Monitoring CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Monitoring CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Monitoring CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Monitoring CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of personal computing, the central processing unit (CPU) is the heart of any system. Its performance, measured in gigahertz (GHz), dictates how efficiently your computer can handle demanding tasks, from gaming and video editing to multitasking and web browsing. However, high-performance comes at a cost – heat. As the CPU processes information, it generates heat, which can significantly impact its stability and longevity if left unchecked. This is where monitoring CPU temperature becomes crucial.
Understanding CPU Temperature and Its Importance
CPU temperature represents the internal heat generated by the processor during operation. It is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F). While a certain level of heat is normal, exceeding a specific threshold can lead to performance degradation, instability, and even permanent damage to the processor.
Why Monitor CPU Temperature?
- Performance Optimization: Excessive heat can cause the CPU to throttle its performance, resulting in sluggishness and lag. Monitoring temperature allows you to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize cooling solutions to maintain peak performance.
- Hardware Protection: High temperatures can damage the CPU, leading to hardware failure and costly repairs. Monitoring temperature enables proactive intervention, preventing potential damage.
- Troubleshooting Issues: Sudden temperature spikes or consistent high temperatures can indicate underlying issues like faulty fans, insufficient cooling, or overclocking problems. Monitoring provides vital clues for troubleshooting.
Methods for Monitoring CPU Temperature in Windows 10
Several methods are available for monitoring CPU temperature in Windows 10. These include:
1. Task Manager:
- Windows Task Manager offers a built-in solution for basic temperature monitoring.
- Access it by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Navigate to the Performance tab.
- Select CPU from the available options.
- The CPU usage graph provides a visual representation of CPU activity. While not a direct temperature reading, it can indicate potential heat issues if the CPU usage consistently stays high.
2. BIOS/UEFI Settings:
- Most modern motherboards include temperature sensors that can be accessed through the BIOS or UEFI setup.
- Access the BIOS by restarting your computer and pressing the designated key (usually Del, F2, or Esc) during the boot sequence.
- Navigate to the Monitor or Hardware Monitor section to find CPU temperature readings.
- Note that BIOS temperature readings may differ slightly from those displayed in operating system-based monitoring tools.
3. Third-Party Software:
- Numerous third-party software applications offer more comprehensive and customizable CPU temperature monitoring options.
- Popular choices include:
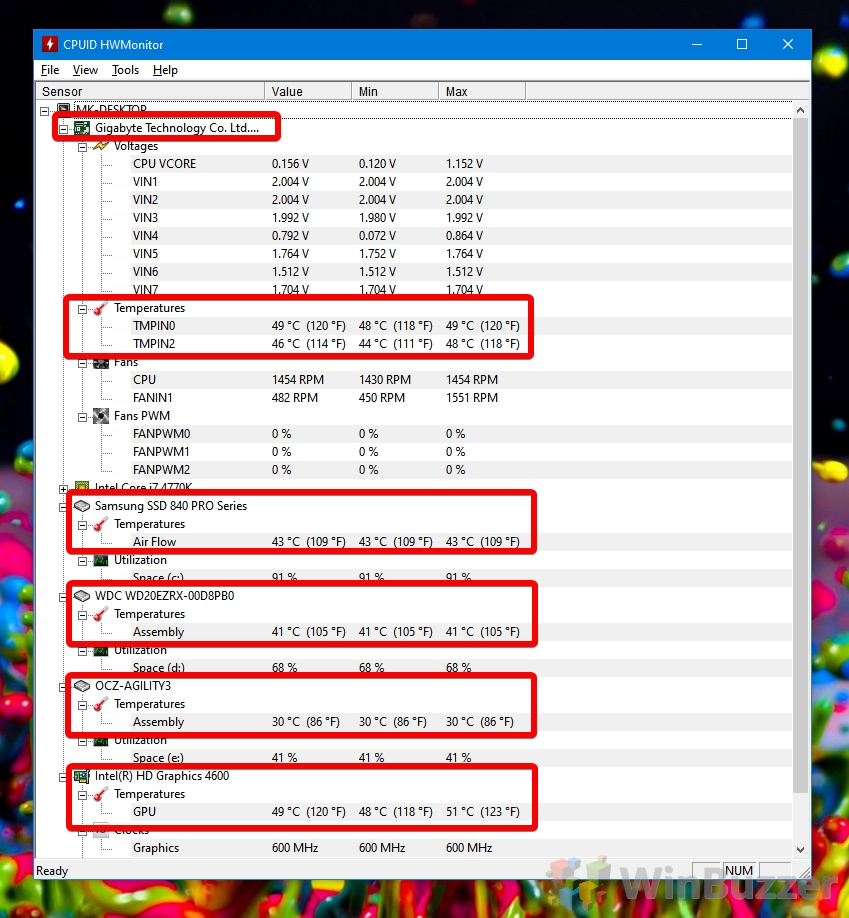
- HWMonitor: Provides real-time readings for various hardware components, including CPU temperature.
