Managing Fast Startup in Windows 11 with Intune: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Managing Fast Startup in Windows 11 with Intune: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Managing Fast Startup in Windows 11 with Intune: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Managing Fast Startup in Windows 11 with Intune: A Comprehensive Guide
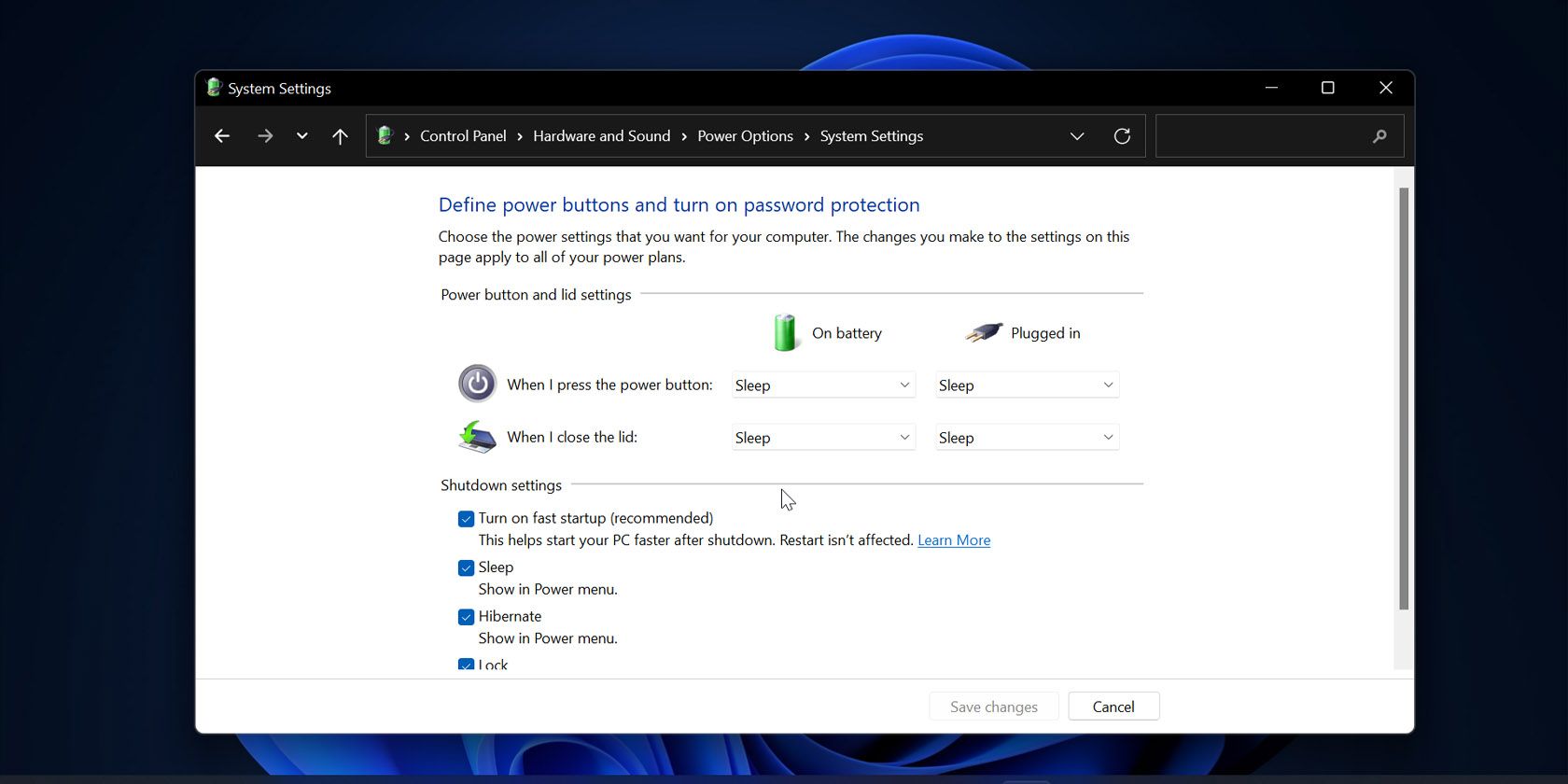
Fast startup, a feature introduced in Windows 8, is designed to accelerate system boot times by utilizing a hybrid shutdown approach. While beneficial for user experience, it can sometimes present challenges for IT administrators in managing and troubleshooting Windows 11 devices. This article delves into the intricacies of disabling fast startup within the Intune framework, examining the reasons behind this decision, the implementation process, and the potential advantages it offers.
