Navigating the Windows 11 Landscape: System Requirements and Beyond
Related Articles: Navigating the Windows 11 Landscape: System Requirements and Beyond
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Windows 11 Landscape: System Requirements and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Windows 11 Landscape: System Requirements and Beyond
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Windows 11 Landscape: System Requirements and Beyond
- 3.1 The Foundation of Compatibility: Minimum and Recommended Specifications
- 3.2 Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Importance of System Requirements
- 3.3 Addressing Compatibility Concerns: Understanding Exclusions and Workarounds
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Tips for Ensuring Compatibility and Smooth Transition
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Windows 11 Landscape: System Requirements and Beyond

Microsoft’s Windows 11, the latest iteration of its iconic operating system, promises a host of new features and improvements, from a revamped user interface to enhanced security measures. However, before embarking on the Windows 11 journey, it’s crucial to understand the system requirements that will ensure a smooth and optimal experience.
The Foundation of Compatibility: Minimum and Recommended Specifications
Windows 11, like its predecessors, necessitates a specific set of hardware components to function effectively. These specifications fall into two categories: minimum and recommended.
Minimum System Requirements:
- Processor: 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster with 2 or more cores.
- RAM: 4 gigabytes (GB)
- Storage: 64 GB or larger storage device
- System Firmware: UEFI, Secure Boot capable
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module 2.0
- Graphics Card: Compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.x driver
- Display: High Definition (720p) display, 9 inches or greater in diagonal size
Recommended System Requirements:
- Processor: 1.5 GHz or faster with 4 or more cores
- RAM: 8 GB or more
- Storage: 128 GB or larger SSD
- System Firmware: UEFI, Secure Boot enabled
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module 2.0
- Graphics Card: Compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.x driver
- Display: Full HD (1080p) display, 10 inches or greater in diagonal size
These requirements serve as a guide, ensuring that your system possesses the necessary capabilities to support Windows 11’s features and performance. Meeting the minimum requirements guarantees basic functionality, while exceeding them with recommended specifications allows for a more robust and responsive experience.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Importance of System Requirements
While the minimum and recommended specifications provide a fundamental framework, it’s essential to delve deeper into the significance of each requirement.
- Processor (CPU): The CPU is the brain of your computer, responsible for executing instructions and processing data. A faster processor with multiple cores enhances performance, particularly for demanding tasks such as gaming, video editing, and multitasking.
- RAM (Memory): RAM acts as temporary storage for data actively being used by your computer. More RAM allows for smoother operation, especially when running multiple programs simultaneously.
- Storage (Hard Drive): The hard drive stores all your files, operating system, and applications. A larger and faster storage device, like an SSD, significantly improves boot times, application loading speeds, and overall system responsiveness.
- System Firmware (UEFI): UEFI is a modern firmware standard that offers improved security and boot performance compared to its predecessor, BIOS. Secure Boot is a feature within UEFI that helps prevent unauthorized software from loading at startup.
- TPM (Trusted Platform Module): TPM is a hardware security module that encrypts and protects sensitive data. Windows 11 utilizes TPM 2.0 for enhanced security, safeguarding your system from malicious attacks.
- Graphics Card (GPU): The GPU handles graphics rendering and visual processing. A powerful GPU is crucial for high-quality visuals in games and demanding applications.
- Display: A high-resolution display enhances the visual experience, providing sharper text and images. The minimum screen size requirement ensures optimal usability and readability.
