Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators
Related Articles: Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators
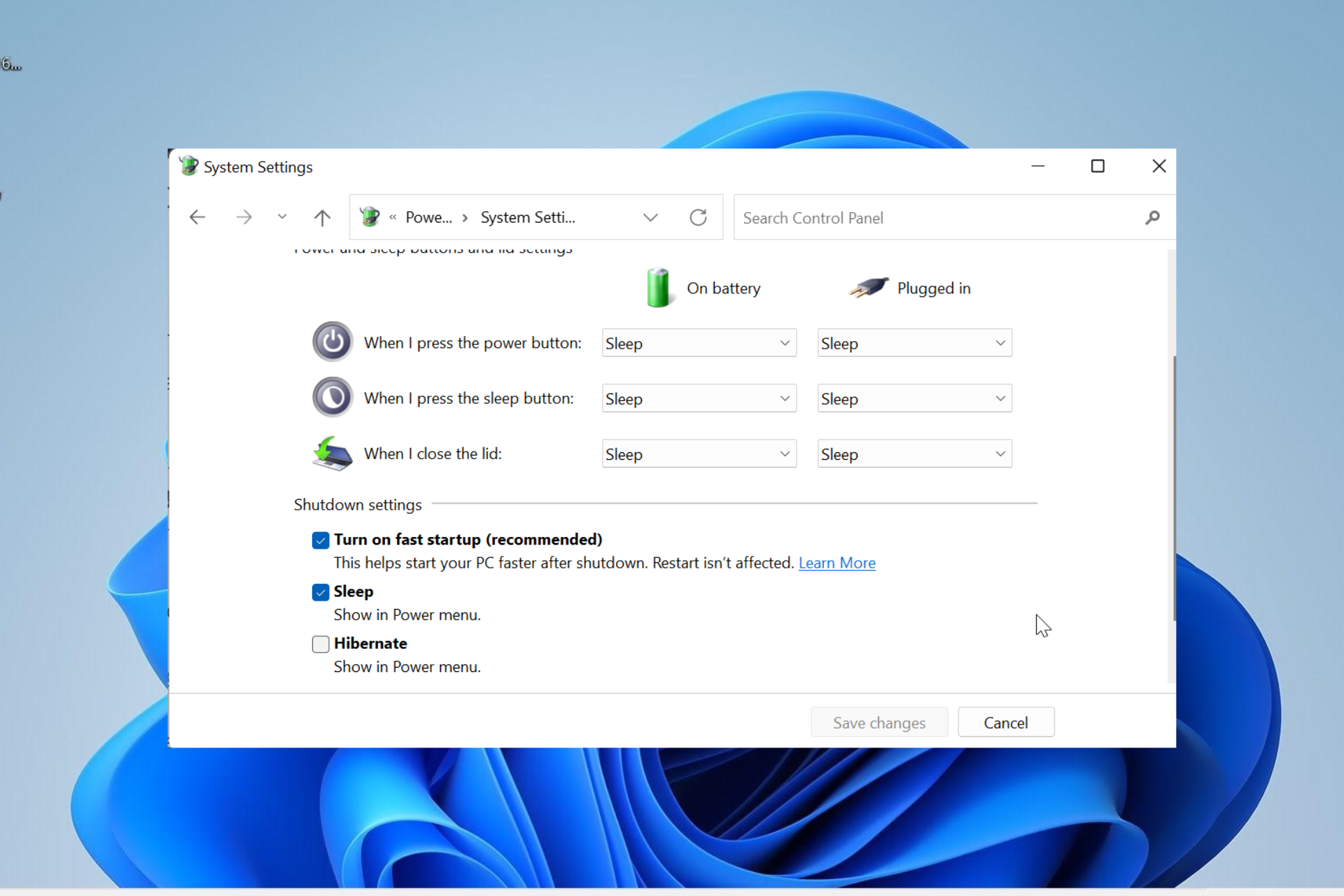
Windows 11’s "Fast Startup" feature, while designed to expedite system boot times, can sometimes present challenges for administrators. This feature, which combines a hybrid shutdown with hibernation, can lead to complications during system maintenance, troubleshooting, or specific software deployments. This article delves into the intricacies of disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11 through Group Policy Objects (GPOs), providing a comprehensive understanding of its implications and practical guidance for administrators.
