Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Deep Dive into Tabbed Browsing in Windows Explorer
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Deep Dive into Tabbed Browsing in Windows Explorer
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Deep Dive into Tabbed Browsing in Windows Explorer. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Deep Dive into Tabbed Browsing in Windows Explorer
The modern digital landscape demands efficient navigation and streamlined workflows. While web browsers have long embraced the convenience of tabbed browsing, Windows Explorer, the cornerstone of file management in Microsoft’s operating system, remained largely untouched by this innovation for years. However, the introduction of tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer, a feature initially available in Windows 10 and later expanded to Windows 11, has significantly enhanced user experience, offering a more intuitive and productive way to interact with files and folders.
This article delves into the nuances of this feature, exploring its benefits, functionalities, and potential limitations, providing a comprehensive understanding of how it empowers users to navigate the digital landscape with greater efficiency.
The Rise of Tabbed Browsing: A Paradigm Shift in User Experience
Tabbed browsing, popularized by web browsers, revolutionized the way users interacted with online content. It allowed multiple web pages to be open simultaneously within a single window, eliminating the need for constant window switching and maximizing screen real estate. This paradigm shift in user experience, focused on streamlining and maximizing efficiency, has now extended to Windows Explorer, offering a similar level of convenience and productivity to file management.
Navigating Files and Folders with Ease: The Benefits of Tabbed Browsing in Windows Explorer
The integration of tabbed browsing into Windows Explorer brings a multitude of benefits, transforming the way users interact with their files and folders:
-
Streamlined Workflow: Users can now open multiple folders or drives in separate tabs within a single window, eliminating the need to constantly open and close individual windows. This significantly reduces clutter on the desktop and allows for a more focused and efficient workflow.
-
Enhanced Organization: Tabbed browsing provides a visual organization system for files and folders. Users can easily switch between different locations within a project or navigate different areas of their system with a simple click, enhancing their ability to manage and access files effectively.
-
Increased Productivity: The ability to access multiple folders simultaneously without switching windows saves valuable time and effort. This allows users to work on multiple tasks concurrently, enhancing overall productivity.
-
Contextual Navigation: Tabbed browsing promotes contextual navigation, allowing users to easily move between related folders and files within a project or task. This streamlined approach reduces the time spent searching for specific files and enhances the overall flow of work.
-
Improved Memory Management: By keeping multiple folders open in tabs, users can avoid the need to constantly remember file locations, leading to a more streamlined and intuitive workflow. This is especially beneficial when working with large amounts of data or multiple projects simultaneously.
Exploring the Functionality of Tabbed Browsing in Windows Explorer
Tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer offers a range of functionalities designed to enhance user experience and productivity:
-
Creating and Managing Tabs: Users can create new tabs by simply dragging a folder or drive from the navigation pane into the main window. Tabs can be easily closed by clicking the "X" button, or by right-clicking on the tab and selecting "Close Tab".
-
Tab Navigation: Navigating between tabs is as simple as clicking on the desired tab. Users can also use the keyboard shortcuts "Ctrl + Tab" and "Ctrl + Shift + Tab" to switch between tabs.
-
Tab Grouping: While not a standard feature, some third-party extensions for Windows Explorer offer tab grouping functionalities, allowing users to group related tabs for easier organization and navigation.
-
Tab Customization: Users can customize the appearance of tabs by adjusting their size, color, and font settings. This allows for a more personalized and visually appealing user interface.
-
Drag and Drop Functionality: Users can easily drag and drop files between tabs, facilitating efficient file transfer and organization.
Navigating the Landscape: Addressing Potential Limitations
While tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer offers significant benefits, it’s important to acknowledge potential limitations:
-
Resource Consumption: Opening multiple tabs can consume more system resources, potentially leading to slower performance, especially on older computers with limited RAM.
-
Compatibility Issues: Some third-party applications or utilities may not fully support tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer, leading to potential compatibility issues.
-
Limited Functionality: While tabbed browsing significantly enhances Windows Explorer, it does not yet offer all the features available in web browsers, such as the ability to pin tabs or create tab groups.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: How do I enable tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer?
A: Tabbed browsing is a built-in feature in Windows 10 and Windows 11. It should be enabled by default. If you don’t see tabs in your Windows Explorer window, make sure you are running a supported version of Windows and that the feature is not disabled in your settings.
Q: Can I use tabbed browsing with multiple windows of Windows Explorer?
A: No, tabbed browsing is a feature that operates within a single window of Windows Explorer. You cannot have multiple windows of Windows Explorer open with tabs.
Q: What are the keyboard shortcuts for tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer?
A: The primary keyboard shortcut for tabbed browsing is "Ctrl + Tab" to switch to the next tab. "Ctrl + Shift + Tab" will switch to the previous tab.
Q: Can I customize the appearance of tabs in Windows Explorer?
A: While you can customize the size and font of the tab titles, there is no built-in functionality to change the color or appearance of the tabs themselves.
Q: Are there any third-party extensions that enhance tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer?
A: Yes, several third-party extensions and utilities are available that offer additional features for tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer, such as tab grouping, tab pinning, and enhanced customization options.
Tips for Maximizing Efficiency with Tabbed Browsing
- Organize Tabs Logically: Group related tabs together to streamline workflow and improve navigation.
- Utilize Keyboard Shortcuts: Mastering keyboard shortcuts for tab navigation can significantly enhance efficiency.
- Explore Third-Party Extensions: Consider using third-party extensions to expand the functionality of tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer.
- Keep Tabs Clean: Regularly close unused tabs to reduce resource consumption and maintain a clear workspace.
Conclusion: Embracing a Streamlined Future
Tabbed browsing in Windows Explorer represents a significant leap forward in file management, offering a more intuitive, efficient, and productive user experience. By streamlining workflows, enhancing organization, and promoting contextual navigation, this feature empowers users to navigate the digital landscape with greater ease and efficiency. While there are potential limitations to consider, the benefits of tabbed browsing far outweigh any drawbacks. As technology evolves, we can expect to see further enhancements and refinements to this feature, making it an indispensable tool for navigating the ever-expanding digital world.

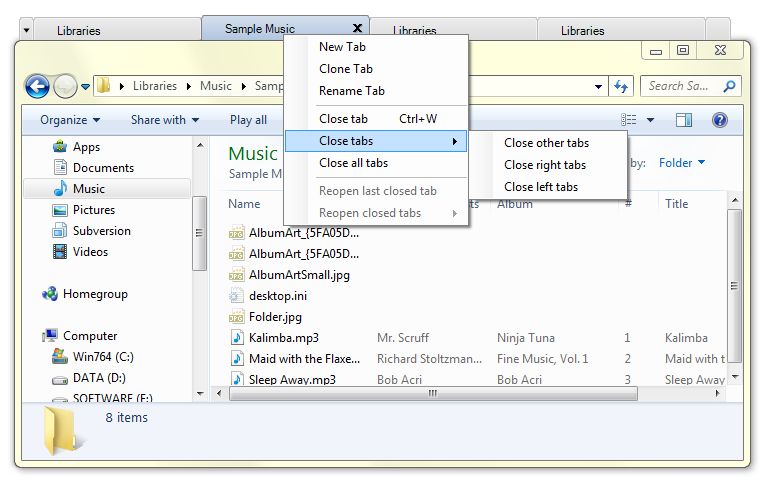




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Deep Dive into Tabbed Browsing in Windows Explorer. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!