Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: 7th Generation Processors and Windows 11
Related Articles: Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: 7th Generation Processors and Windows 11
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: 7th Generation Processors and Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: 7th Generation Processors and Windows 11
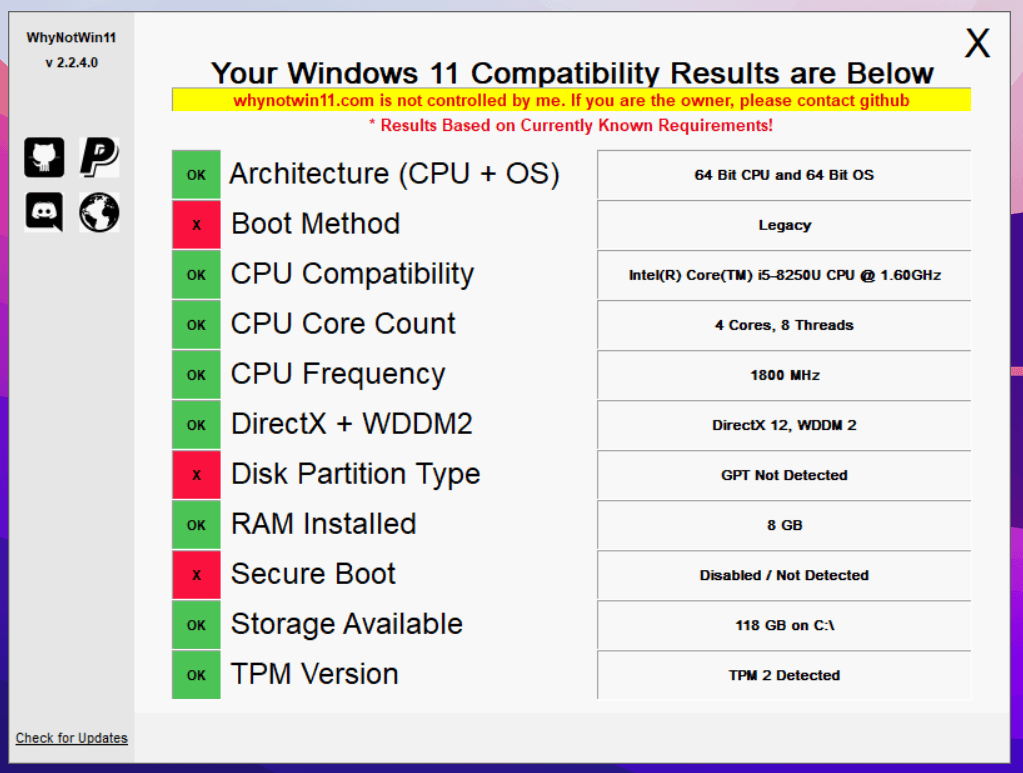
The question of whether a 7th generation processor can run Windows 11 is a common one, especially for users seeking to upgrade their existing systems. While the answer is not a simple "yes" or "no," understanding the intricacies of processor generations and operating system compatibility is crucial for making informed decisions.
The Genesis of Processor Generations:
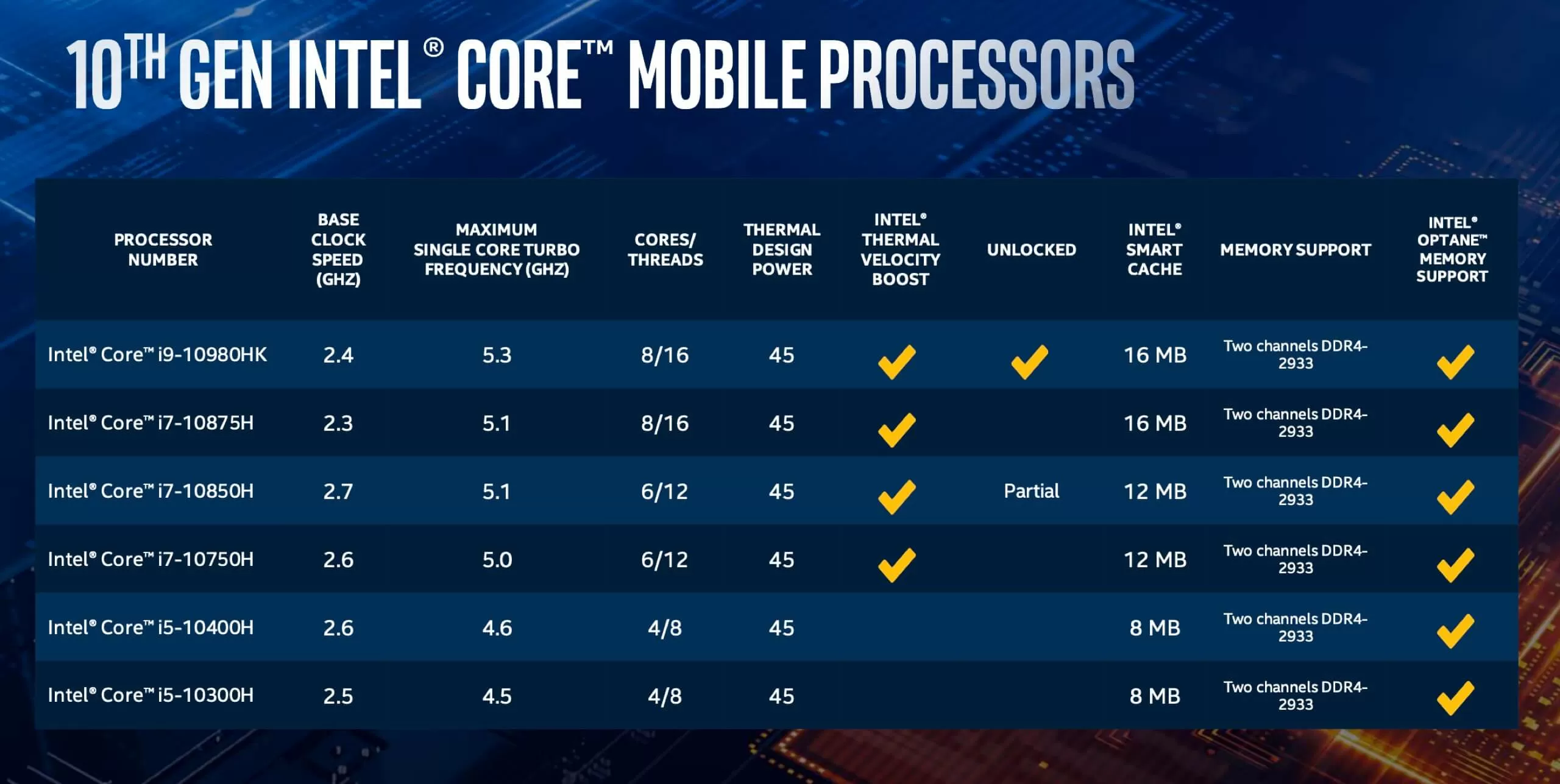