Understanding Fast Startup
Fast Startup, introduced in Windows 8, aims to significantly reduce boot times by leveraging a combination of hibernation and shutdown. When a user chooses to "shutdown" their system, Windows 11 doesn’t fully shut down but rather enters a state where the kernel and device drivers remain loaded in memory. Upon restarting, the system can quickly resume operation by loading these elements from memory, bypassing the traditional boot process.
The Need for Disabling Fast Startup
While Fast Startup generally provides a faster boot experience, certain situations necessitate its disabling. These include:
- System Maintenance: When performing system updates, installing new drivers, or running disk maintenance tools, Fast Startup can interfere with these processes. The loaded kernel and drivers might not reflect the updated state, potentially causing conflicts or errors.
- Troubleshooting: During troubleshooting, disabling Fast Startup ensures a clean boot, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis of system issues. It eliminates the potential interference from partially loaded components.
- Software Deployment: Some software applications, particularly those requiring specific system states or configurations, might not function correctly with Fast Startup enabled. Disabling it ensures a consistent and predictable environment for these applications.
- Security Concerns: In certain scenarios, where security is paramount, disabling Fast Startup can provide an additional layer of protection. This is because it prevents the system from loading potentially vulnerable drivers and components during the boot process.
Disabling Fast Startup with Group Policy Objects (GPOs)
Group Policy Objects (GPOs) provide a powerful mechanism for managing and configuring settings across multiple computers within a domain. Disabling Fast Startup through GPOs offers several advantages:
- Centralized Control: Administrators can manage Fast Startup settings for an entire domain from a single location, eliminating the need to manually configure each computer individually.
- Consistency: GPOs ensure uniform settings across all managed computers, preventing inconsistencies that might arise from individual user configurations.
- Security: GPOs can enforce policies, preventing users from accidentally enabling Fast Startup, ensuring a secure and consistent system environment.
Steps to Disable Fast Startup using GPOs:
- Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC): Navigate to the "Start" menu, search for "gpmc.msc," and press Enter.
- Create or Edit a GPO: Create a new GPO or locate an existing one that applies to the desired computers. Right-click on the GPO and select "Edit."
- Navigate to the Relevant Policy: In the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to the following path: "Computer Configuration" -> "Administrative Templates" -> "System" -> "Shutdown"
- Locate the "Turn off fast startup" Policy: Double-click on the "Turn off fast startup" policy.
- Enable the Policy: Select the "Enabled" option and click "OK."
Additional Considerations:
- Restart Required: After applying the GPO, a restart of the affected computers is required for the changes to take effect.
- Deployment Strategies: Consider the deployment strategy for the GPO, ensuring it targets the appropriate computer groups.
- Monitoring and Verification: Monitor the impact of the policy change and verify that Fast Startup is indeed disabled on the targeted computers.
FAQs Regarding Disabling Fast Startup
Q: Will disabling Fast Startup significantly impact boot times?
A: Yes, disabling Fast Startup will likely result in slightly longer boot times compared to when it is enabled. However, the difference is generally minimal and may not be noticeable for most users.
Q: Can I disable Fast Startup for specific user accounts?
A: GPOs primarily target computer configurations, not individual user accounts. To disable Fast Startup for specific user accounts, you would need to use Local Group Policy Editor or registry modifications on the individual computers.
Q: Is disabling Fast Startup necessary for all computers?
A: Disabling Fast Startup is not always necessary. It is primarily recommended for situations where system maintenance, troubleshooting, or specific software deployments require a clean boot environment.
Q: What are the potential drawbacks of disabling Fast Startup?
A: Disabling Fast Startup might lead to slightly longer boot times, but it is generally a minor inconvenience compared to the benefits it provides in certain scenarios.
Tips for Managing Fast Startup
- Documenting the Policy: Maintain a clear record of the GPO configuration, including the targeted computers and the reasons for disabling Fast Startup.
- Testing and Evaluation: Thoroughly test the impact of disabling Fast Startup on the targeted systems before deploying the policy to a larger group.
- User Communication: Inform users about the changes to Fast Startup settings, explaining the reasons behind the policy and any potential impact on boot times.
Conclusion
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11 through Group Policy Objects offers administrators a powerful tool for managing system settings and ensuring a consistent and predictable environment. While Fast Startup generally enhances boot times, there are specific scenarios where disabling it becomes crucial for system maintenance, troubleshooting, or software deployments. By carefully considering the potential benefits and drawbacks, administrators can leverage GPOs to effectively manage Fast Startup settings and optimize the system environment for their specific needs.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide for Administrators. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!