playing a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data and protecting against malware. Windows 11 mandates the presence of TPM 2.0 for enhanced security and system integrity.
The Dilemma: TPM 2.0 and 7th Generation Processors
While some 7th generation processors may have TPM 2.0, it is not a universal feature across the entire line. This leaves many users with 7th generation processors facing a challenge – either upgrading their motherboard to one with integrated TPM 2.0 or exploring alternative solutions to install Windows 11.
Exploring Solutions for Windows 11 Installation
1. Upgrading the Motherboard: The most straightforward solution is to upgrade the motherboard to one that supports TPM 2.0. This involves a significant investment, but it ensures full compatibility and security features.
2. Using a Software TPM: Some motherboards may not have a dedicated TPM chip but offer a software-based TPM emulation. This can be activated through the BIOS settings and can potentially allow for Windows 11 installation. However, software TPMs may not offer the same level of security as a hardware-based TPM.
3. Bypassing the Requirements (Not Recommended): Some users attempt to bypass the Windows 11 system requirements using unofficial methods. This approach is strongly discouraged as it can compromise system security and potentially lead to software instability.
Importance of Compatibility and Security
The compatibility issue highlights the importance of understanding system requirements before upgrading to a new operating system. Windows 11’s stricter requirements are designed to enhance security and performance, but they also necessitate careful consideration of hardware compatibility.
Benefits of Upgrading to Windows 11 (When Compatible)
For those with compatible hardware, Windows 11 offers a range of benefits:
- Enhanced Security: TPM 2.0 and other security features in Windows 11 provide a robust defense against cyber threats.
- Performance Improvements: Windows 11 is optimized for modern hardware, leading to improved performance and responsiveness.
- Modern User Interface: The new interface features a sleek design and intuitive navigation.
- Integration with Microsoft Services: Windows 11 seamlessly integrates with Microsoft services like OneDrive and Teams.
FAQs
Q: Can I install Windows 11 on a computer with a 7th generation Intel processor?
A: While some 7th generation processors may be compatible, it is not guaranteed. The presence of a TPM 2.0 chip is crucial for Windows 11 installation.
Q: How do I check if my computer has a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: You can access the BIOS settings to check for a TPM 2.0 option. Alternatively, you can use the Windows 11 PC Health Check app to assess compatibility.
Q: What are the alternatives to Windows 11 for my 7th generation processor?
A: Windows 10 continues to be a viable option for users with older hardware. Linux distributions are also a popular choice for those seeking a stable and customizable operating system.
Tips
- Research Compatibility: Before attempting to install Windows 11, thoroughly research the compatibility of your specific 7th generation processor.
- Check BIOS Settings: Explore your BIOS settings for options related to TPM 2.0 or software TPM emulation.
- Consider Upgrading: If compatibility is a concern, consider upgrading your motherboard to one that supports TPM 2.0.
- Explore Alternatives: Evaluate other operating systems like Windows 10 or Linux distributions if Windows 11 compatibility is an issue.
Conclusion
The compatibility of Intel 7th generation processors with Windows 11 is a complex issue. While some processors may support the necessary features, many lack TPM 2.0, hindering installation. Users with 7th generation processors should carefully assess their system’s compatibility and explore solutions like motherboard upgrades or alternative operating systems to ensure a smooth and secure computing experience. The decision to upgrade to Windows 11 should be based on a thorough understanding of hardware requirements and a clear assessment of the benefits and potential challenges involved.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility with Intel 7th Generation Processors. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!