Managing Network Bandwidth: A Guide to Optimizing SMB Performance
Related Articles: Managing Network Bandwidth: A Guide to Optimizing SMB Performance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Managing Network Bandwidth: A Guide to Optimizing SMB Performance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Managing Network Bandwidth: A Guide to Optimizing SMB Performance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Managing Network Bandwidth: A Guide to Optimizing SMB Performance
- 3.1 Understanding Bandwidth Throttling
- 3.2 The Importance of Bandwidth Throttling for SMBs
- 3.3 Implementing Bandwidth Throttling: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding Bandwidth Throttling
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Bandwidth Throttling
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Managing Network Bandwidth: A Guide to Optimizing SMB Performance
In the modern digital landscape, network bandwidth is a precious resource, especially for Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs). As businesses grow and rely increasingly on data-intensive applications like cloud storage, video conferencing, and file sharing, managing bandwidth effectively becomes crucial to maintain smooth operations and user satisfaction. One powerful tool for achieving this is bandwidth throttling.
Understanding Bandwidth Throttling
Bandwidth throttling is a network management technique that controls the amount of data transmitted over a network connection. It allows administrators to prioritize specific applications or users, ensuring that critical processes receive adequate bandwidth while preventing others from consuming excessive resources. This proactive approach helps optimize network performance, prevent bottlenecks, and enhance overall productivity.
The Importance of Bandwidth Throttling for SMBs
For SMBs, bandwidth throttling offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Network Performance: By allocating bandwidth strategically, SMBs can ensure that critical applications like business-critical software, email, and web servers receive priority, preventing slowdowns and interruptions. This optimizes overall network performance and improves employee productivity.