Understanding the Mechanics of Fast Startup
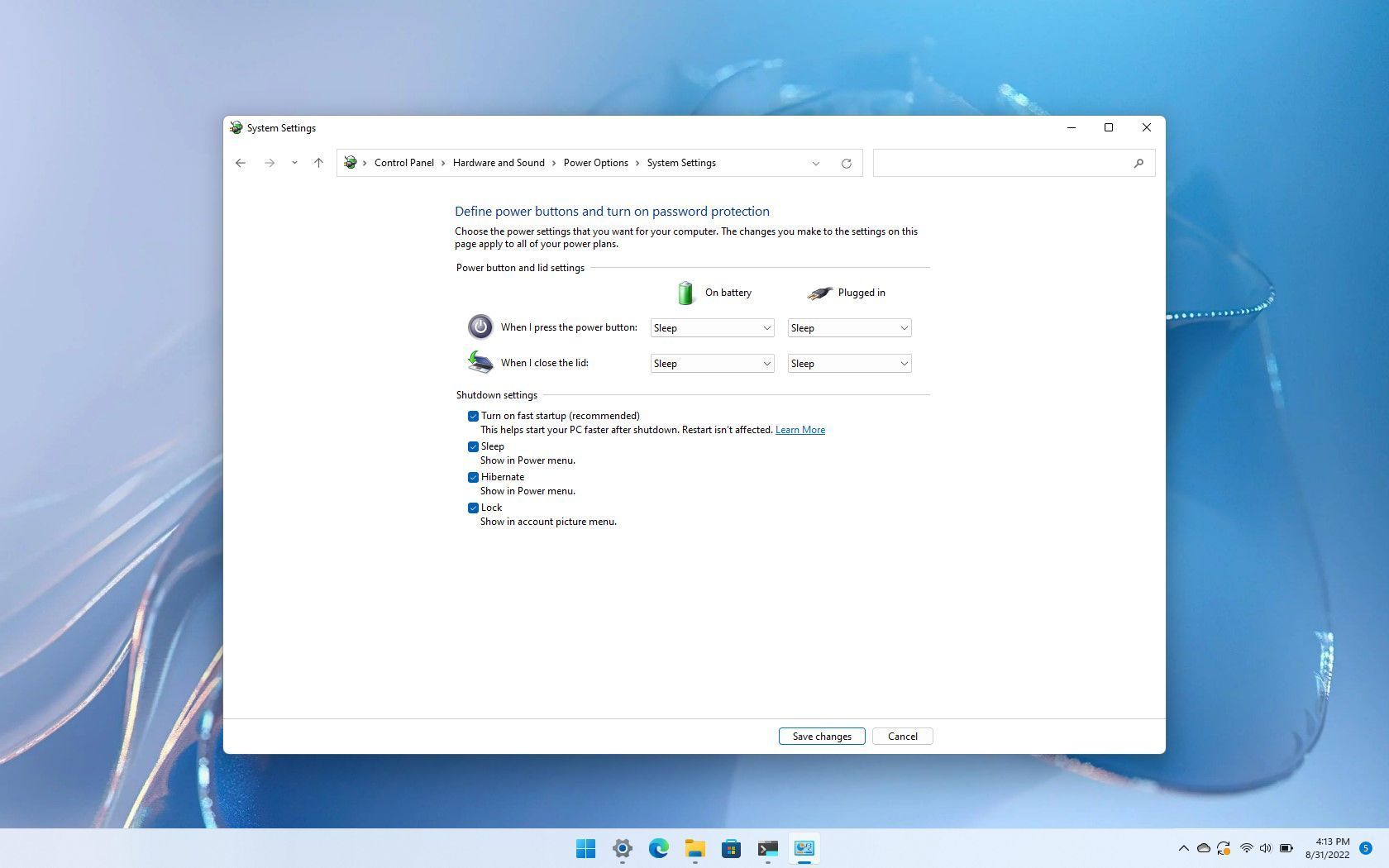
Fast startup achieves its speed boost by combining elements of a traditional shutdown with hibernation. When a system utilizes fast startup, it does not fully shut down. Instead, it saves the current system state to a hibernation file (hiberfil.sys) and then enters a low-power state. Upon reboot, the system loads the saved state from the hibernation file, effectively skipping the lengthy boot process. This results in faster boot times, but it also creates a state of "suspended animation" where the system is not truly shut down.
