Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Balanced Perspective
Related Articles: Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Balanced Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Balanced Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Balanced Perspective
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Balanced Perspective
- 3.1 Understanding the Mechanics of Fast Startup
- 3.2 The Advantages of Fast Startup
- 3.3 The Potential Drawbacks of Fast Startup
- 3.4 Balancing the Benefits and Drawbacks
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Optimizing Fast Startup
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Balanced Perspective
Windows 11, like its predecessors, offers a feature known as "Fast Startup" designed to expedite the boot process. While its aim is to reduce the time it takes for your computer to become operational, it comes with certain trade-offs that warrant careful consideration. This article delves into the intricacies of Fast Startup, exploring its benefits and drawbacks, and ultimately providing a comprehensive understanding of its impact on your Windows 11 experience.
Understanding the Mechanics of Fast Startup
Fast Startup is not a simple reboot, nor is it a true hibernation mode. It cleverly combines aspects of both. When you enable Fast Startup, Windows 11 does not fully shut down when you click "Shut down." Instead, it enters a hybrid state where:
- The operating system kernel and device drivers remain loaded in memory. This significantly reduces the time needed to restart, as these crucial components are already loaded.
- User applications and open programs are closed. This ensures a clean slate for the next session, preventing lingering issues from previous sessions.
- The system’s state is saved to a special hibernation file. This file acts as a snapshot of the system’s configuration, allowing for a quick restoration of the user environment upon restarting.
This hybrid approach allows Windows 11 to boot up much faster than a traditional shutdown, as the system does not have to go through the entire boot process from scratch. However, this efficiency comes at a cost.
The Advantages of Fast Startup
- Reduced boot time: The most apparent benefit of Fast Startup is its ability to drastically shorten the time it takes to start your computer. This translates to a more responsive and efficient user experience, especially for tasks that require quick access to the system.
- Improved system responsiveness: Since the operating system kernel and drivers are already loaded, applications and programs can launch faster, leading to a smoother and more responsive user experience.
- Enhanced power efficiency: Fast Startup can contribute to improved power efficiency by reducing the time the system spends in a fully powered-on state. This can be particularly beneficial for users who frequently reboot their systems.
The Potential Drawbacks of Fast Startup
While Fast Startup offers several advantages, it is not without its drawbacks:
- Potential for data loss: Because Fast Startup does not fully shut down the system, there is a small risk of data loss in the event of a power outage or system crash. If the system is not properly shut down before a power failure, the hibernation file may become corrupted, leading to data loss.
- Compatibility issues: Certain hardware or software configurations may not be fully compatible with Fast Startup. This can lead to unexpected behavior, such as system instability or application crashes.
- Security concerns: While the risk is generally low, Fast Startup can introduce potential security vulnerabilities. This is because the system’s state is stored in a hibernation file, which could be susceptible to unauthorized access or malware infection.
- Limited troubleshooting options: Fast Startup can complicate troubleshooting efforts, as it prevents a clean system boot. This can make it more difficult to diagnose and resolve system issues.
Balancing the Benefits and Drawbacks
The decision of whether to enable Fast Startup ultimately depends on your individual needs and priorities. Here are some factors to consider:
- System stability: If you experience frequent system crashes or instability, disabling Fast Startup may be a prudent choice. This will ensure a clean boot and allow for more effective troubleshooting.
- Data integrity: If you work with sensitive data or frequently perform tasks that require a high level of data integrity, disabling Fast Startup might be advisable. This will minimize the risk of data loss in the event of a power failure.
- Security concerns: If you are concerned about security vulnerabilities, disabling Fast Startup can reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your system’s state.
- Boot time: If you prioritize a quick boot time and are comfortable with the potential risks, enabling Fast Startup can significantly improve your user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Does Fast Startup affect my battery life?
A: Fast Startup can potentially improve battery life by reducing the time the system spends in a fully powered-on state. However, the impact on battery life is generally minimal and may vary depending on individual usage patterns and hardware specifications.
Q: How do I enable or disable Fast Startup in Windows 11?
