Navigating the Windows 11 Fast Boot Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Windows 11 Fast Boot Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Windows 11 Fast Boot Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Windows 11 Fast Boot Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
The "Fast Boot" feature in Windows 11, often referred to as "Fast Startup," is a powerful tool designed to accelerate the boot process, significantly reducing the time it takes for your computer to become operational. However, this seemingly beneficial feature can sometimes present challenges for users, particularly when dealing with specific scenarios like troubleshooting or accessing advanced boot options. Disabling Fast Boot, while seemingly counterintuitive, can be a necessary step in resolving certain issues and enhancing troubleshooting capabilities.
Understanding the Mechanics of Fast Boot
Fast Boot in Windows 11 essentially operates by a hybrid approach, combining elements of a traditional cold boot and a hibernation state. When the system is shut down with Fast Boot enabled, Windows does not completely power down but rather saves the system’s state to a hibernation file. This file contains the necessary information to quickly restore the system to its previous state upon the next boot. This method, while efficient, can lead to complications in certain scenarios.
Why Disabling Fast Boot Might Be Necessary
While Fast Boot is generally beneficial, its use can create limitations in specific situations. Here are some common reasons why disabling Fast Boot might be required:
-
Troubleshooting Issues: When encountering boot-related problems, disabling Fast Boot can provide a cleaner environment for diagnosing and resolving the issue. By eliminating the hybrid boot process, you gain access to a more straightforward boot sequence, allowing for better error identification and troubleshooting.
-
Accessing Advanced Boot Options: Disabling Fast Boot grants access to advanced boot options, including the ability to enter the BIOS/UEFI settings, boot from a USB drive, or use system recovery tools. These options are often inaccessible when Fast Boot is enabled.
-
Compatibility with Certain Software and Hardware: Some software and hardware configurations might not function optimally with Fast Boot enabled. Disabling the feature can resolve compatibility issues and ensure smooth operation.
-
Data Recovery: In scenarios involving data recovery, disabling Fast Boot can be crucial. It allows for a full system shutdown, ensuring that all data is properly saved and accessible during the recovery process.
Navigating the Disabling Process
Disabling Fast Boot in Windows 11 requires access to the BIOS/UEFI settings, the system’s fundamental software that controls hardware functions. The process can vary slightly depending on the specific motherboard manufacturer, but the general steps remain consistent:
-
Accessing the BIOS/UEFI:
- Restart your computer and repeatedly press the designated key (usually Delete, F2, F10, or Esc) during the boot process to enter the BIOS/UEFI setup. The specific key will be displayed on the screen during the initial boot sequence.
-
Locating the Fast Boot Setting:
- Navigate through the BIOS/UEFI menus using the arrow keys. Look for a section labeled "Boot," "Advanced Boot Options," or something similar. Within this section, you should find a setting related to "Fast Boot," "Quick Boot," or "Fast Startup."
-
Disabling Fast Boot:
- Use the arrow keys to select the Fast Boot option and change its setting to "Disabled," "Off," or "Legacy Boot." The exact terminology may vary depending on the BIOS/UEFI interface.
-
Saving Changes:
- Once you have disabled Fast Boot, press the designated key to save the changes. This key is usually "F10," "Enter," or "Esc." Your computer will restart, applying the new settings.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Will disabling Fast Boot significantly affect my computer’s boot speed?
A: Disabling Fast Boot will increase the boot time, but the difference is usually minimal, especially on modern computers with fast storage drives.
Q: Can I re-enable Fast Boot after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable Fast Boot by following the same steps as described above, simply changing the setting back to "Enabled" or "On."
Q: Is there any risk associated with disabling Fast Boot?
A: Disabling Fast Boot is generally safe and does not pose any significant risk to your system. However, it’s always advisable to back up your important data before making any major system changes.
Q: Why is Fast Boot still enabled after I disabled it in the BIOS/UEFI?