- Resource Optimization: Bandwidth throttling helps manage network resources effectively by preventing bandwidth-intensive applications from monopolizing the network. This prevents bottlenecks and ensures that all applications and users receive a fair share of bandwidth, leading to a more balanced and efficient network.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing bandwidth usage, SMBs can potentially reduce their network costs. Throttling can help control data usage and prevent unnecessary bandwidth consumption, which can translate into lower monthly bills.
- Improved Security: Bandwidth throttling can be used to restrict access to certain websites or applications, enhancing network security by limiting exposure to potential threats and malware.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Bandwidth throttling is a key component of QoS, allowing administrators to prioritize specific types of traffic based on their importance. This ensures that time-sensitive applications like video conferencing and online meetings receive the bandwidth they need for a smooth and uninterrupted experience.
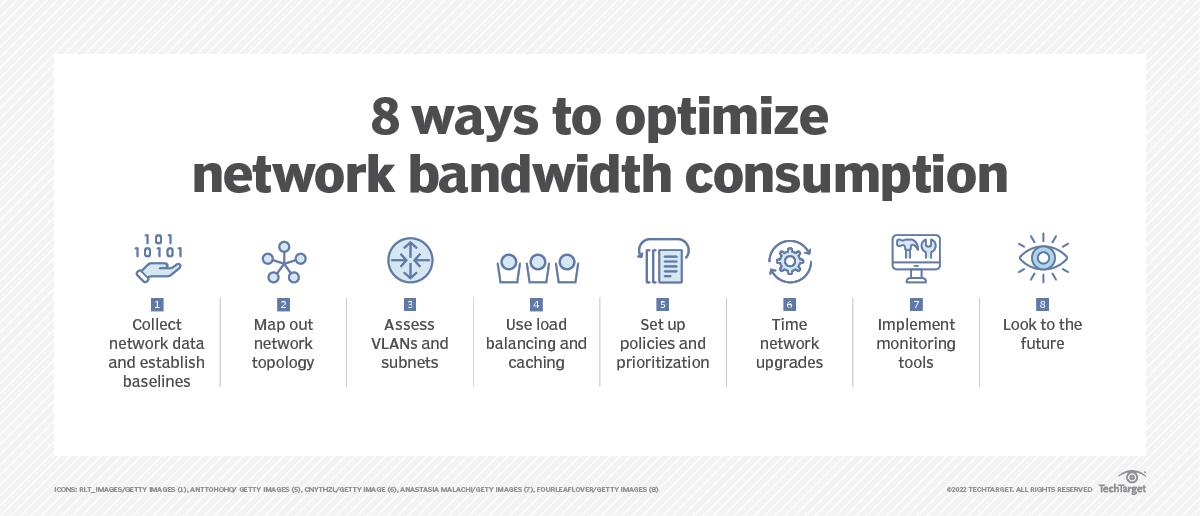
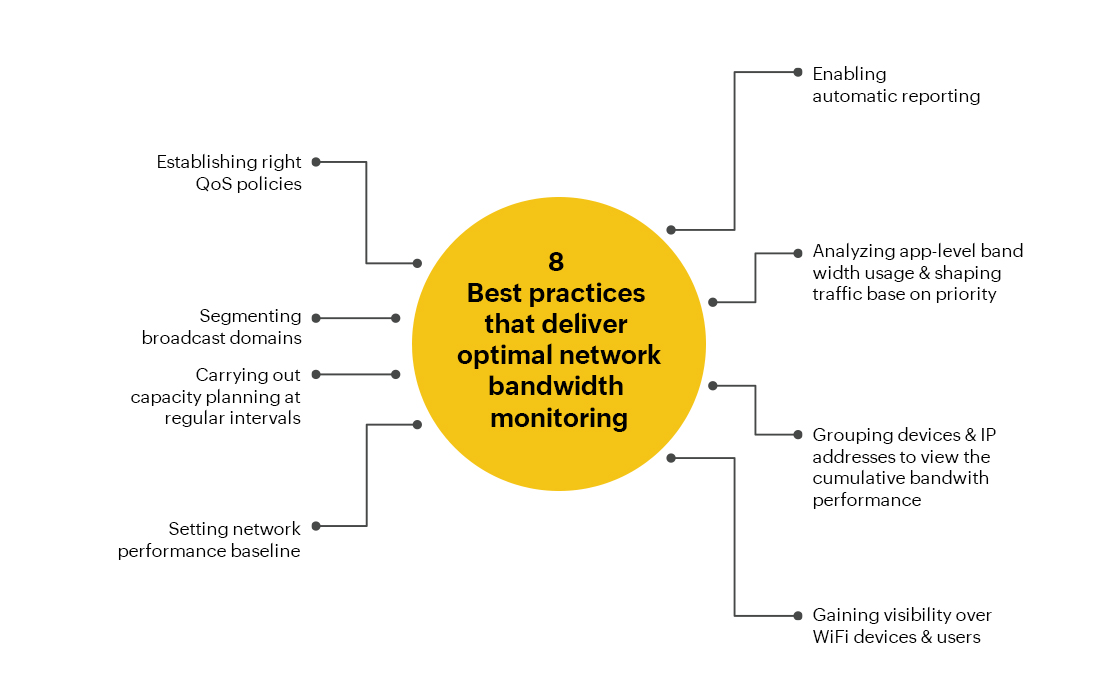
Implementing Bandwidth Throttling: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing bandwidth throttling involves several steps:
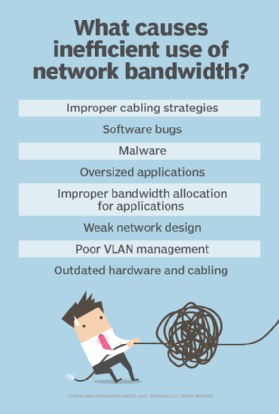
- Identify Network Bottlenecks: Analyze network traffic patterns to identify applications or users that consume excessive bandwidth. Tools like network monitoring software can provide valuable insights into network usage and help pinpoint potential bottlenecks.
- Define Bandwidth Allocation: Determine the desired bandwidth allocation for different applications and users. This process requires careful consideration of business needs and priorities.
- Configure Bandwidth Throttling Settings: Most routers and network switches offer bandwidth throttling capabilities. Configure these settings to implement the desired bandwidth allocation for different applications or users.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly monitor the network performance and adjust bandwidth throttling settings as needed. This ensures that the configuration remains optimal and meets evolving business needs.
FAQs Regarding Bandwidth Throttling
Q: What are the potential drawbacks of bandwidth throttling?
A: While bandwidth throttling offers numerous benefits, it can also have some drawbacks. If not implemented carefully, it can lead to:
- Reduced Network Performance: If throttling is applied too aggressively, it can lead to slower speeds for certain applications or users.
- User Frustration: Users may experience slowdowns or interruptions if their access to specific applications is restricted.
