Navigating the Gates: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Firewall Port Management
Related Articles: Navigating the Gates: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Firewall Port Management
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Gates: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Firewall Port Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Gates: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Firewall Port Management
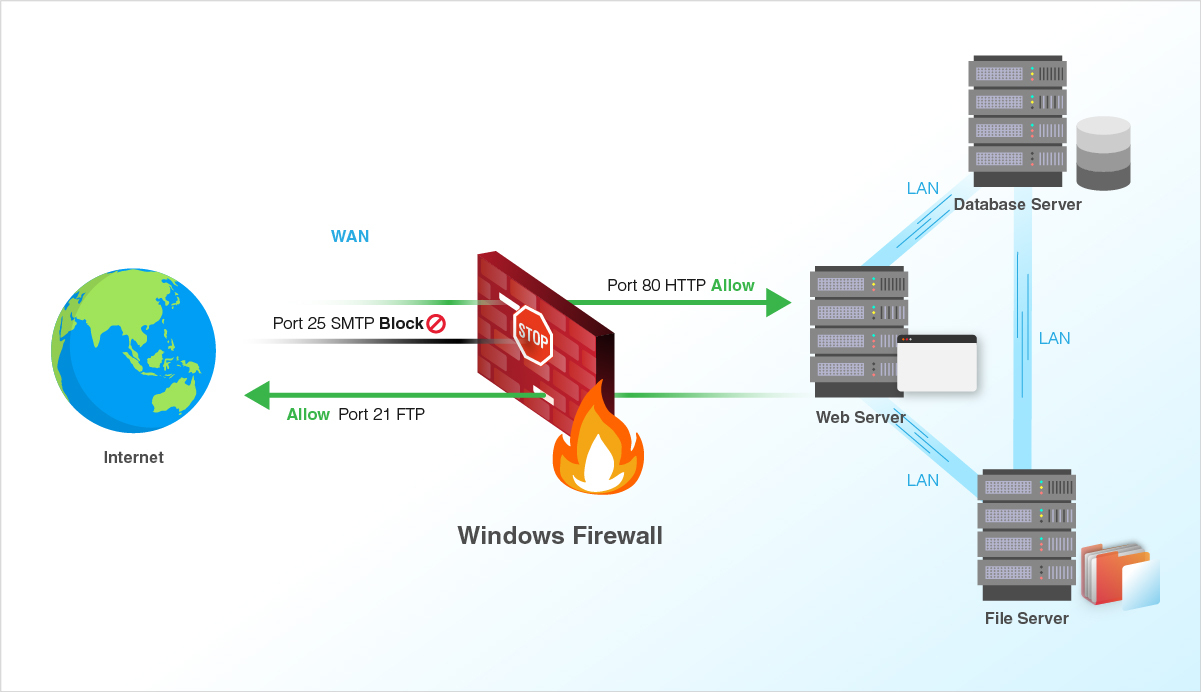
In the digital landscape, where information flows freely, security is paramount. Windows Firewall, a built-in defensive shield, plays a crucial role in safeguarding your computer from malicious actors. While it diligently blocks unwanted access, there are times when specific applications require access to the outside world, necessitating the opening of ports. This act of selectively granting access, however, requires careful consideration and a thorough understanding of the implications. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process of managing Windows Firewall ports, providing a clear understanding of the underlying concepts and best practices.
Understanding the Basics: Ports and Their Role in Communication
Imagine your computer as a bustling city with numerous buildings, each representing a different application or service. These buildings, however, cannot communicate with each other directly. They need a system of designated entry and exit points, known as ports. Each port is assigned a unique number, acting as a virtual address that identifies a specific application or service.
When a program needs to communicate with another computer, it sends a message through a specific port. The receiving computer uses the port number to identify the intended application or service and process the incoming message.