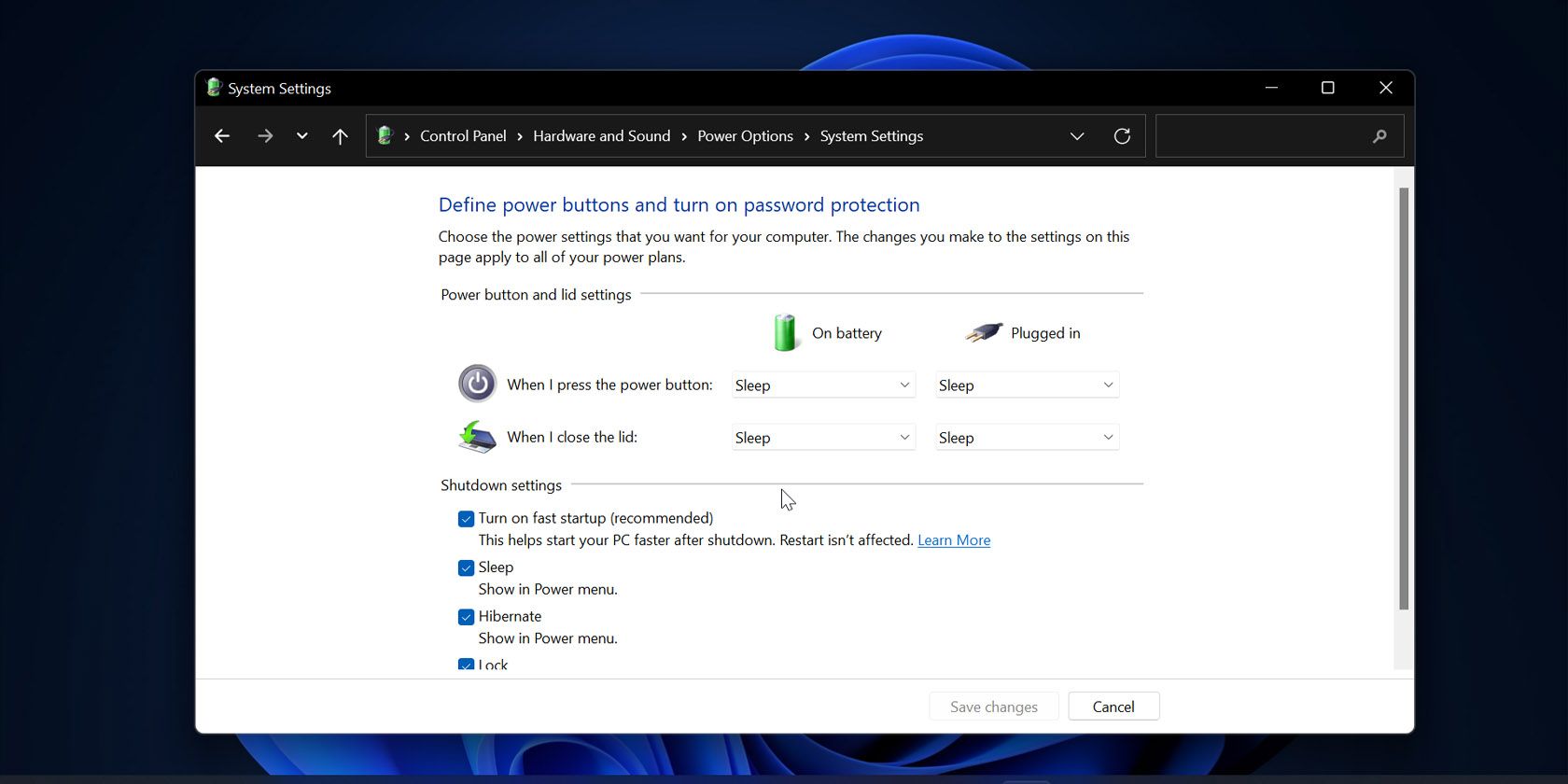
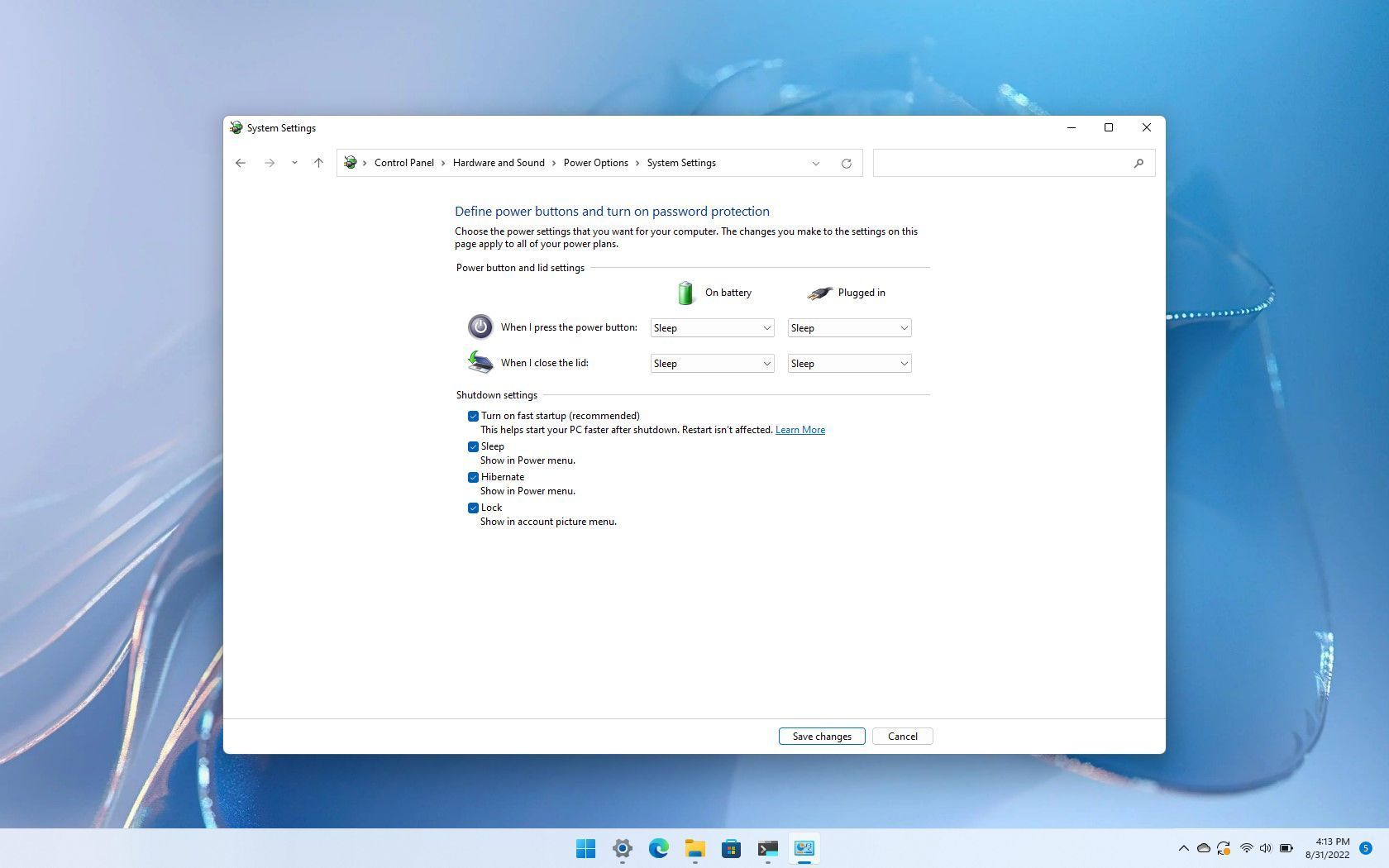
A: In some cases, Fast Boot might still be enabled even after disabling it in the BIOS/UEFI. This could be due to a separate setting within Windows itself. You can check this by going to "Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Power Options" and selecting "Choose what the power buttons do." Under "Shutdown settings," ensure the "Turn on fast startup" option is unchecked.
Tips for Optimizing Boot Performance
-
Minimize Startup Programs: Reducing the number of programs that automatically launch at startup can significantly improve boot speed. You can manage startup programs through the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) or by navigating to "System > Apps > Startup" in the Windows Settings.
-
Optimize Disk Space: Regularly clearing unnecessary files and programs from your hard drive can free up space and improve overall system performance, including boot speed.
-
Defragment Your Hard Drive: Regularly defragmenting your hard drive can organize data more efficiently, making it easier for the system to access files and resulting in faster boot times.
-
Upgrade Your Storage Drive: If your computer uses a traditional hard drive (HDD), upgrading to a solid-state drive (SSD) can dramatically improve boot speed and overall system performance.
Conclusion
While Fast Boot is generally a beneficial feature, there are specific scenarios where disabling it might be necessary for optimal system performance, troubleshooting, or accessing advanced boot options. Understanding the mechanics of Fast Boot and its potential limitations allows for informed decision-making regarding its use. By following the steps outlined in this guide, users can navigate the disabling process effectively, ensuring a smooth and efficient computing experience. Remember, understanding the nuances of your system’s settings and functionalities empowers you to troubleshoot issues, enhance performance, and optimize your overall computing experience.


![How to Enable or Turn On Fast Startup on Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aO2eIvIHUlU/maxresdefault.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Windows 11 Fast Boot Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!