Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators
Related Articles: Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators
In the realm of operating system administration, efficient disk management is paramount. Windows 11, with its advanced features and functionalities, offers a robust disk management tool that empowers administrators to effectively manage storage space, optimize performance, and ensure data integrity. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Disk Management in Windows 11, providing a detailed understanding of its capabilities, functionalities, and best practices.
Understanding Disk Management in Windows 11
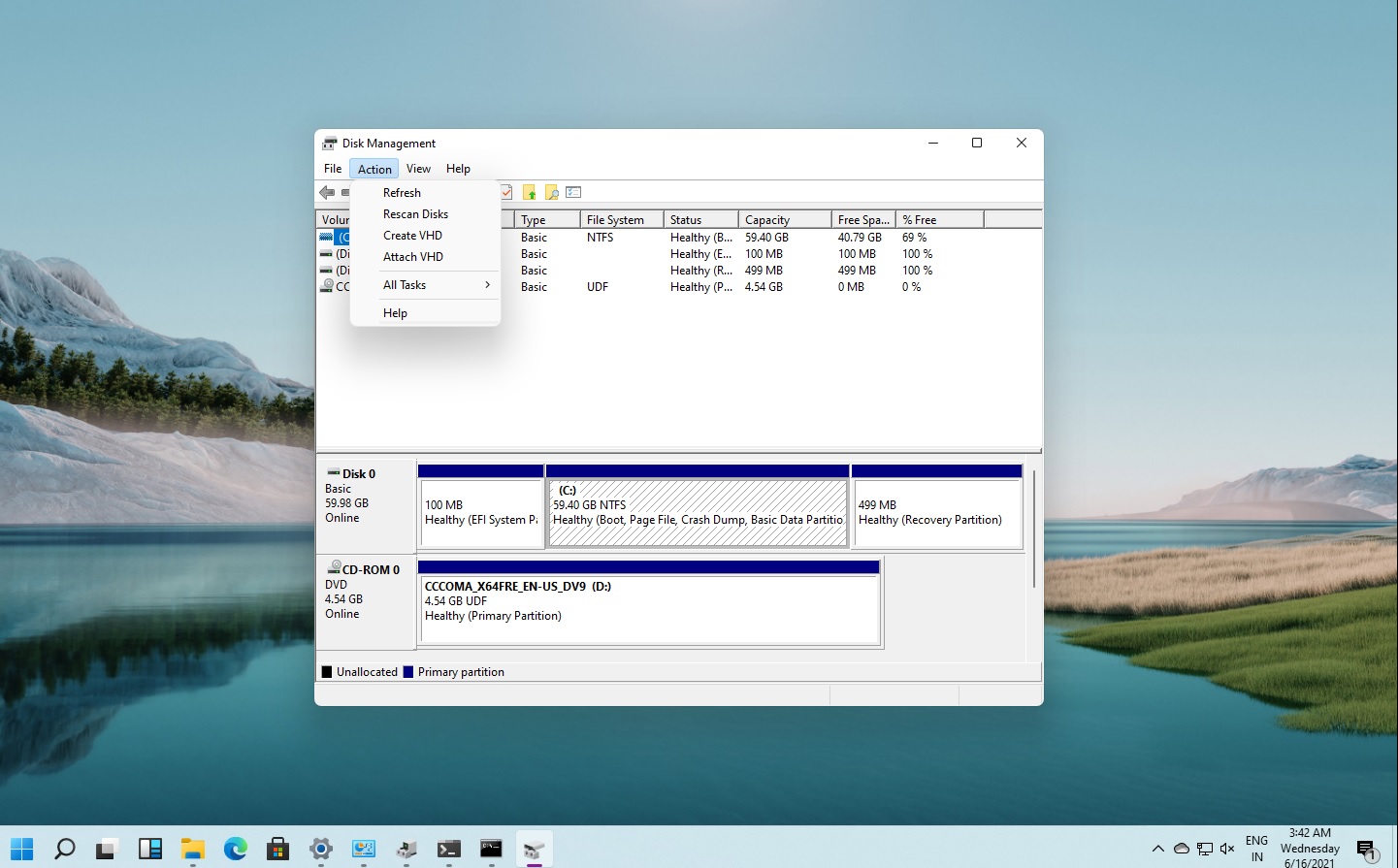
Disk Management is an integral component of Windows 11, serving as a centralized hub for managing all aspects of storage within the operating system. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows administrators to perform a wide range of tasks, including:
- Creating and formatting partitions: Dividing physical disks into logical sections, each with its own file system and formatting.
