Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Disk Management: The Foundation of Storage Control
- 3.2 Accessing the Disk Management Console: The Gateway to Storage Control
- 3.3 Exploring the Disk Management Interface: A Visual Guide to Your Storage
- 3.4 Essential Disk Management Tasks: Empowering Your Storage Control
- 3.5 Understanding Disk Management Commands: Beyond the GUI
- 3.6 Benefits of Using Disk Management: Optimizing Your Storage Experience
- 3.7 FAQs: Addressing Common Disk Management Queries
- 3.8 Tips for Effective Disk Management: Maximizing Your Storage Control
- 3.9 Conclusion: Mastering Disk Management for Optimized Storage
- 4 Closure
Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
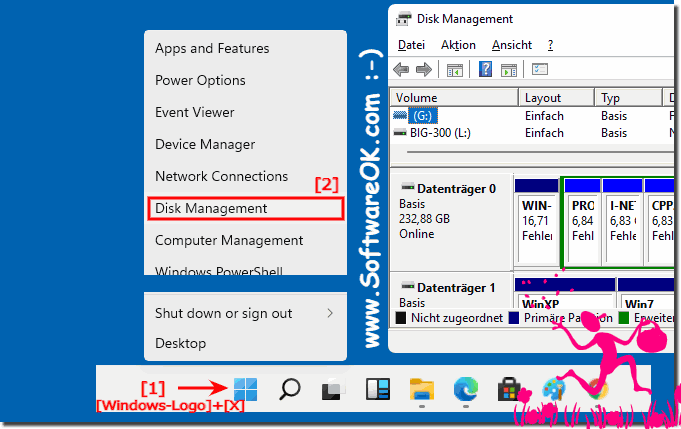
Windows 11, like its predecessors, offers a robust suite of tools for managing hard drives and other storage devices. Among these, the Disk Management console is a powerful utility that empowers users to perform a wide range of tasks, from creating and formatting partitions to managing volumes and troubleshooting storage-related issues. This article delves into the intricacies of Disk Management in Windows 11, providing a comprehensive overview of its capabilities, functionalities, and best practices.
Understanding Disk Management: The Foundation of Storage Control
Disk Management is a built-in graphical user interface (GUI) tool that allows users to visualize and interact with the physical storage devices connected to their Windows 11 computer. It provides a centralized platform for managing partitions, volumes, and other storage-related aspects.
Key Concepts:
- Disk: A physical storage device, such as a hard disk drive (HDD), solid-state drive (SSD), or USB flash drive.
- Partition: A logical division of a disk, creating separate storage spaces.
- Volume: A formatted partition that the operating system can access and use to store files.
- File System: The structure used by the operating system to organize and access data on a volume, such as NTFS or FAT32.
Accessing the Disk Management Console: The Gateway to Storage Control
The Disk Management console can be accessed in two ways:
-
Through the Start Menu:
- Click on the Start button.
- Search for "Disk Management" and select the corresponding result.
-
Through File Explorer:
- Open File Explorer (Windows key + E).
- Navigate to This PC.
- Right-click on "This PC" and select "Manage."
- In the Computer Management window, expand "Storage" and then click on "Disk Management."