Why Consider Disabling Fast Startup?
While fast startup generally enhances the user experience, there are specific scenarios where disabling it becomes a strategic decision for IT administrators:
- Troubleshooting and Recovery: Disabling fast startup allows for a clean boot process, crucial for diagnosing and resolving system issues. Without the saved state from hibernation, the system starts from scratch, enabling administrators to identify problematic drivers, services, or applications that might be causing boot failures or performance issues.
- Data Integrity and Security: Fast startup’s reliance on the hibernation file can introduce potential vulnerabilities. In the event of a power outage or system crash, the hibernation file might become corrupted, leading to data loss or boot errors. Disabling fast startup eliminates this risk, ensuring a clean and secure boot process.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Certain industries or regulatory bodies might mandate the complete shutdown of systems for security or compliance reasons. Disabling fast startup ensures that systems are fully powered down, fulfilling these requirements.
- System Optimization: Fast startup can negatively impact system performance in specific situations. For instance, if the hibernation file becomes excessively large, it can consume significant disk space and slow down the system’s overall performance. Disabling fast startup can alleviate this issue.
Disabling Fast Startup in Intune: A Step-by-Step Approach
Intune, Microsoft’s cloud-based mobile device management (MDM) solution, provides a robust framework for managing and configuring Windows 11 devices. Disabling fast startup within Intune is a straightforward process, requiring the creation and deployment of a configuration profile:
- Navigate to Intune: Log in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center and navigate to Devices > Configuration profiles.
- Create a New Profile: Click on Create profile and select Windows 10 and later as the platform. Choose Administrative Templates as the profile type.
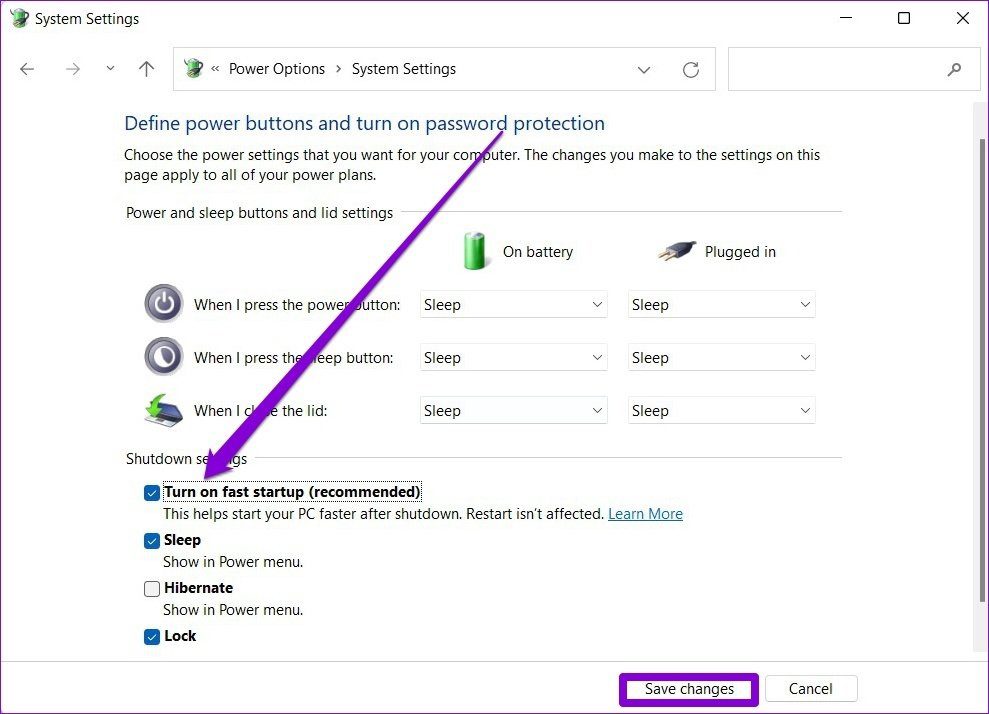
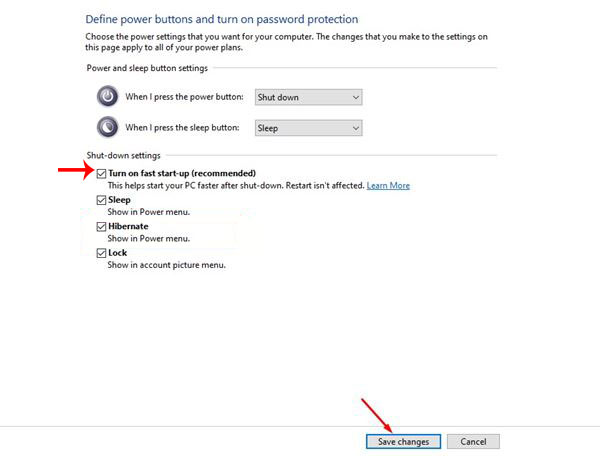
- Select the Setting: Under Administrative Templates, navigate to System > Power Management > Sleep settings. Locate the setting Turn off fast startup.
- Configure the Setting: Set the Turn off fast startup setting to Enabled. This will effectively disable fast startup on the target devices.
- Assign the Profile: Select the appropriate user or device groups to which you want to apply the configuration profile.
- Deploy and Monitor: Save the profile and deploy it to the target devices. Monitor the deployment status and ensure the setting has been successfully applied.
Considerations and Best Practices
While disabling fast startup can offer advantages, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Impact on Boot Times: Disabling fast startup will inevitably increase boot times, as the system will need to go through the full boot process. This might impact user experience, especially for users accustomed to fast startup’s speed.