- Managing volumes: Creating, extending, shrinking, and deleting volumes, which are the actual storage units used by the operating system.
- Assigning drive letters: Defining the alphabetical identifier for each volume, making it accessible in Windows Explorer.
- Performing basic disk operations: Initializing disks, converting between MBR and GPT partitioning schemes, and checking for errors.
- Managing dynamic disks: Utilizing advanced features like spanning and striping for enhanced storage capacity and performance.
- Setting up RAID configurations: Creating redundant arrays of independent disks (RAID) for data protection and improved performance.
Navigating Disk Management
Accessing Disk Management in Windows 11 is straightforward:
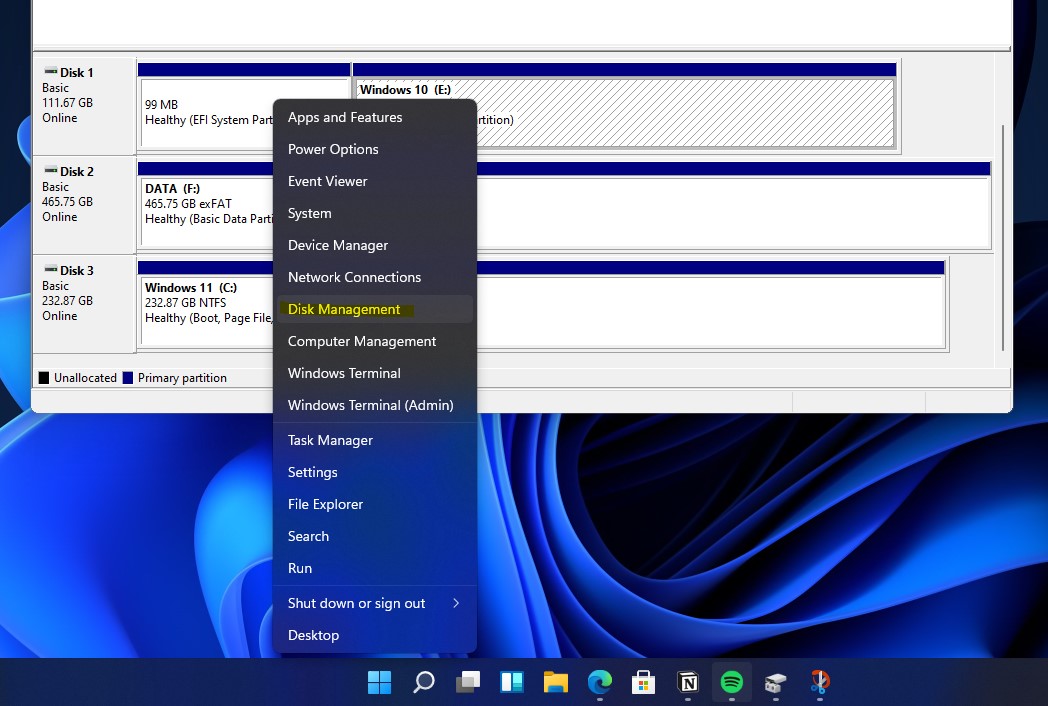
- Press the Windows key + X to open the Quick Link menu.
- Select Disk Management from the list.
