Navigating the Complexities of Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows 11, like its predecessors, offers a feature called "fast startup" designed to expedite the boot process. This feature, however, can sometimes pose challenges for users, particularly those dealing with specific system configurations or troubleshooting issues. This article delves into the nuances of fast startup in Windows 11, providing a detailed understanding of its mechanisms, potential drawbacks, and effective methods for deactivating it.
Understanding the Mechanics of Fast Startup
Fast startup, also known as "hybrid shutdown," combines elements of traditional shutdown and hibernation. When a user initiates a shutdown, the operating system does not fully shut down but rather saves the current system state to a hibernation file. This file, containing essential kernel data and loaded drivers, allows for a quicker boot-up process by skipping the standard initialization sequence.
The advantages of fast startup are undeniable. It significantly reduces boot times, leading to a more responsive and efficient user experience. However, this functionality comes with inherent complexities that can affect certain user scenarios.
The Potential Drawbacks of Fast Startup
While fast startup offers a streamlined boot experience, it can introduce complications in specific situations:
- Troubleshooting Issues: Fast startup can hinder troubleshooting efforts. Since the system does not undergo a complete shutdown, certain diagnostic tools and utilities might fail to function correctly. This can impede the identification and resolution of system errors or hardware malfunctions.
- Compatibility Challenges: Some software applications or hardware devices might not be fully compatible with the fast startup mode. This incompatibility can lead to unexpected behavior, crashes, or performance issues.
- Data Recovery Complications: When fast startup is enabled, the system does not completely close all open files and applications. This can create difficulties during data recovery processes, as data may not be fully written to disk and could be potentially lost.
- Increased System Resource Consumption: Fast startup maintains a significant portion of the system’s memory and resources in a semi-active state, potentially leading to increased resource consumption and impacting overall system performance.
Disabling Fast Startup: A Practical Approach
For users encountering issues related to fast startup or requiring a more controlled shutdown process, disabling this feature is recommended. Windows 11 provides a straightforward method to deactivate fast startup through the Control Panel.
Steps to Disable Fast Startup:
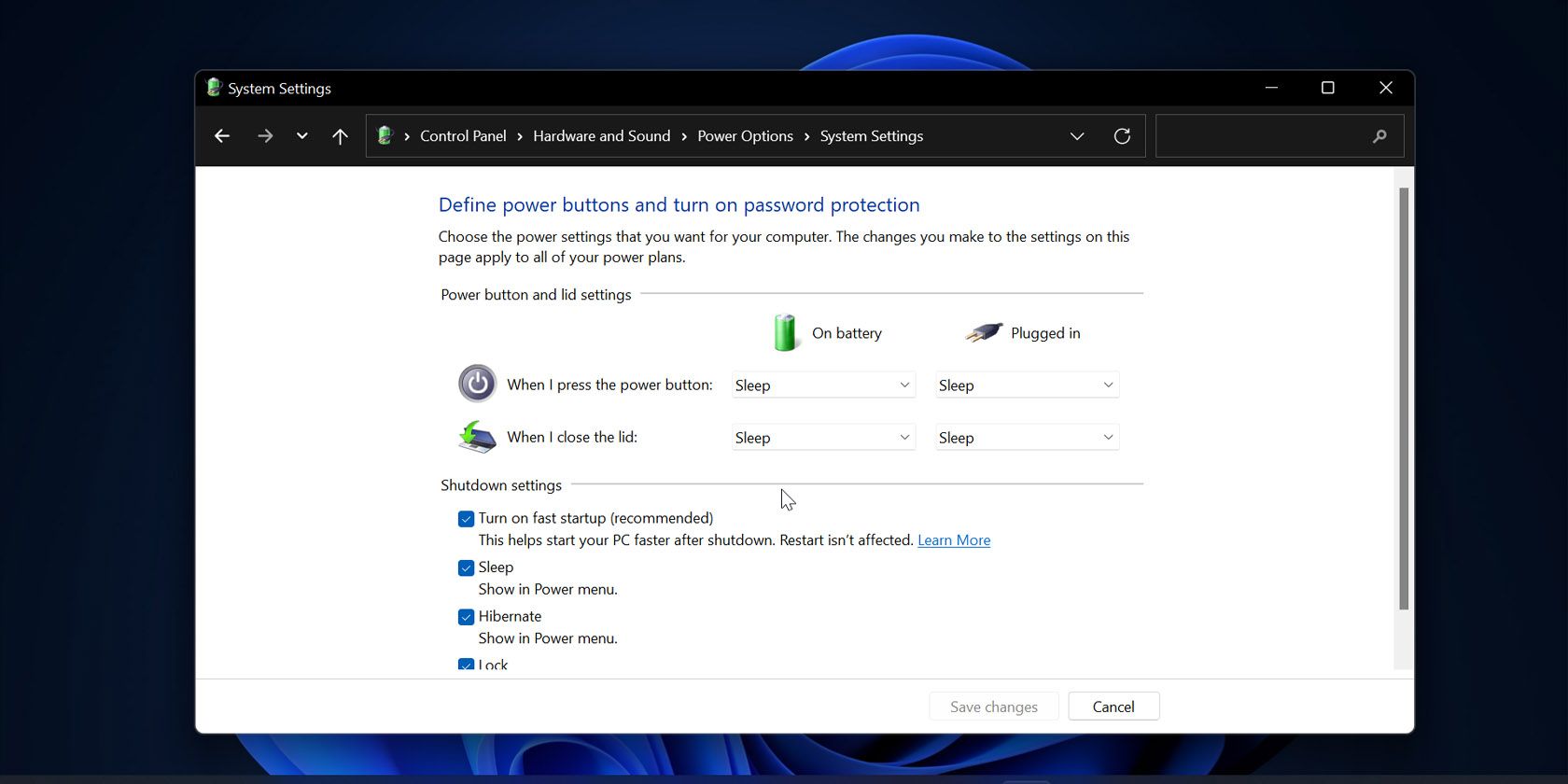
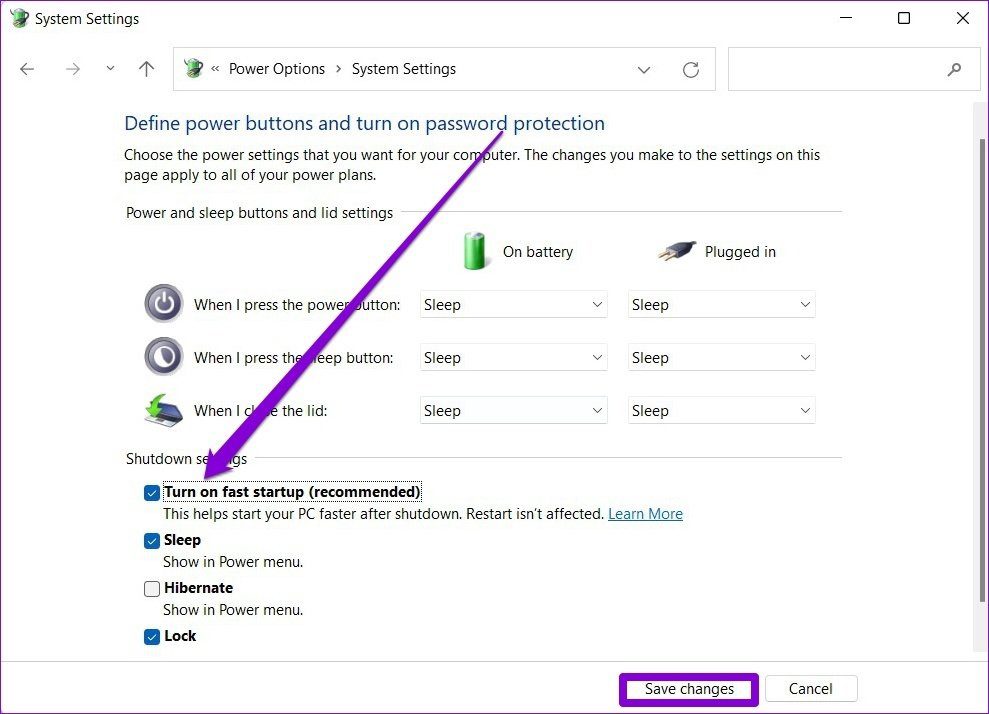
- Access the Control Panel: Navigate to the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
- Locate Power Options: Within the Control Panel, locate the "Power Options" section.