- Alternative Solutions: Explore alternative approaches to address specific concerns without resorting to disabling fast startup. For instance, consider using a dedicated antivirus solution that can scan the hibernation file for potential threats or implement stricter power management policies to minimize the risk of data loss due to power outages.
- User Communication: Inform users about the change and provide clear explanations for disabling fast startup. This will help manage expectations and ensure a smooth transition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is disabling fast startup necessary for all devices?
A: No. Disabling fast startup is primarily recommended for devices where data integrity, security, or troubleshooting are paramount. For general-purpose devices, fast startup can enhance user experience.
Q: Will disabling fast startup affect other system settings?
A: Disabling fast startup primarily impacts the boot process and does not directly affect other system settings. However, it’s crucial to ensure that other power management settings are appropriately configured to maintain optimal system performance.
Q: Can I disable fast startup for specific user groups or devices?
A: Yes. Intune allows you to target configuration profiles to specific user groups or devices, enabling granular control over the fast startup setting.
Tips for Managing Fast Startup with Intune
- Utilize Group Policies: In addition to Intune, you can leverage group policies to manage fast startup settings on domain-joined devices.
- Monitor Deployment Status: Regularly monitor the deployment status of configuration profiles to ensure they are successfully applied and remain effective.
- Implement System Monitoring: Utilize system monitoring tools to track device performance and identify potential issues related to power management settings.
- Document Configuration Changes: Maintain a detailed record of configuration changes, including the rationale for disabling fast startup, to facilitate troubleshooting and future adjustments.
Conclusion
Disabling fast startup in Windows 11 using Intune can be a strategic decision for IT administrators seeking to enhance system security, simplify troubleshooting, or comply with regulatory requirements. By understanding the rationale behind this choice, implementing the configuration process correctly, and considering best practices, administrators can optimize device management and ensure a secure and reliable computing environment. Remember, the decision to disable fast startup should be based on a careful assessment of specific needs and potential trade-offs, always prioritizing the overall health and security of the managed devices.

![How to Enable or Turn On Fast Startup on Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aO2eIvIHUlU/maxresdefault.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Managing Fast Startup in Windows 11 with Intune: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!