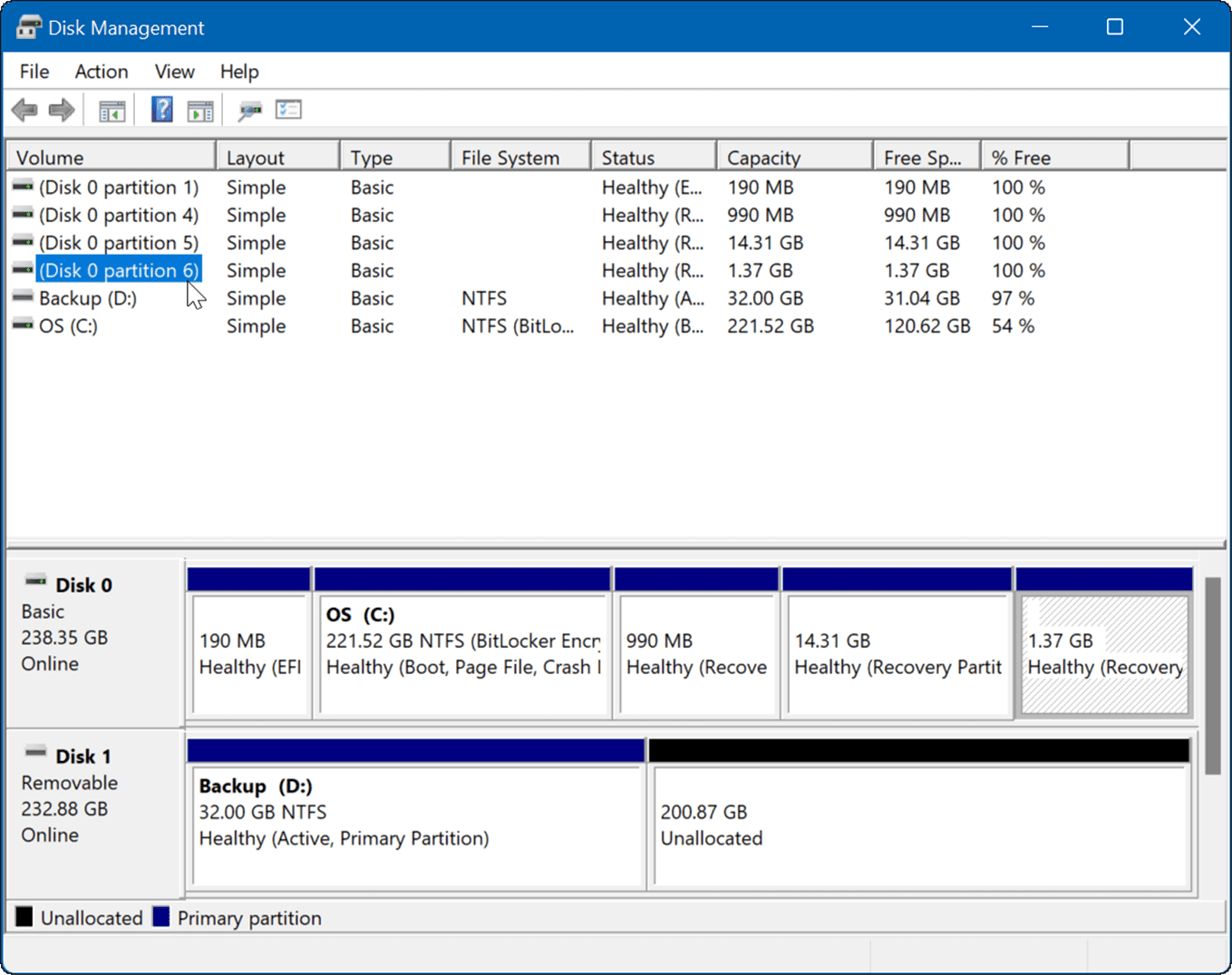
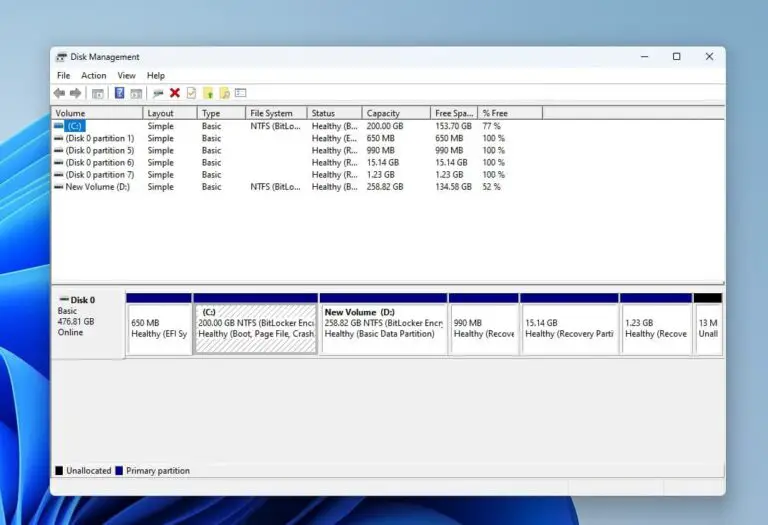
The Disk Management console will appear, displaying a graphical representation of all connected disks and their partitions.
Essential Disk Management Tasks
1. Creating and Formatting Partitions:
- Right-click on an unallocated space on the disk you wish to partition.