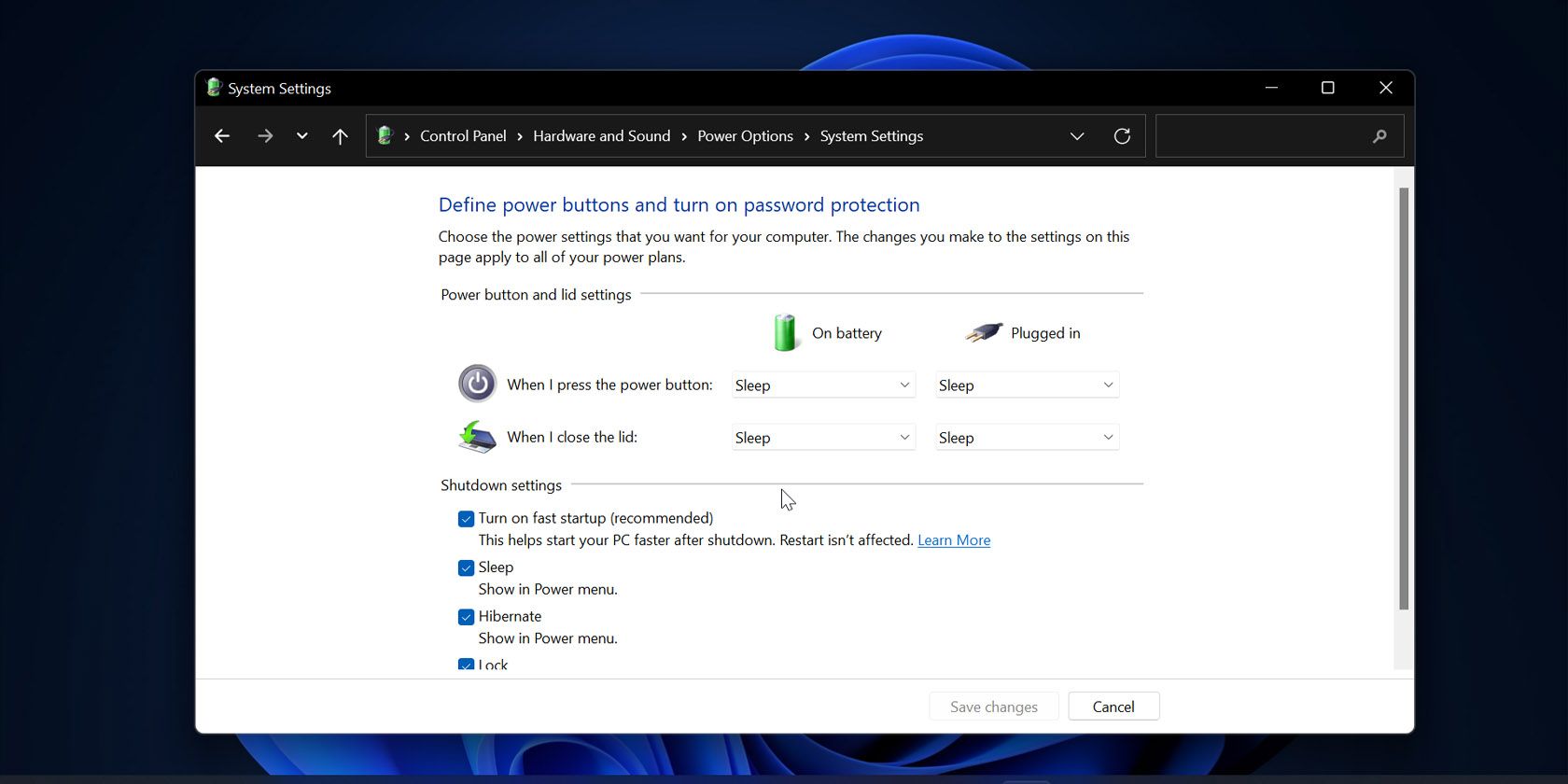
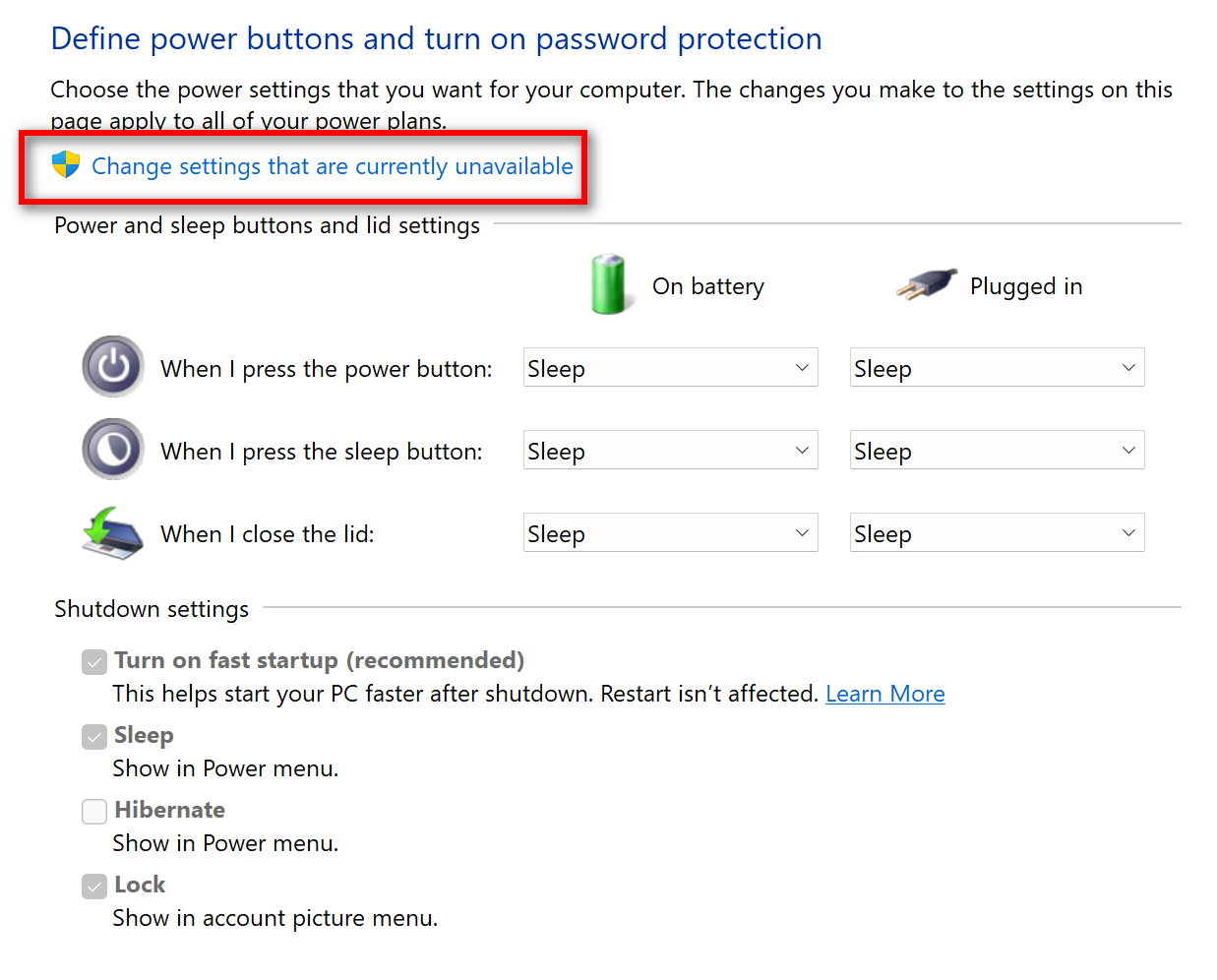
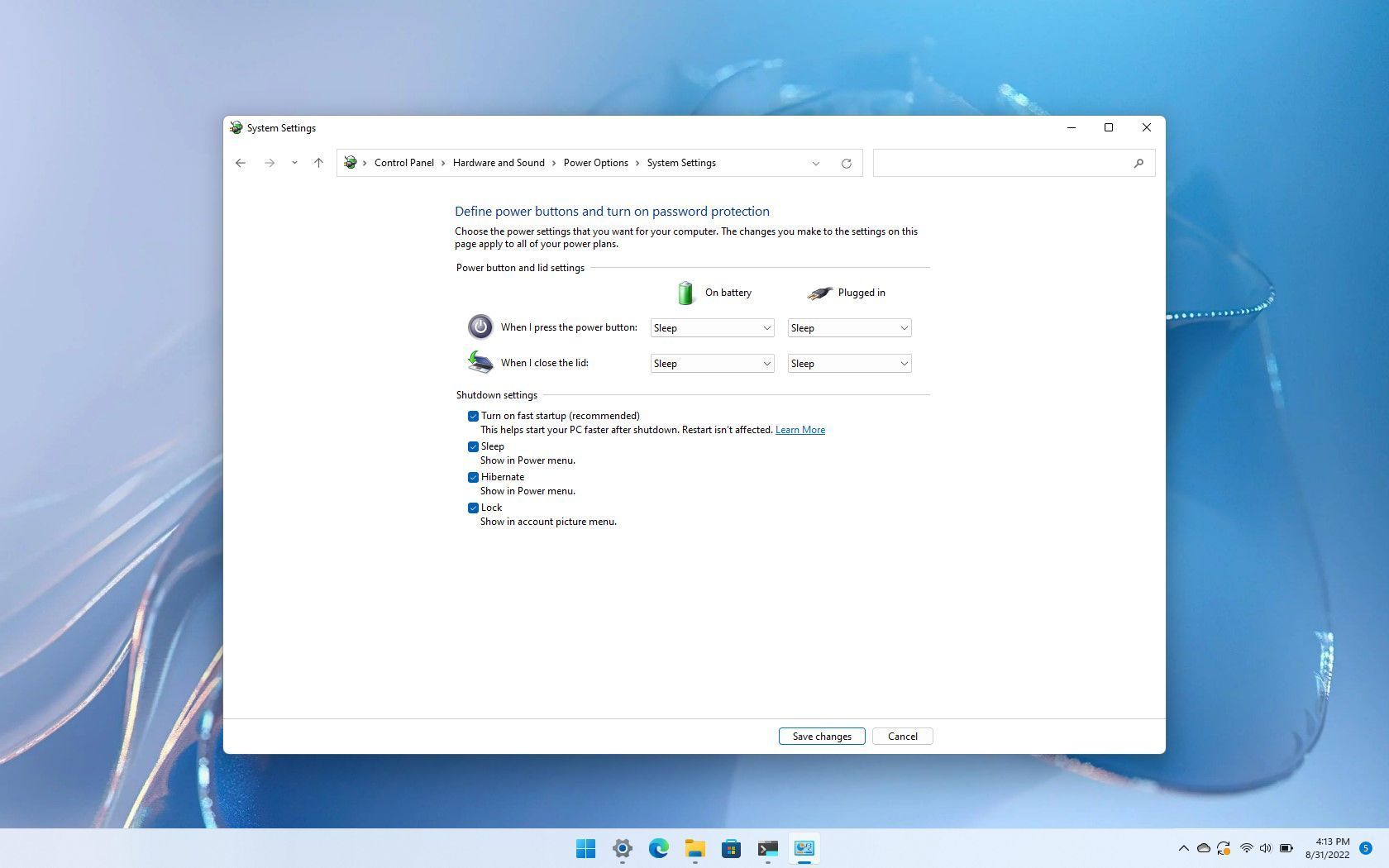
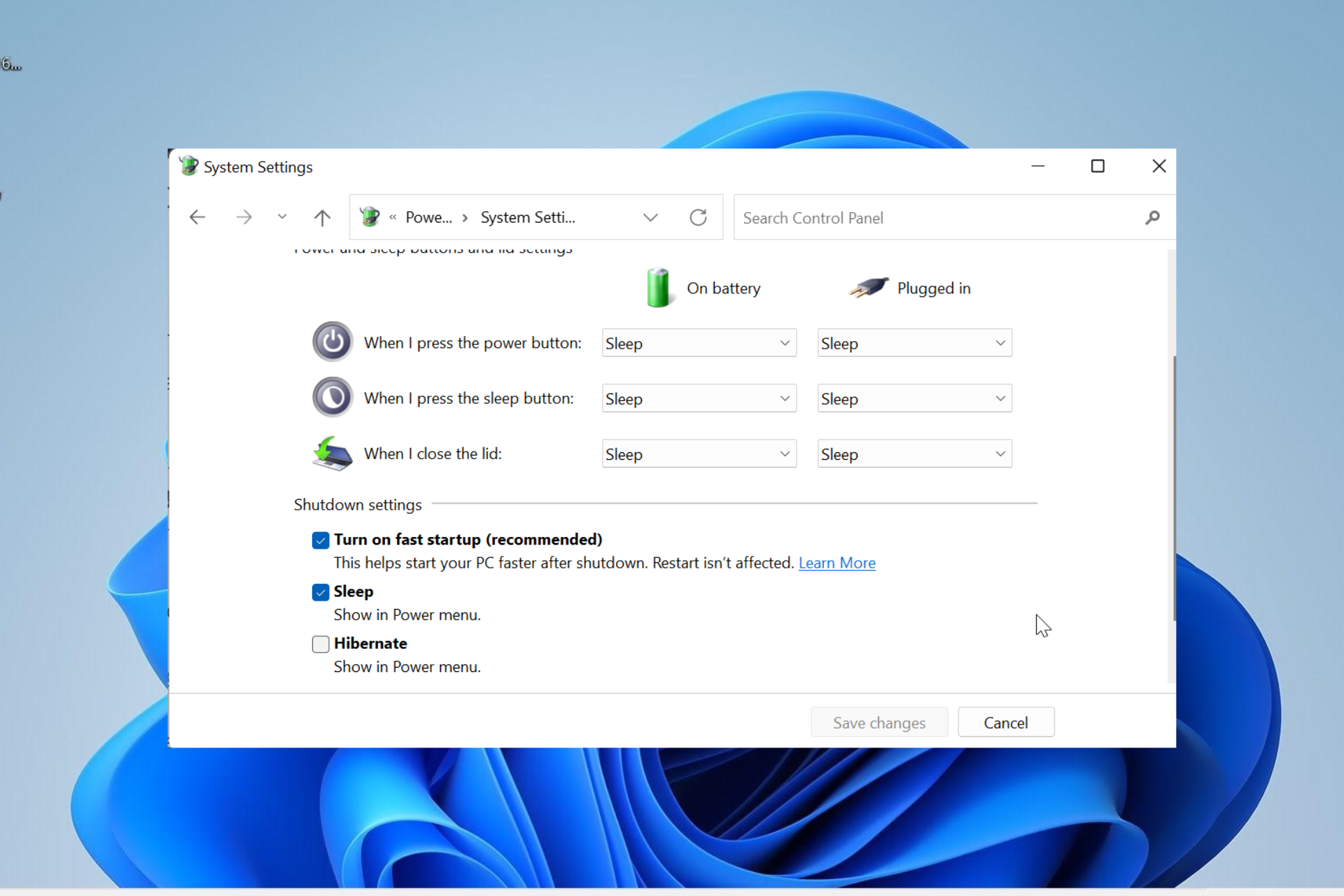
A: To enable or disable Fast Startup in Windows 11, follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel.
- Navigate to Hardware and Sound > Power Options.
- On the left-hand side, click Choose what the power buttons do.
- Click Change settings that are currently unavailable.
- Check or uncheck the box next to Turn on fast startup (recommended).
- Click Save changes.
Q: Can I use Fast Startup with a dual-boot system?
