Mastering the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Tool in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Mastering the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Tool in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mastering the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Tool in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mastering the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Tool in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mastering the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Tool in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Foundation: What is DISM?
- 3.2 Essential DISM Commands for Windows 11: A Comprehensive Overview
- 3.3 Practical Applications of DISM Commands in Windows 11
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Tips for Using DISM Commands Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Mastering the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Tool in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
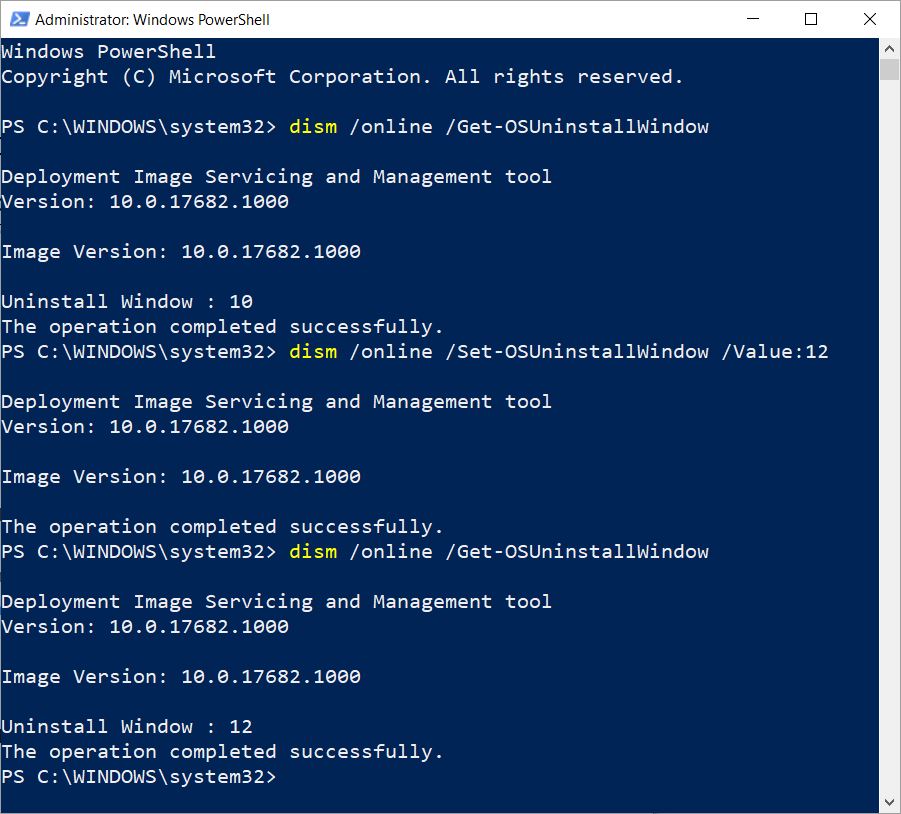
The Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool is a powerful command-line utility in Windows 11 that allows administrators and users to manage and repair Windows images and installations. Its versatility extends beyond basic maintenance, enabling advanced tasks like customizing system components, integrating updates, and even troubleshooting corrupted system files. This article delves into the intricacies of DISM commands in Windows 11, providing a comprehensive understanding of its capabilities and applications.
Understanding the Foundation: What is DISM?
DISM is a versatile tool that primarily operates on Windows images, which are essentially compressed packages containing the necessary files and configurations for installing or repairing a Windows operating system. These images can be mounted as virtual drives, enabling access to their contents for modification and management.
DISM commands are executed through the command prompt or PowerShell, offering a wide range of functionalities. They are categorized into various groups, each addressing specific aspects of image management, including:
- Image Servicing: This group of commands focuses on manipulating the content of Windows images, enabling tasks like adding or removing features, updating system files, and applying language packs.
- Image Management: These commands manage the lifecycle of Windows images, encompassing operations like mounting and unmounting images, creating new images, and applying custom configurations.
- Package Management: DISM provides commands for managing Windows packages, including installing, removing, and updating them.
- Repair and Recovery: DISM plays a crucial role in repairing corrupted Windows installations, restoring system files, and resolving various system errors.
Essential DISM Commands for Windows 11: A Comprehensive Overview
1. Mounting and Unmounting Windows Images:
-
Dism /Mount-Image /ImageFile:
/MountDir: : Mounts a Windows image file as a virtual drive, allowing access to its contents. -
Dism /Unmount-Image /MountDir:
/Commit : Unmounts the mounted image, committing any changes made during the session. -
Dism /Unmount-Image /MountDir:
/Discard : Unmounts the mounted image, discarding any changes made during the session.
2. Managing Windows Features:
-
Dism /Online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:
: Enables a specific Windows feature. -
Dism /Online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:
: Disables a specific Windows feature. - Dism /Online /Get-Features: Lists all available Windows features on the system.
3. Updating System Files and Packages:
- Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth: Scans the system for corrupted files and attempts to repair them using the Windows Update repository.
- Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth: Scans the system for corrupted files and reports any found issues.
- Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanup: Starts the component cleanup process, removing unused system files to free up disk space.
-
Dism /Online /Add-Package /PackagePath:
: Adds a new Windows package to the system. -
Dism /Online /Remove-Package /PackageName:
: Removes a specific Windows package from the system. - Dism /Online /Get-Packages: Lists all installed Windows packages on the system.
4. Managing Language Packs:
-
Dism /Online /Add-Package /PackagePath:
: Adds a new language pack to the system. -
Dism /Online /Remove-Package /PackageName:
: Removes a specific language pack from the system. - Dism /Online /Get-Packages: Lists all installed language packs on the system.
5. Creating and Managing Windows Images:
-
Dism /Capture-Image /ImageFile:
/CaptureDir: : Creates a new Windows image from a specified directory. -
Dism /Apply-Image /ImageFile:
/ApplyDir: : Applies a Windows image to a specified directory, effectively reinstalling the system. -
Dism /Export-Image /ImageFile:
/ExportDir: : Exports the contents of a Windows image to a specified directory.
6. Advanced Operations:
-
Dism /Get-WimInfo /WimFile:
: Provides information about a Windows image file, including its size, compression level, and other details. -
Dism /Get-Drivers /ImageFile:
: Lists all drivers included in a Windows image. -
Dism /Get-Packages /ImageFile:
: Lists all packages included in a Windows image.
Practical Applications of DISM Commands in Windows 11
The versatility of DISM commands extends beyond basic system maintenance, offering solutions for a wide range of scenarios:
-
Repairing Corrupted System Files: DISM’s
RestoreHealthcommand is invaluable for repairing corrupted system files, often encountered after system crashes or malware infections. It leverages the Windows Update repository to replace damaged files, ensuring system stability. - Customizing Windows Installations: DISM enables the addition or removal of Windows features, tailoring the operating system to specific requirements. This is particularly useful for optimizing system performance by removing unnecessary components or for deploying specialized configurations for specific user groups.
- Managing Language Packs: DISM simplifies the process of adding or removing language packs, enabling users to switch between different languages seamlessly. This is particularly beneficial for multilingual environments or when deploying Windows installations for global audiences.
- Creating and Applying Custom Images: DISM facilitates the creation of customized Windows images, incorporating specific drivers, applications, or configurations. These images can be deployed on multiple systems, ensuring consistent setups and reducing manual configuration efforts.
-
Troubleshooting System Errors: DISM’s
ScanHealthcommand assists in identifying potential system issues, providing valuable information for troubleshooting. Its ability to scan for corrupted files and report any inconsistencies offers a starting point for resolving system errors and restoring stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can DISM be used to upgrade Windows 11?
While DISM is not the primary tool for upgrading Windows 11, it can be used to prepare an existing installation for an upgrade. By running the Cleanup-Image command with the StartComponentCleanup option, users can free up disk space and ensure a smoother upgrade process.
2. How can I use DISM to create a bootable USB drive for Windows 11 installation?
DISM is not directly involved in creating bootable USB drives. The process typically involves using the Windows Media Creation Tool or the Rufus utility, which leverage DISM internally for image manipulation.
3. What are the prerequisites for using DISM commands?
To use DISM commands, users need administrative privileges on the system. Additionally, access to the Windows Update repository is required for certain commands, like RestoreHealth.
4. Can I use DISM to repair a corrupted Windows installation on another computer?
Yes, DISM can be used to repair a corrupted Windows installation on another computer. However, it requires a bootable USB drive containing the Windows 11 installation files and the Dism command-line tool.
5. Are there any alternatives to DISM for managing Windows images?
While DISM is a powerful tool, other alternatives exist, such as the Windows Imaging and Configuration Designer (WICD) and the Deployment Workbench. However, DISM remains the primary command-line utility for managing Windows images and installations.
Tips for Using DISM Commands Effectively
- Use Elevated Command Prompt or PowerShell: To execute DISM commands, open the Command Prompt or PowerShell as administrator.
- Understand the Command Syntax: Pay close attention to the syntax of DISM commands, including the required parameters and options.
-
Utilize the
/HelpOption: For detailed information about a specific DISM command, use the/Helpoption, e.g.,Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Help. - Back Up Important Data: Before making any significant changes using DISM, ensure a backup of important data to prevent accidental data loss.
- Consult Microsoft Documentation: For comprehensive information and detailed examples, refer to the official Microsoft documentation on DISM commands.
Conclusion
DISM commands in Windows 11 provide a powerful and versatile toolkit for managing and repairing Windows images and installations. From basic maintenance tasks like cleaning up system files to advanced operations like customizing system components and creating custom images, DISM offers a wide range of functionalities. By understanding the various DISM commands and their applications, users can effectively manage their Windows systems, troubleshoot system errors, and create customized installations tailored to specific needs. With its comprehensive capabilities and user-friendly interface, DISM remains an indispensable tool for administrators and users alike, empowering them to maintain and optimize their Windows 11 experience.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mastering the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Tool in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!