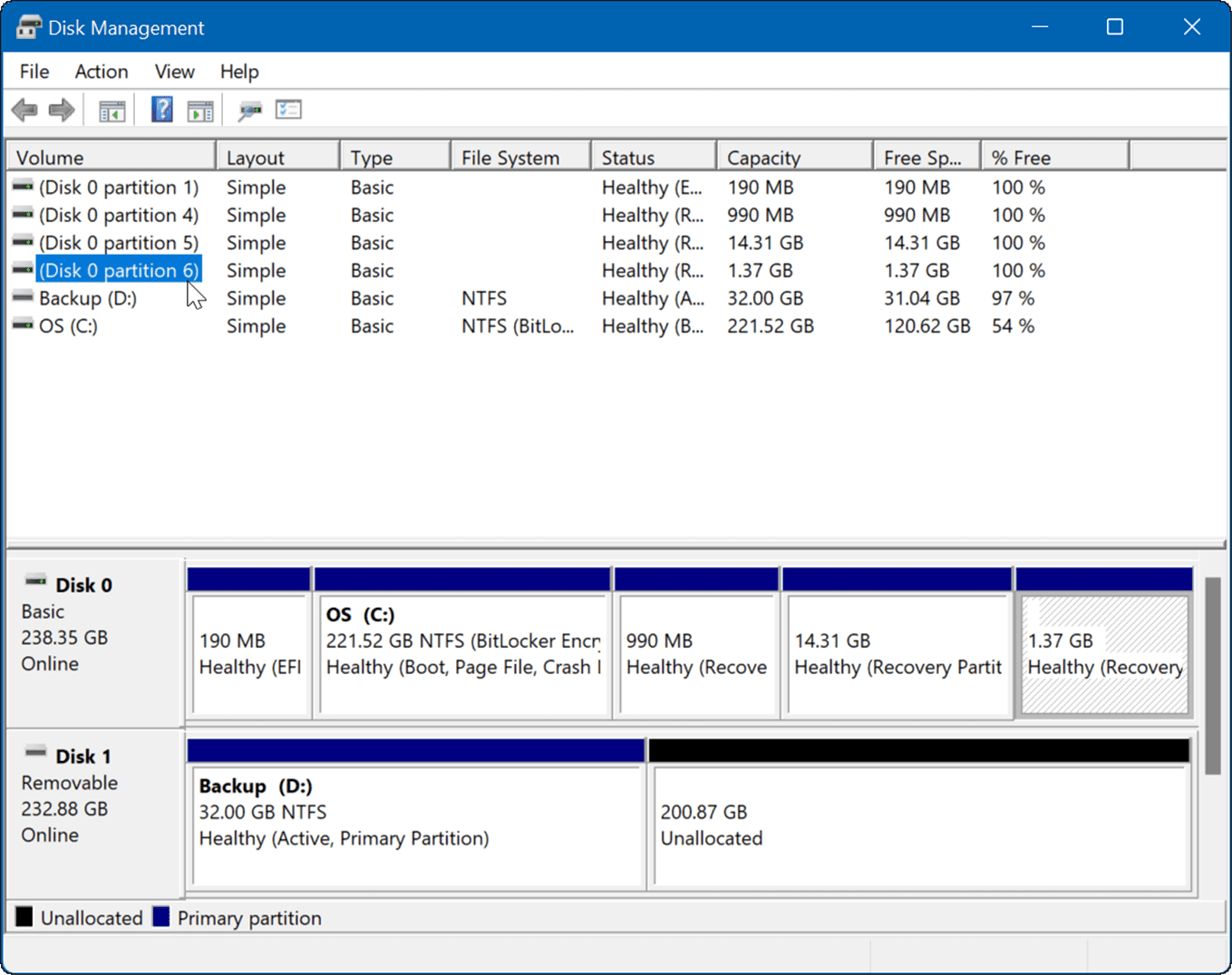
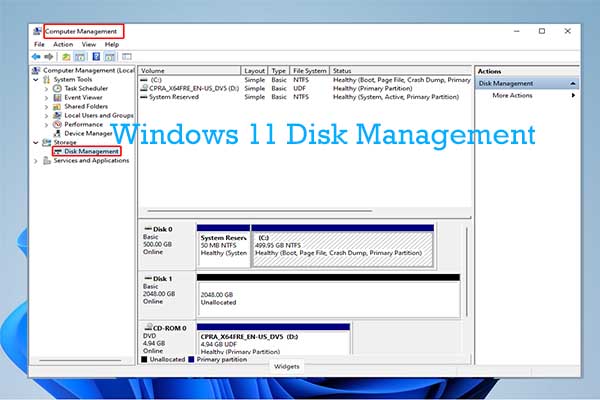
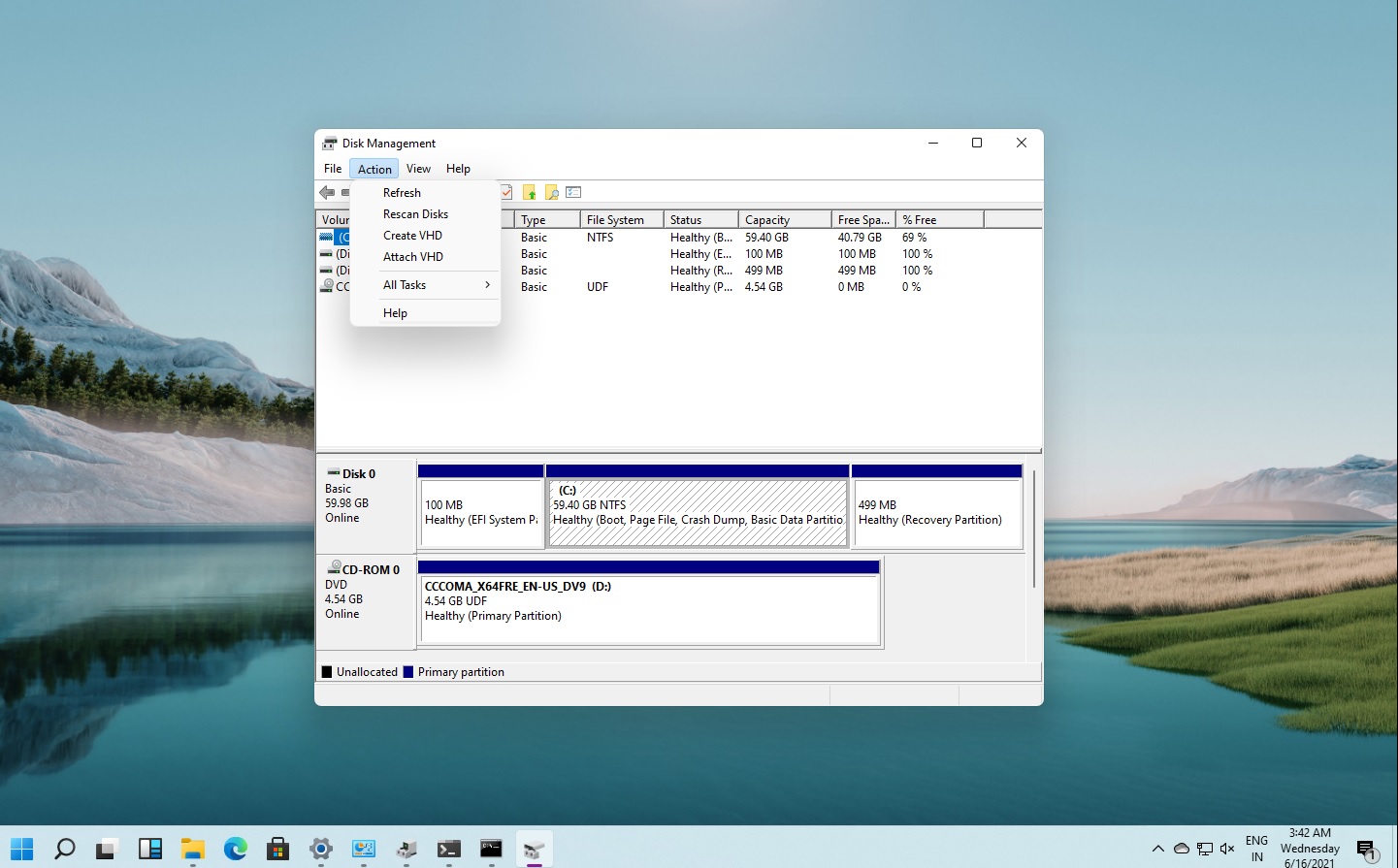
Exploring the Disk Management Interface: A Visual Guide to Your Storage
The Disk Management console presents a graphical representation of your connected storage devices. It displays:
- Disk Overview: A list of all connected disks, each identified by a disk number (Disk 0, Disk 1, etc.).
- Disk Layout: A visual representation of each disk, showing its partitions and volumes.
- Volume Information: Details about each volume, including its drive letter, file system, size, and status.
Essential Disk Management Tasks: Empowering Your Storage Control
Disk Management provides a variety of tools for managing storage devices. Here are some of the most common tasks:
1. Creating and Formatting Partitions:
-
Creating a Partition:
- Right-click on unallocated space on a disk.
- Select "New Simple Volume."
- Follow the wizard to define the size of the partition and assign a drive letter.
-
Formatting a Partition:
- Right-click on the partition.
- Select "Format."
- Choose the desired file system (NTFS, FAT32, etc.) and assign a volume label.
2. Managing Volumes:
-
Changing Drive Letter:
- Right-click on the volume.
- Select "Change Drive Letter and Paths."
- Choose a new drive letter.
-
Extending a Volume:
- Right-click on the volume you want to extend.
- Select "Extend Volume."
- Select the unallocated space to add to the volume.
-
Shrinking a Volume:
- Right-click on the volume you want to shrink.