- Choose "Choose what the power buttons do": Click on the "Choose what the power buttons do" option.
- Select "Change settings that are currently unavailable": Click on the "Change settings that are currently unavailable" link.
- Disable "Turn on fast startup (recommended)": Uncheck the box next to "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
- Save Changes: Click on the "Save Changes" button to apply the modifications.
Alternative Methods for Disabling Fast Startup
Beyond the Control Panel, users can leverage command prompt commands to disable fast startup. This method provides an alternative approach for advanced users or those who prefer a command-line interface.
Command Prompt Method:
- Open Command Prompt: Search for "cmd" in the Windows search bar and run it as administrator.
-
Execute the Command: Type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /h off - Confirm the Change: The command will disable fast startup, and the system will prompt for a restart to apply the changes.
Understanding the Importance of Disabling Fast Startup
Disabling fast startup offers several advantages for specific user scenarios:
- Enhanced Troubleshooting: Disabling fast startup allows for a complete system shutdown, enabling comprehensive diagnostic tools and utilities to function correctly. This facilitates the identification and resolution of system errors or hardware malfunctions.
- Improved Compatibility: Disabling fast startup ensures that all software applications and hardware devices operate optimally without encountering compatibility issues. This eliminates unexpected behavior, crashes, or performance problems.
- Reliable Data Recovery: A complete shutdown guarantees that all open files and applications are properly closed, ensuring data integrity during recovery processes. This minimizes the risk of data loss and facilitates efficient recovery efforts.
- Optimized System Resources: Disabling fast startup reduces system resource consumption, freeing up memory and processing power for other tasks. This can lead to improved overall system performance and responsiveness.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns Regarding Fast Startup
Q1: Is it necessary to disable fast startup for all users?
A: Disabling fast startup is not universally required. For the majority of users, fast startup provides a convenient and efficient boot experience. However, specific scenarios, such as troubleshooting, compatibility issues, or data recovery, may necessitate its deactivation.
Q2: Does disabling fast startup increase boot times?
A: Yes, disabling fast startup will lead to slightly longer boot times compared to the fast startup mode. However, this increase is typically minimal and should not significantly impact the user experience.
Q3: Can I enable fast startup again after disabling it?
A: Yes, enabling fast startup after disabling it is possible. You can follow the same steps mentioned earlier to re-enable the feature through the Control Panel or command prompt.
Q4: Is there any impact on system performance after disabling fast startup?
A: Disabling fast startup can potentially improve overall system performance, particularly in situations where resource consumption is a concern. However, the impact on performance is generally minor and may vary depending on individual system configurations.
Tips for Optimizing System Performance After Disabling Fast Startup
- Consider a Clean Boot: A clean boot involves starting Windows with a minimal set of drivers and programs, allowing for effective troubleshooting and performance optimization.
- Run Disk Cleanup: Regularly running Disk Cleanup can free up disk space and enhance system performance by removing unnecessary files and temporary data.
- Optimize System Settings: Explore system settings like visual effects, background processes, and startup programs to customize your system for optimal performance.
- Update Drivers: Ensure all system drivers are up to date to ensure optimal hardware functionality and minimize compatibility issues.
Conclusion
Fast startup in Windows 11 offers a convenient and efficient boot experience for most users. However, understanding its complexities and potential drawbacks is essential. Disabling fast startup provides a solution for specific scenarios, including troubleshooting, compatibility issues, and data recovery. By carefully considering the benefits and drawbacks of this feature, users can make informed decisions regarding its activation or deactivation, ensuring a seamless and optimized computing experience.



![How to Enable or Turn On Fast Startup on Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aO2eIvIHUlU/maxresdefault.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!