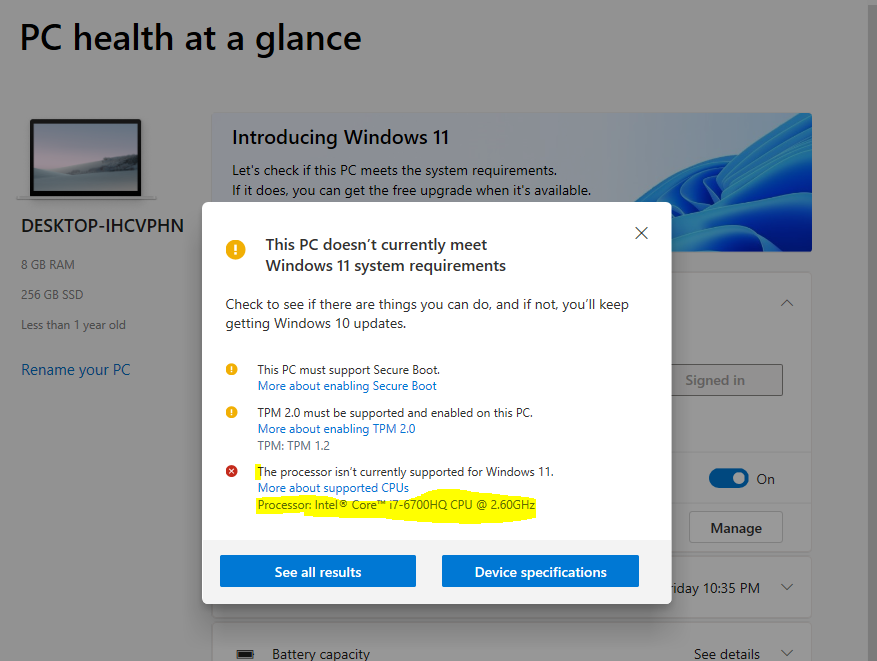
Addressing Compatibility Concerns: Understanding Exclusions and Workarounds
While Windows 11 aims for broad compatibility, certain older systems might not meet the minimum requirements. This is primarily due to the security enhancements and performance optimization that necessitate modern hardware.
Exclusions:
- Older Processors: Processors released before the 7th generation Intel Core series (Kaby Lake) and AMD Ryzen series are not officially supported.
- Lack of TPM 2.0: Systems without TPM 2.0 hardware are not compatible with Windows 11.
Workarounds:
- TPM Emulation: In some cases, it might be possible to enable TPM emulation in your system’s BIOS settings, allowing for a workaround. However, this is not a guaranteed solution and might not be supported by all motherboards.
- Upgrade to a Compatible System: The most reliable solution is to upgrade to a system that meets the minimum requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can I upgrade to Windows 11 from Windows 10?
A: Yes, you can upgrade to Windows 11 from Windows 10 if your system meets the minimum requirements. However, it’s recommended to check for compatibility using the PC Health Check app available on Microsoft’s website.
Q: What if my system doesn’t meet the requirements?
A: If your system doesn’t meet the minimum requirements, you can either upgrade to a compatible system or continue using Windows 10. Windows 10 will continue to receive security updates until October 14, 2025.
Q: Is there a way to bypass the TPM 2.0 requirement?
A: While there are some workarounds, such as TPM emulation, they are not officially supported and may not be reliable. It’s generally recommended to upgrade to a system with TPM 2.0 for optimal security and compatibility.
Q: What are the benefits of upgrading to Windows 11?
A: Windows 11 offers a host of benefits, including:
- Improved User Interface: A redesigned Start menu, a streamlined taskbar, and a more intuitive interface enhance user experience.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced security features like TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot protect your system from malware and unauthorized access.
- Performance Optimization: Windows 11 is optimized for modern hardware, delivering faster boot times, smoother multitasking, and improved application performance.
- New Features: Windows 11 introduces new features like Android app support, improved gaming capabilities, and a focus on productivity.
Tips for Ensuring Compatibility and Smooth Transition
- Check System Requirements: Before upgrading, use the PC Health Check app to verify your system’s compatibility with Windows 11.
- Backup Your Data: Always create a backup of your important files and data before upgrading to avoid potential data loss.
- Update Drivers: Ensure that your drivers are up to date, especially graphics drivers, to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
- Clean Up Your System: Remove unnecessary files and programs to free up storage space and improve system performance.
- Review System Settings: Familiarize yourself with Windows 11’s settings and customize them to your preferences.
Conclusion
Windows 11 presents a compelling upgrade for users seeking a modern, secure, and feature-rich operating system. However, understanding the system requirements is crucial to ensure a seamless and successful transition. By carefully evaluating your system’s capabilities and taking necessary steps, you can navigate the Windows 11 landscape with confidence and enjoy the benefits it offers.



![Windows 11 System Requirements [Recommended] 2023](https://mywebshosting.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/windows-11-system-requirements.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Windows 11 Landscape: System Requirements and Beyond. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!