Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Virtualization and its Benefits
- 3.2 Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10
- 3.3 Common Questions and Concerns
- 3.4 Tips for Effective Virtualization
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide

Virtualization, the process of running a virtual operating system (OS) within a host operating system, has become an indispensable tool for a wide range of users. Whether you’re a developer testing software, a system administrator managing multiple environments, or a casual user experimenting with different operating systems, virtualization offers numerous advantages. Windows 10, with its built-in support for virtualization, provides a robust platform for this technology. This guide delves into the process of enabling virtualization on Windows 10, explaining its importance, outlining the necessary steps, and addressing common questions.
Understanding Virtualization and its Benefits
Virtualization allows users to create virtual machines (VMs) – essentially, self-contained computers within their existing operating system. These VMs can run different operating systems, including older versions of Windows, Linux distributions, or even specialized server operating systems. This capability unlocks a multitude of benefits:
- Testing and Development: Virtualization provides a safe and isolated environment for software development and testing. Developers can experiment with different operating systems, software versions, and configurations without affecting their primary system.
- Application Isolation: Running applications within VMs prevents conflicts and ensures that they do not interfere with other programs on the host system. This is particularly useful for applications that require specific configurations or older versions of software.
- Multitasking and Resource Management: Virtualization allows users to run multiple operating systems and applications simultaneously, maximizing the utilization of system resources. This is especially beneficial for users who need to work with multiple applications or environments.
- Legacy Software Compatibility: Virtualization enables users to run older software applications that are no longer compatible with newer operating systems. This preserves access to critical software and prevents the need to upgrade or replace existing systems.
- Cost Savings: Virtualization can reduce the need for physical hardware, as multiple VMs can run on a single physical machine. This translates to lower energy consumption, reduced maintenance costs, and simplified management.
Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10
To enable virtualization on Windows 10, you need to ensure that your system meets the following prerequisites:
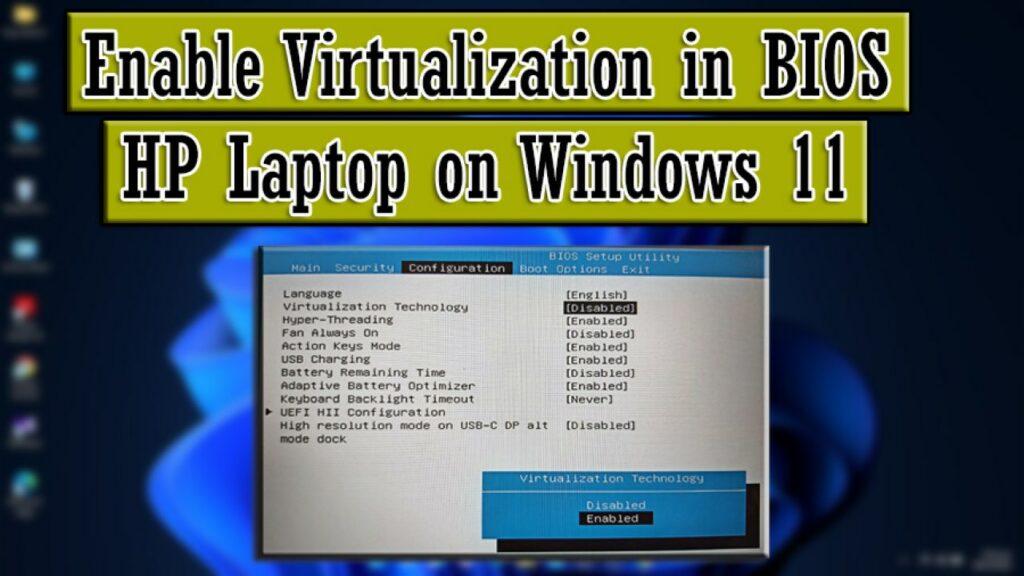
- Processor Support: Your processor must support virtualization technology, such as Intel VT-x or AMD-V. This feature is typically enabled by default, but you can verify it through your BIOS settings.
- BIOS Settings: Access your BIOS settings by restarting your computer and pressing the appropriate key (usually F2, F10, or Del) during the boot process. Navigate to the "Advanced" or "Security" section and look for options related to virtualization, such as "Virtualization Technology," "Intel VT-x," or "AMD-V." Ensure these options are enabled.
