Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding and Resolving Error Code 0x8007000d in Windows 11
Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding and Resolving Error Code 0x8007000d in Windows 11
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding and Resolving Error Code 0x8007000d in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding and Resolving Error Code 0x8007000d in Windows 11

Windows 11, like any complex operating system, can encounter various errors during its operation. One such error, denoted by the hexadecimal code 0x8007000d, signifies a common issue: access denied. This error message indicates that the operating system is unable to access a specific file, folder, or system resource due to insufficient permissions. While the error message itself is concise, the root cause can be multifaceted, requiring a systematic approach to diagnosis and resolution.
Delving into the Causes: Unraveling the Mystery of Access Denied
The error code 0x8007000d can stem from a variety of underlying causes, each necessitating a tailored solution. The most common culprits include:
- Insufficient User Permissions: The current user account might lack the necessary privileges to access the targeted file, folder, or system resource. This is a frequent scenario when working with system files or protected folders.
- Corrupted User Profile: A corrupted user profile can lead to access denied errors, as the system might be unable to correctly authenticate and validate the user’s permissions.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible or malfunctioning software can interfere with the operating system’s access to specific files or resources, triggering the error.
- Malware Interference: Malicious software can manipulate system permissions, leading to restricted access and the error code 0x8007000d.
- Hard Drive Errors: Physical errors on the hard drive can disrupt file access, resulting in the error.
- System File Corruption: Corrupted system files, often a consequence of software installations or updates, can lead to the error.
- Incorrectly Configured System Settings: Misconfigured system settings, including file sharing and security policies, can restrict access to files and resources.
Navigating the Solution: A Step-by-Step Guide to Reclaiming Access
Addressing the error code 0x8007000d requires a methodical approach, starting with the simplest solutions and progressing to more complex troubleshooting steps. The following steps provide a comprehensive guide:
1. Verify User Permissions:
- Check User Account Type: Ensure the current user account has administrator privileges. If not, try logging in with an administrator account.
- Modify File or Folder Permissions: Right-click the affected file or folder, select "Properties," navigate to the "Security" tab, and modify permissions to grant the current user full control.
2. Troubleshoot User Profile Issues:
- Create a New User Account: If suspecting a corrupted user profile, create a new administrator account and attempt the operation. If successful, transfer data from the old profile to the new one.
- Repair User Profile: If the issue persists, try repairing the user profile using the "sfc /scannow" command in Command Prompt (run as administrator).
3. Identify and Resolve Software Conflicts:
- Uninstall Suspicious Software: If the error appeared after installing new software, consider uninstalling it to see if the problem resolves.
- Run System File Checker: The "sfc /scannow" command can repair corrupted system files that might be causing conflicts.
4. Scan for Malware:
- Run Antivirus Software: Perform a full system scan with your antivirus software to detect and remove any potential malware.
- Use Malware Removal Tools: If the antivirus doesn’t detect anything, consider using specialized malware removal tools.
5. Check Hard Drive Health:
- Run Hard Drive Diagnostic Tools: Utilize built-in tools like "chkdsk" or third-party diagnostic software to check for hard drive errors.
- Consider Hard Drive Replacement: If a physical error is detected, replacing the hard drive might be necessary.
6. Repair Corrupted System Files:
- Run System File Checker: The "sfc /scannow" command can repair corrupted system files.
- Use DISM Tool: The "DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth" command can repair system image corruption.
7. Review and Adjust System Settings:
- Verify File Sharing Settings: Ensure that file sharing is enabled and properly configured.
- Check Security Policies: Review system security policies to ensure they are not blocking access to specific files or resources.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
Q: What are the common symptoms of error code 0x8007000d?
A: The most prominent symptom is the inability to access specific files, folders, or system resources. This can manifest in various ways:
- Error messages: Windows might display error messages indicating "access denied" or "you do not have permission to access this folder."
- Inability to open files: You might be unable to open specific files, even if you have the necessary software.
- Restricted access to folders: Certain folders, like the system folders, might become inaccessible.
- Software installation failures: Software installations might fail due to insufficient permissions.
Q: Can this error be related to specific software or programs?
A: Yes, the error code 0x8007000d can be associated with specific software programs, particularly those requiring administrative privileges or accessing system files. For instance, antivirus software, system optimization tools, or certain game installations might trigger this error if permissions are not correctly configured.
Q: Does this error indicate a serious problem with my computer?
A: While the error code 0x8007000d can be frustrating, it does not necessarily indicate a serious problem with your computer. In most cases, it can be resolved through troubleshooting steps outlined above. However, if the error persists after attempting these solutions, seeking professional help from a qualified technician is recommended.
Q: How can I prevent this error from happening again?
A: Preventing the recurrence of this error requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Maintain Regular System Updates: Keep your operating system and software updated to patch security vulnerabilities and address known issues.
- Regularly Scan for Malware: Utilize antivirus software and perform regular system scans to prevent malware infections.
- Be Cautious with Software Installations: Only download software from trusted sources and carefully review permissions during installation.
- Back Up Your Data: Regularly back up your important data to prevent data loss in case of system errors or hard drive failures.
Tips: Practical Guidance for Effective Troubleshooting
- Document the Error: Note the specific file, folder, or program associated with the error for accurate troubleshooting.
- Use System Restore: If the error appeared recently, consider using System Restore to revert to a previous working state.
- Run in Safe Mode: Boot into Safe Mode to isolate the problem and troubleshoot without interfering software.
- Consult Online Resources: Utilize online forums and communities for troubleshooting tips and solutions specific to your scenario.
Conclusion: Empowering Users to Resolve Access Denied Errors
The error code 0x8007000d, while seemingly cryptic, represents a common access denied issue in Windows 11. By understanding the underlying causes and following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this article, users can effectively diagnose and resolve this error, reclaiming access to files, folders, and system resources. Remember, a systematic approach, coupled with patience and perseverance, is key to navigating the labyrinth of access denied errors and restoring smooth system operation.


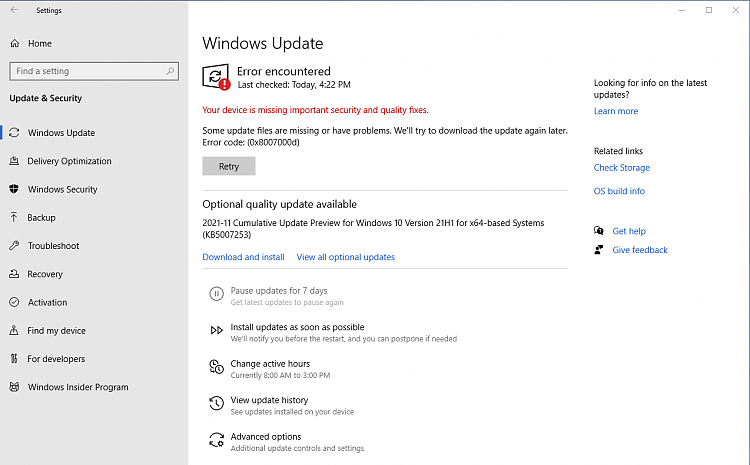

![Error Code 0x8007000d - Windows 10/11 Update Failure [Fixed]](https://www.winchatsupport.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/error-code-0x8007000d.png)
![How To Fix Windows Update Error Code 0x8007000d in Windows 11/10 [Solution] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/c-imUpTnaUE/maxresdefault.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding and Resolving Error Code 0x8007000d in Windows 11. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!