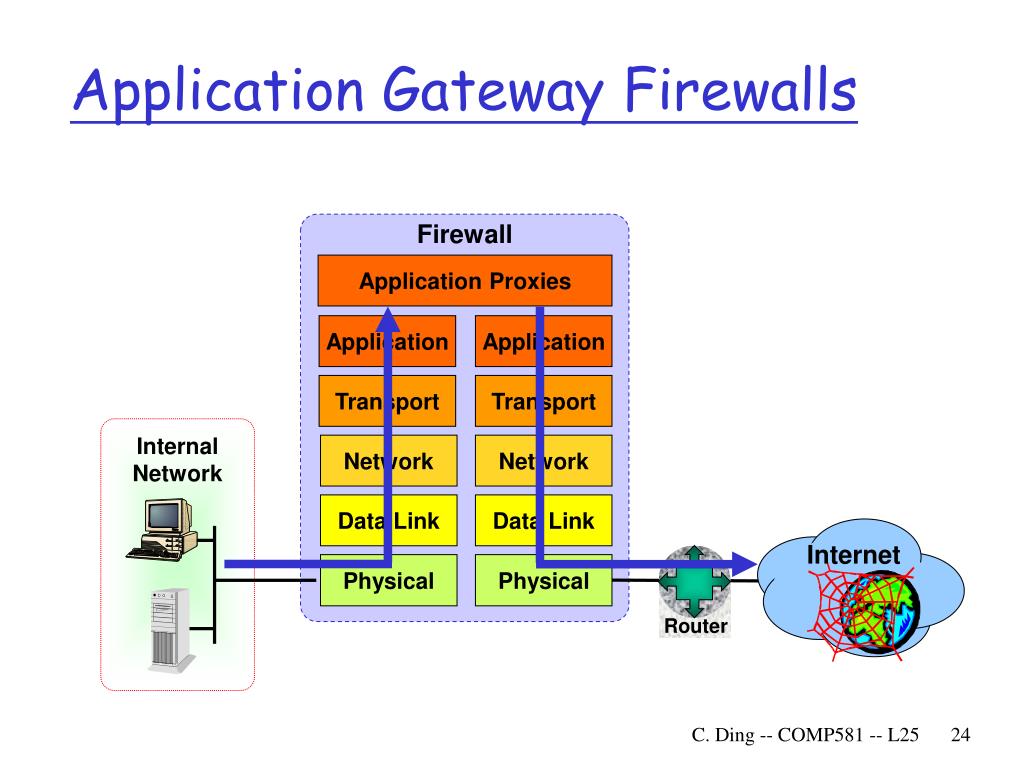
The Importance of Windows Firewall: A Protective Barrier
Windows Firewall acts as a vigilant gatekeeper, monitoring incoming and outgoing network traffic. By default, it blocks all unsolicited connections, effectively preventing malicious actors from gaining access to your computer. This default configuration provides a strong foundation for security, but it can also hinder the functionality of legitimate applications requiring external communication.
Enabling Ports: Granting Controlled Access
When a specific application requires access to the outside world, you need to open the corresponding port in Windows Firewall. This allows the application to communicate freely, while still maintaining a secure environment by restricting access to only the necessary ports.
Types of Ports: Inbound and Outbound
Ports are categorized into two types:
- Inbound ports: These allow external computers to connect to your computer. For example, if you are running a web server, you need to open port 80 to allow incoming requests from web browsers.
- Outbound ports: These allow your computer to connect to external computers. For example, if you are using an email client, it might require access to a specific port to send and receive emails.