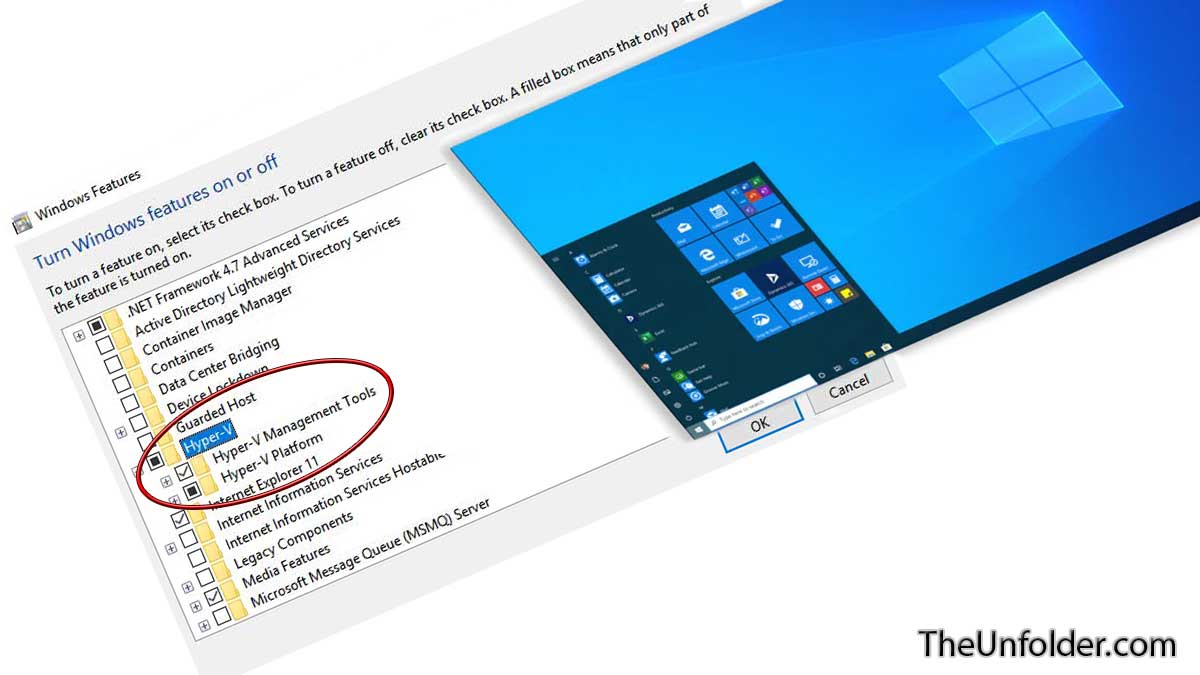
- Windows Features: Windows 10 includes a built-in feature called "Hyper-V," which provides the necessary tools for running VMs. You need to enable this feature through the Control Panel.
Steps to Enable Hyper-V:
- Open Control Panel: Press the Windows key + X and select "Control Panel."
- Navigate to Programs: Click on "Programs" and then select "Turn Windows features on or off."
- Enable Hyper-V: In the list of features, check the box next to "Hyper-V."
- Restart: Click "OK" and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Once Hyper-V is enabled, you can install and configure virtual machines using tools like Hyper-V Manager or third-party virtualization software like VMware Workstation or Oracle VirtualBox.
Common Questions and Concerns
1. Will enabling virtualization affect my system performance?
Enabling virtualization does consume a small amount of system resources, but its impact on performance is usually minimal, especially on modern systems with sufficient RAM and processing power. However, if you experience significant performance degradation, you can adjust the VM settings to reduce resource allocation.
2. What are the security implications of virtualization?
Virtualization, like any technology, comes with its own set of security considerations. It’s crucial to use strong passwords, keep your operating systems and virtualization software updated, and avoid downloading software from untrusted sources.
3. Can I use other virtualization software alongside Hyper-V?
Windows 10 only allows one virtualization platform to be active at a time. If you want to use another virtualization software, such as VMware Workstation or Oracle VirtualBox, you need to disable Hyper-V first.
4. What are the best practices for using virtualization?
- Allocate sufficient RAM and CPU resources to your VMs.
- Regularly back up your VM data.
- Use strong passwords and enable security features.
- Keep your operating systems and virtualization software updated.
Tips for Effective Virtualization
- Optimize VM settings: Adjust the CPU cores, RAM allocation, and hard drive size to match the specific needs of your VMs.
- Use snapshots: Create regular snapshots of your VMs to preserve their state and allow you to revert to previous versions if necessary.
- Utilize shared folders: Share folders between your host system and VMs to easily transfer files and access resources.
- Explore advanced features: Hyper-V and other virtualization software offer a range of advanced features, such as network bridging, live migration, and resource management tools.
Conclusion
Enabling virtualization on Windows 10 empowers users with a powerful tool for testing, development, application isolation, and legacy software compatibility. Understanding the process, addressing common questions, and implementing best practices will ensure a smooth and secure virtualization experience. By leveraging this technology, users can unlock new possibilities and optimize their computing environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Enabling Virtualization on Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!