- Select "Shrink Volume."
- Specify the amount of space to shrink.
3. Advanced Operations:
-
Converting a Basic Disk to Dynamic Disk:
- Right-click on the disk.
- Select "Convert to Dynamic Disk."
-
Creating a RAID Configuration:
- Right-click on the disk.
- Select "Create RAID Volume."
- Follow the wizard to create a RAID configuration.
-
Initializing a Disk:
- Right-click on the disk.
- Select "Initialize Disk."
- Choose the disk style (MBR or GPT).
Understanding Disk Management Commands: Beyond the GUI
While the Disk Management console provides a user-friendly interface, Windows 11 also offers a powerful command-line interface (CLI) for managing storage devices. The diskpart command is a versatile tool that can be used to perform a wide range of tasks, including:
-
Creating and Formatting Partitions:
-
diskpart(opens the diskpart command prompt) -
list disk(lists all connected disks) -
select disk <disk number>(selects the target disk) -
create partition primary size=<size in MB>(creates a primary partition) -
format fs=ntfs quick(formats the partition with NTFS file system) -
assign letter=<drive letter>(assigns a drive letter to the partition)
-
-
Managing Volumes:
-
list volume(lists all volumes) -
select volume <volume number>(selects the target volume) -
change letter=<drive letter>(changes the drive letter of the volume) -
extend size=<size in MB>(extends the volume) -
shrink desired= <size in MB>(shrinks the volume)
-
-
Advanced Operations:
-
convert dynamic(converts a basic disk to a dynamic disk) -
online disk <disk number>(brings a disk online) -
offline disk <disk number>(takes a disk offline)
-
Benefits of Using Disk Management: Optimizing Your Storage Experience
Using Disk Management effectively offers numerous benefits, including:
- Organized Storage: Creating partitions and volumes allows users to organize their data logically, making it easier to manage and access.
- Enhanced Performance: Formatting partitions with the appropriate file system can optimize storage performance and efficiency.
- Data Security: Creating separate partitions for different purposes can help protect sensitive data by isolating it from other files.
- Troubleshooting Issues: Disk Management can help identify and resolve storage-related issues, such as disk errors or partition problems.
- Advanced Configurations: Disk Management allows users to implement advanced storage configurations, such as RAID, to enhance performance and data redundancy.
FAQs: Addressing Common Disk Management Queries
Q1: What is the difference between a basic disk and a dynamic disk?
A: A basic disk is the default disk type in Windows, allowing for simple partition management. Dynamic disks offer advanced features like spanning volumes across multiple disks and RAID configurations.
Q2: Can I shrink a system partition?
A: Yes, you can shrink a system partition, but it’s recommended to do so with caution. Ensure you have enough free space on the system drive and back up important data before shrinking.
Q3: What happens if I delete a partition?
A: Deleting a partition will erase all data on that partition. Ensure you have backed up any important data before deleting a partition.
Q4: How do I recover data from a deleted partition?
A: Data recovery software can help recover data from deleted partitions. However, success is not guaranteed, and it’s crucial to avoid writing new data to the drive to increase the chances of recovery.
Q5: What is the best file system for my needs?
A: NTFS is the recommended file system for most Windows users, offering advanced features like file compression and security. FAT32 is suitable for older operating systems and devices that require compatibility.
Tips for Effective Disk Management: Maximizing Your Storage Control
- Backup Regularly: Back up your data regularly to avoid data loss in case of disk failure or accidental deletion.
- Use a Disk Defragmenter: Defragmenting your hard drive can improve performance by reorganizing fragmented files.
- Monitor Disk Space: Regularly check disk space usage to ensure you have enough free space for new files.
- Use Disk Cleanup: Run Disk Cleanup regularly to remove unnecessary files and free up disk space.
- Keep Your Operating System Updated: Update your operating system regularly to ensure you have the latest disk management features and security patches.
Conclusion: Mastering Disk Management for Optimized Storage
Disk Management is a powerful tool that empowers Windows 11 users to manage their storage devices effectively. By understanding the basics of partitions, volumes, and file systems, and utilizing the various features of Disk Management, users can optimize their storage experience, ensuring data security, performance, and organization. Whether through the user-friendly graphical interface or the versatile command-line tools, Disk Management provides the tools necessary to effectively manage and control your storage environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mastering Disk Management in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!