- Core Temp: Focuses specifically on CPU temperature monitoring, displaying individual core temperatures.
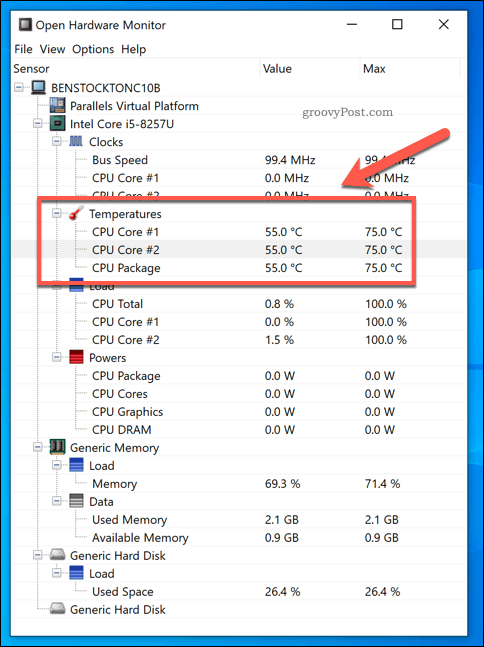
- Open Hardware Monitor: A free and open-source alternative offering detailed temperature readings.
- MSI Afterburner: Primarily known for its overclocking capabilities, but also includes a powerful temperature monitoring tool.
4. Command Prompt:
- The Windows Command Prompt can be used to retrieve basic CPU temperature information.
- Open the Command Prompt (search for "cmd" in the Start menu).
- Run the following command: wmic sensors get Temperature
- This command displays the temperature readings from various sensors, including the CPU.
Interpreting CPU Temperature Readings
Understanding what constitutes a safe CPU temperature range is crucial. While ideal temperatures vary depending on the CPU model, a general guideline is:
- Idle: 30-45°C (86-113°F)
- Under Load: 60-80°C (140-176°F)
Exceeding these ranges can indicate potential overheating issues. However, it’s important to note that these are just general guidelines. Consult your CPU manufacturer’s specifications for specific temperature thresholds.
Addressing High CPU Temperatures
If you notice consistently high CPU temperatures, there are several steps you can take to address the issue:
- Check Cooling System: Ensure that your CPU cooler is properly installed and functioning correctly. Clean dust and debris from the cooler and its fins.
- Repaste CPU: Over time, thermal paste can dry out, reducing its heat transfer efficiency. Consider reapplying thermal paste to the CPU.
- Improve Airflow: Ensure adequate airflow within your computer case. Consider adding additional fans or adjusting fan settings.
- Reduce Overclocking: If you’ve overclocked your CPU, consider reducing the clock speed to lower temperatures.
- Limit Background Processes: Close unnecessary programs and background processes that can contribute to CPU load and heat generation.
- Optimize Power Settings: Select a balanced or power-saving power plan to reduce CPU performance and heat generation.
FAQs about CPU Temperature Monitoring
Q: What is the ideal CPU temperature?
A: The ideal CPU temperature varies depending on the specific CPU model. However, a general guideline is 30-45°C (86-113°F) at idle and 60-80°C (140-176°F) under load.
Q: What happens if my CPU overheats?
A: Overheating can lead to performance degradation, system instability, and potentially permanent damage to the CPU.
Q: How often should I monitor my CPU temperature?
A: It’s a good practice to monitor your CPU temperature regularly, especially when running demanding applications.
Q: Can I damage my CPU by monitoring its temperature?
A: No, monitoring CPU temperature does not damage the CPU.
Q: What is thermal throttling?
A: Thermal throttling is a mechanism that automatically reduces CPU performance to prevent overheating.
Q: What is the difference between CPU temperature and CPU usage?
A: CPU temperature refers to the internal heat generated by the processor, while CPU usage represents the percentage of the CPU’s processing power being utilized.
Tips for Effective CPU Temperature Monitoring
- Choose the Right Monitoring Tool: Select a tool that provides comprehensive temperature readings, customizable alerts, and user-friendly interface.
- Set Realistic Temperature Thresholds: Configure alerts for temperatures that exceed safe operating ranges for your CPU.
- Monitor Regularly: Check CPU temperature periodically, especially when running demanding tasks.
- Address Issues Proactively: Don’t ignore high temperatures. Take steps to address overheating issues before they escalate.
Conclusion
Monitoring CPU temperature is an essential practice for maintaining optimal performance, protecting your hardware, and troubleshooting potential issues. By understanding the importance of temperature monitoring, utilizing appropriate tools, and taking proactive steps to address overheating, you can ensure the longevity and stability of your computer system. Remember, a cool CPU is a happy CPU, and a happy CPU translates to a smooth and efficient computing experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Monitoring CPU Temperature in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!