Processor generations, often denoted by numerical designations like 7th generation, represent significant advancements in processor technology. Each new generation introduces improvements in architecture, performance, power efficiency, and features. Intel and AMD, the primary processor manufacturers, release new generations periodically, with each generation building upon the strengths of its predecessor.
Windows 11’s Compatibility Requirements:
Windows 11, Microsoft’s latest operating system, brings a range of new features and functionalities. However, to ensure optimal performance and stability, it has specific hardware requirements. One of the most crucial requirements is the processor.
The Role of the Processor in Compatibility:
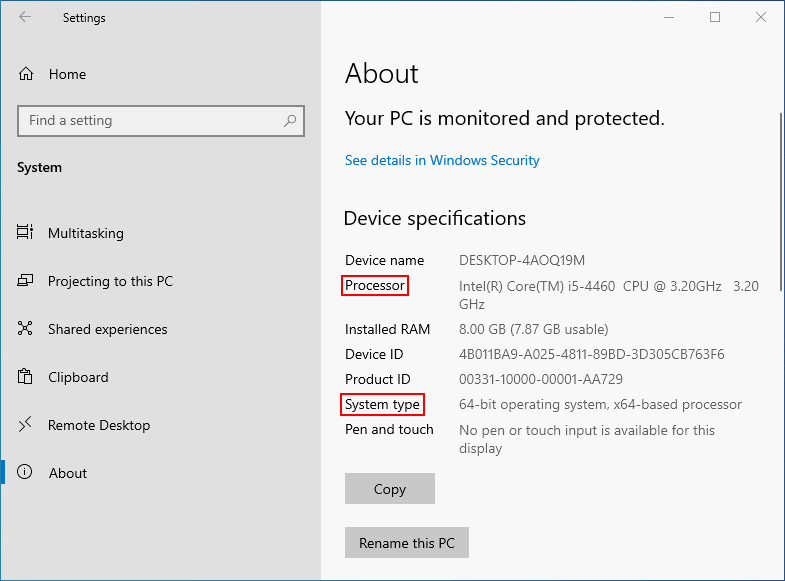
The processor, also known as the CPU (Central Processing Unit), is the brain of a computer. It handles all the computational tasks, from running applications to displaying graphics. Windows 11 leverages specific processor capabilities for its core functionalities, making processor compatibility a critical factor.