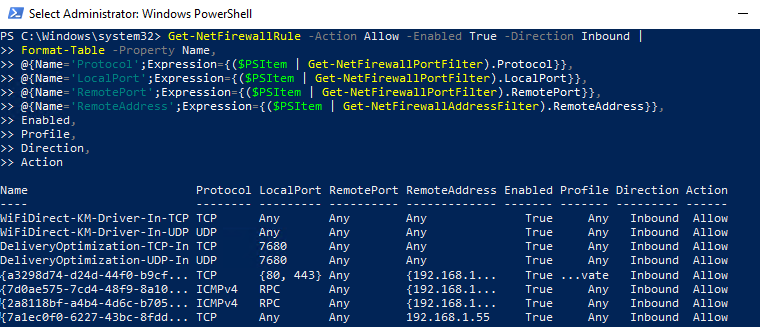
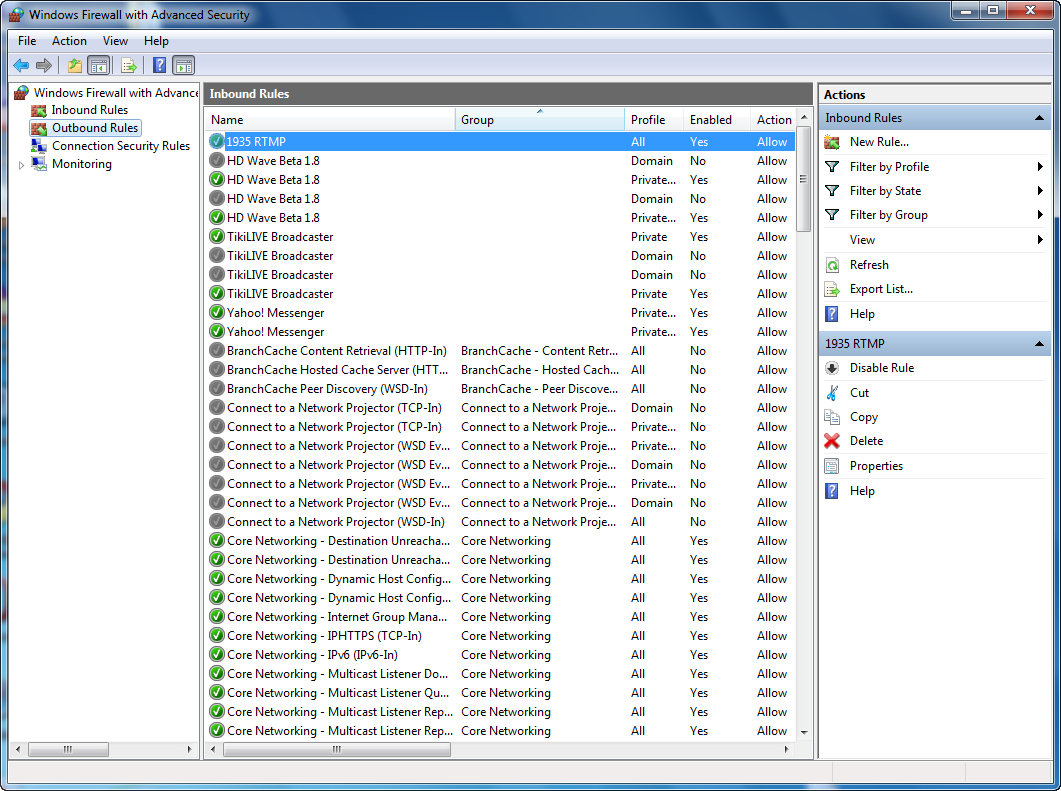
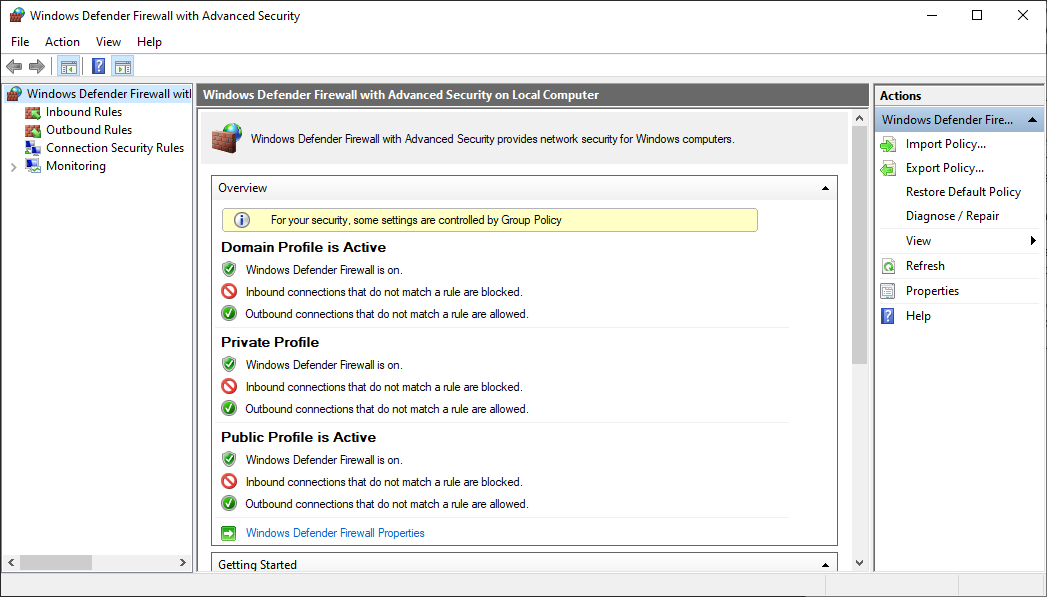
Navigating the Windows Firewall Interface
To manage firewall rules, you can use the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security interface:
- Access the interface: Open the Control Panel, search for "Windows Firewall," and click on "Windows Firewall with Advanced Security."
- Navigate to inbound/outbound rules: The interface provides separate sections for managing inbound and outbound rules.
- Create a new rule: To open a port, you need to create a new rule. Select "Inbound Rules" or "Outbound Rules" depending on the type of access you want to grant.
-
Specify the rule details: When creating a new rule, you need to provide specific information, including:
- Rule name: A descriptive name for the rule.
- Rule type: Choose between "Port," "Program," or "Custom."
- Protocol: Select the communication protocol (e.g., TCP, UDP).
- Specific local ports: Enter the port number or range of ports you want to open.
- Action: Choose between "Allow connection" or "Block connection."
- Scope: Define the scope of the rule (e.g., apply to specific network interfaces, users, or computers).
- Apply the rule: Once the rule is created, it will be applied to your firewall.
Understanding the Risks: Balancing Security and Functionality
While opening ports can enhance functionality, it also introduces a potential security risk. If an attacker discovers an open port, they could exploit it to gain unauthorized access to your computer. Therefore, it is crucial to:
- Only open ports that are absolutely necessary: Avoid opening ports for applications that do not require external access.
- Use strong passwords and security measures: Ensure that your computer and applications are protected with strong passwords and up-to-date security software.
- Monitor firewall logs: Regularly review firewall logs to detect any suspicious activity.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
1. What are the risks associated with opening ports?
Opening ports can create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. This could lead to data breaches, malware infections, or unauthorized access to your computer.