A: Fast Startup is generally compatible with dual-boot systems. However, it is important to ensure that the operating system you are booting into supports Fast Startup.
Q: Can I use Fast Startup with a virtual machine?
A: Fast Startup is not typically recommended for use with virtual machines. This is because virtual machines often require a clean boot to function properly.
Tips for Optimizing Fast Startup
- Keep your system clean: Regularly remove unnecessary files and programs to ensure optimal system performance and minimize the size of the hibernation file.
- Update your drivers: Ensure that your system drivers are up-to-date to improve compatibility with Fast Startup.
- Disable unnecessary startup programs: Limit the number of programs that start automatically when you boot your computer to reduce the time it takes for the system to become fully operational.
- Consider using a solid-state drive (SSD): SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), which can further enhance the benefits of Fast Startup.
Conclusion
Fast Startup in Windows 11 is a valuable feature that can significantly improve your system’s boot time and responsiveness. However, it is crucial to be aware of the potential drawbacks, including data loss risks, compatibility issues, and security vulnerabilities. By carefully considering your individual needs and priorities, you can make an informed decision about whether to enable or disable Fast Startup, ultimately optimizing your Windows 11 experience. Remember, the key is to strike a balance between speed and security, ensuring that your system operates reliably and efficiently while protecting your data.


![How to Enable or Turn On Fast Startup on Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aO2eIvIHUlU/maxresdefault.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Balanced Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!