7th Generation Processors and Windows 11: A Closer Look:
While 7th generation processors were released before Windows 11, their compatibility is not a straightforward issue. Windows 11’s official minimum system requirements specify a processor from the 8th generation or later. However, this does not mean that 7th generation processors are entirely incompatible.
The Importance of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot:
Beyond processor generation, Windows 11 mandates the presence of two security features: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 and Secure Boot. TPM 2.0 is a dedicated security chip on the motherboard that protects system data and performs cryptographic operations. Secure Boot, an embedded security feature, ensures that only authorized operating systems and drivers can load during startup.
The Dilemma of 7th Generation Processors:
While some 7th generation processors might meet the minimum RAM and storage requirements, their lack of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot capabilities presents a significant hurdle. These features are typically integrated into newer motherboards designed for 8th generation and later processors.
Workarounds and Potential Solutions:
For users with 7th generation processors who desire Windows 11, several options exist:
- Motherboard Upgrade: Replacing the motherboard with a newer model that supports TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot is the most reliable solution. However, it involves a significant investment and may require reinstalling the operating system.
- BIOS Updates: Some motherboard manufacturers have released BIOS updates that enable TPM 2.0 emulation, allowing older systems to meet the Windows 11 requirements. However, the availability and effectiveness of these updates vary depending on the motherboard model.
- Windows 11 Installation Bypass: Some users have reported success in installing Windows 11 on 7th generation systems by bypassing the compatibility check. This method involves modifying the installation files and may compromise system security and stability. It is not recommended for novice users.
Understanding the Risks and Benefits:
While installing Windows 11 on a 7th generation system might be achievable, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks:
- Performance Issues: Older processors might struggle to handle the demands of Windows 11, leading to slowdowns, crashes, and reduced battery life.
- Security Vulnerabilities: The lack of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot could make the system more vulnerable to malware and security threats.
- Lack of Support: Microsoft does not officially support Windows 11 on systems with 7th generation processors, limiting access to updates and technical assistance.
Weighing the Options:
The decision of whether to upgrade to Windows 11 on a 7th generation system requires careful consideration of the risks and benefits. If the system is nearing its end of life or the performance is already lagging, investing in a new system with a compatible processor might be a more sensible choice. However, if the system is still functional and the user is willing to accept the potential risks, exploring the available workarounds might be an option.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: Does my 7th generation processor definitely not support Windows 11?
A: While Windows 11 officially requires an 8th generation processor or later, some 7th generation processors might be compatible through BIOS updates or workarounds. However, this is not guaranteed, and the risks associated with these methods should be considered.
Q: What are the benefits of upgrading to Windows 11?
A: Windows 11 offers a range of benefits, including improved security features, enhanced performance, a modern user interface, and better integration with Microsoft services.
Q: What are the drawbacks of using Windows 11 on a 7th generation system?
A: Potential drawbacks include performance issues, security vulnerabilities, lack of official support, and potential instability.
Q: Can I upgrade my motherboard to support Windows 11?
A: Yes, upgrading to a motherboard that supports TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot is a viable solution. However, it involves a significant investment and might require reinstalling the operating system.
Q: What are some alternative operating systems for my 7th generation processor?
A: Linux-based operating systems, such as Ubuntu and Fedora, are known for their compatibility with older hardware and offer a wide range of software options.
Tips for Users with 7th Generation Processors:
- Check for BIOS updates: Consult your motherboard manufacturer’s website for BIOS updates that might enable TPM 2.0 emulation.
- Consider alternative operating systems: If Windows 11 is not feasible, explore Linux-based operating systems that are compatible with older hardware.
- Prioritize system security: If you choose to install Windows 11 through workarounds, ensure you implement strong security measures to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Backup your data: Before making any significant system changes, back up your important data to avoid data loss.
Conclusion:
The compatibility of 7th generation processors with Windows 11 is a complex issue that requires careful consideration. While some workarounds might allow installation, the risks of performance issues, security vulnerabilities, and lack of official support should be weighed against the potential benefits. Ultimately, the decision of whether to upgrade to Windows 11 depends on individual needs, system specifications, and risk tolerance. For users seeking the best experience and maximum security, upgrading to a system with a compatible processor is the most reliable option.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: 7th Generation Processors and Windows 11. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!