- Increased Complexity: Implementing and managing bandwidth throttling can require technical expertise and ongoing monitoring.
Q: What are some common use cases for bandwidth throttling in SMBs?
A: Bandwidth throttling is valuable for various scenarios in SMBs, including:
- Prioritizing Business-Critical Applications: Ensuring that applications like CRM, ERP, and accounting software receive sufficient bandwidth for smooth operation.
- Managing High-Bandwidth Applications: Limiting the impact of bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming or file sharing on overall network performance.
- Controlling Employee Internet Usage: Restricting access to specific websites or applications to improve productivity and prevent bandwidth abuse.
- Protecting Network Security: Limiting access to potentially harmful websites or applications to enhance network security.
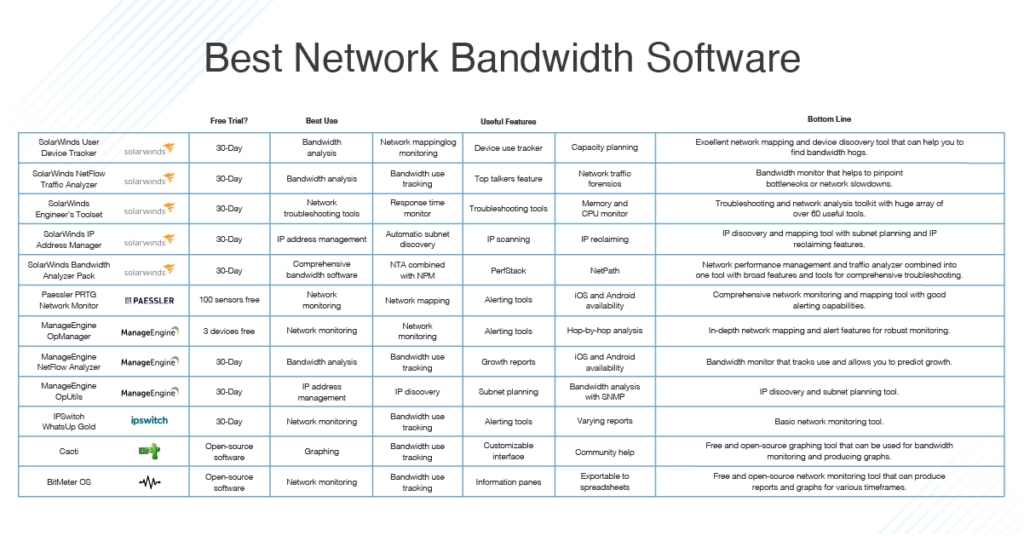
Q: Are there any tools or software that can help with bandwidth throttling?
A: Several tools and software solutions are available to assist SMBs with bandwidth throttling:
- Network Monitoring Software: Tools like SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor and ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer provide comprehensive network insights, including bandwidth usage, and help identify potential bottlenecks.
- Router and Firewall Management Software: Most routers and firewalls offer built-in bandwidth throttling capabilities.
- Third-Party Bandwidth Management Software: Specialized bandwidth management solutions like NetLimiter and Bandwidth Control Pro provide advanced features for controlling network traffic.
Tips for Effective Bandwidth Throttling
- Start with a Baseline: Monitor network traffic patterns and identify typical bandwidth usage before implementing throttling.
- Prioritize Critical Applications: Allocate sufficient bandwidth to applications that are essential for business operations.
- Use a Gradual Approach: Start with moderate throttling settings and adjust them gradually based on network performance and user feedback.
- Monitor and Adjust Regularly: Regularly monitor network performance and adjust throttling settings as needed to optimize bandwidth allocation.
- Communicate with Users: Inform users about bandwidth throttling and its impact on their network experience.
Conclusion
Bandwidth throttling is a powerful tool for optimizing network performance and managing resources effectively in SMBs. By strategically allocating bandwidth, businesses can ensure smooth operations, enhance productivity, and prevent network bottlenecks. However, it’s crucial to implement bandwidth throttling carefully, considering potential drawbacks and adjusting settings based on network needs and user feedback. With careful planning and implementation, bandwidth throttling can be a valuable asset for any SMB seeking to maximize network efficiency and performance.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Managing Network Bandwidth: A Guide to Optimizing SMB Performance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!