- Select "New Simple Volume."
- Follow the wizard prompts to define the volume size, drive letter, file system (e.g., NTFS, FAT32), and volume label.
2. Managing Volumes:
- Right-click on a volume to access various options.
- "Extend Volume" allows expanding the size of a volume by utilizing unallocated space on the same disk.
- "Shrink Volume" reduces the size of a volume, creating unallocated space.
- "Delete Volume" removes a volume and its associated data.
3. Assigning Drive Letters:
- Right-click on a volume and select "Change Drive Letter and Paths."
- Click "Add" to assign a new drive letter.
- Select a letter from the drop-down menu and click "OK."
4. Performing Basic Disk Operations:
- "Initialize Disk" converts a new or uninitialized disk to a specific partitioning style (MBR or GPT).
- "Convert to Dynamic Disk" allows utilizing advanced disk management features like spanning and striping.
- "Check for Errors" scans a disk for errors and attempts to repair them.
5. Managing Dynamic Disks:
- Dynamic disks offer features like spanning (combining multiple disks into a single volume) and striping (distributing data across multiple disks for performance enhancement).
- "Create Volume" within a dynamic disk allows creating simple, spanned, or striped volumes.
- "Extend Volume" can be used to expand a dynamic volume using free space from other dynamic disks.
6. Setting Up RAID Configurations:
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) provides fault tolerance and improved performance.
- Disk Management supports RAID 0 (striping), RAID 1 (mirroring), RAID 5 (parity), and RAID 10 (mirror-stripe).
- To create a RAID configuration, right-click on a disk and select "Create Virtual Disk."
- Follow the wizard prompts to define the RAID level, disks to include, and other parameters.
Optimizing Disk Performance
Beyond basic management, Disk Management offers several features to optimize disk performance:
- Defragmentation: Rearranging fragmented files on a disk to improve access speed.
- Disk Cleanup: Removing unnecessary files like temporary files and system files to free up disk space.
- Disk Optimization: Running a system-wide optimization process to improve overall performance.
Best Practices for Disk Management in Windows 11
- Regularly monitor disk space: Avoid running out of disk space by monitoring usage and deleting unnecessary files.
- Implement a backup strategy: Regularly back up important data to prevent data loss in case of disk failure.
- Use a consistent file system: Choose a file system that best suits your needs (NTFS for most scenarios, FAT32 for compatibility with older systems).
- Consider using dynamic disks: Explore the advantages of dynamic disks for enhanced storage and performance features.
- Optimize disk performance: Utilize defragmentation, Disk Cleanup, and Disk Optimization tools to enhance performance.
FAQs
Q: What are the differences between MBR and GPT partitioning schemes?
A: MBR (Master Boot Record) is an older partitioning scheme limited to 2.2 TB partitions and supports up to four primary partitions. GPT (GUID Partition Table) is a newer scheme that overcomes these limitations, supporting larger partitions and an unlimited number of partitions.
Q: What are the benefits of using RAID configurations?
A: RAID configurations provide fault tolerance, improved performance, and increased storage capacity. RAID 0 offers performance improvements, RAID 1 provides data redundancy, RAID 5 balances performance and fault tolerance, and RAID 10 combines the benefits of RAID 1 and RAID 0.
Q: How can I recover data from a damaged or corrupted disk?
A: Data recovery software can be used to attempt to recover data from a damaged or corrupted disk. However, it is crucial to avoid writing new data to the disk to prevent overwriting the lost data.
Q: What are some common disk errors and how can I troubleshoot them?
A: Common disk errors include file system errors, bad sectors, and disk corruption. These errors can be diagnosed and often resolved using the "Check Disk" utility (CHKDSK) or by running a disk repair tool.
Tips
- Before making any changes to disks, create a system image backup to restore the system to a previous state if necessary.
- Always double-check your actions before making changes to disks to avoid accidental data loss.
- Consider using a third-party disk management tool for advanced features and functionalities.
- Stay updated with the latest Windows 11 updates to benefit from bug fixes and performance improvements related to disk management.
Conclusion
Disk Management in Windows 11 empowers administrators to effectively manage storage space, optimize performance, and safeguard data integrity. By understanding the functionalities and best practices discussed in this guide, administrators can ensure efficient and reliable disk management, contributing to a robust and optimized Windows 11 environment. Regular monitoring, proactive maintenance, and a well-defined backup strategy are crucial components of a successful disk management approach.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!