2. How can I identify the ports that need to be opened?
Consult the documentation for the specific application or service that requires external access. It will typically specify the required ports.
3. Can I close ports that are not in use?
Yes, it is recommended to close any ports that are not actively being used. This reduces the attack surface and enhances security.
4. What are the best practices for managing firewall ports?
- Only open ports that are absolutely necessary.
- Use strong passwords and security measures.
- Monitor firewall logs regularly.
- Keep your operating system and security software up to date.
5. Can I open ports remotely?
Yes, you can manage Windows Firewall remotely using tools like the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) or Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI).
Tips for Effective Port Management
- Prioritize security: Always prioritize security over functionality. Only open ports when absolutely necessary.
- Minimize the attack surface: Close any ports that are not in use.
- Use strong passwords and security measures: Protect your computer and applications with strong passwords and up-to-date security software.
- Monitor firewall logs: Regularly review firewall logs to detect any suspicious activity.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest security threats and best practices for managing Windows Firewall.
Conclusion: Navigating the Digital Landscape with Confidence
Windows Firewall is an essential component of computer security, providing a robust shield against malicious actors. By understanding the principles of port management and following best practices, you can navigate the digital landscape with confidence, ensuring that your computer is protected while maintaining the functionality you need. Remember, security is an ongoing process, and vigilance is key to staying ahead of evolving threats.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Gates: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Firewall Port Management. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!