Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
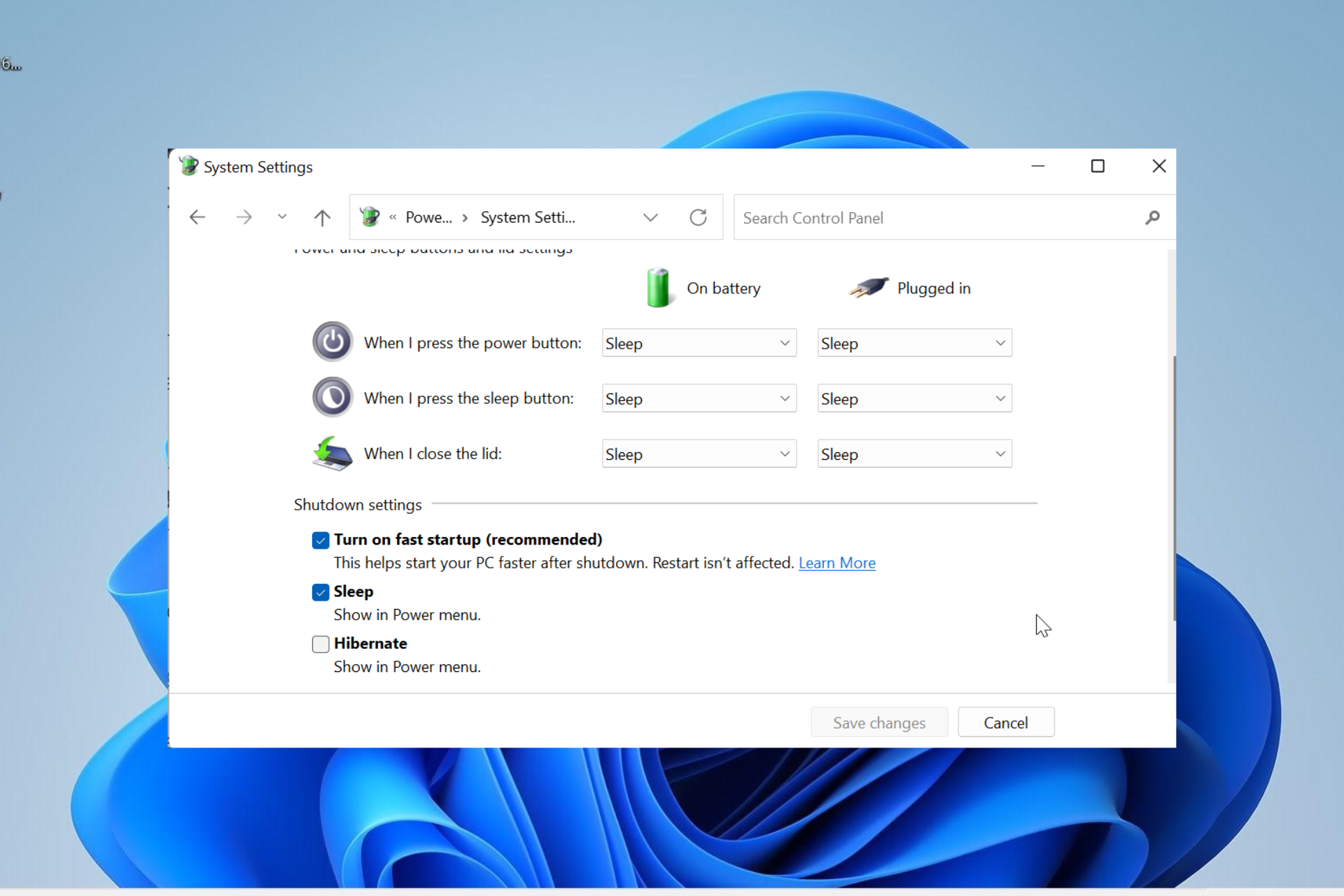
Fast startup, a feature introduced in Windows 8, is designed to expedite the boot process by leveraging a hybrid shutdown mechanism. This approach combines elements of a traditional shutdown with hibernation, enabling Windows to resume faster upon restart. While generally beneficial, fast startup can sometimes interfere with certain tasks, such as troubleshooting or accessing specific files during startup. Disabling fast startup provides greater control over the boot process, allowing users to access a more traditional shutdown experience.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on disabling fast startup in Windows 11 using the Command Prompt (CMD). It will cover the steps involved, explain the underlying mechanisms, and delve into potential benefits and considerations associated with this action.
Understanding Fast Startup
Fast startup works by creating a "hibernation file" containing the system’s current state when the computer is shut down. This file stores the kernel, drivers, and user session data, allowing Windows to skip the lengthy boot process by loading this data directly into memory upon restart. While this speeds up the boot process, it also means that certain files and processes remain loaded in memory, even after a shutdown. This can sometimes lead to issues:
- Troubleshooting: Fast startup can hinder troubleshooting efforts, as certain system files and processes are not fully unloaded during a shutdown. This can make it difficult to diagnose and resolve issues related to specific components or applications.
- Accessing Files: Disabling fast startup allows for full access to all files and folders during startup. This can be crucial when dealing with specific tasks or accessing data that might be unavailable in the hibernation file.
- System Integrity: Disabling fast startup ensures a clean shutdown, ensuring that all processes are terminated properly and system files are saved in their latest state. This can contribute to overall system integrity and stability.
Disabling Fast Startup Using Command Prompt (CMD)
Disabling fast startup in Windows 11 using CMD involves modifying the power settings through the command line interface. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator: Press the Windows key, type "cmd", right-click on the "Command Prompt" option, and select "Run as administrator".
- Execute the Command: Type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /h offThis command disables the hibernation file creation, effectively disabling the fast startup feature.
- Verify the Change: To confirm that fast startup is disabled, you can use the following command:
powercfg /aThis will display a list of power settings. Look for the "Fast Startup" option, which should now be set to "Disabled".
Important Considerations:
- System Performance: Disabling fast startup might slightly increase the boot time. However, this difference is generally minimal and should not be a significant concern for most users.
- Windows Updates: Windows updates may sometimes re-enable fast startup. It’s recommended to check the power settings after each update to ensure it remains disabled.
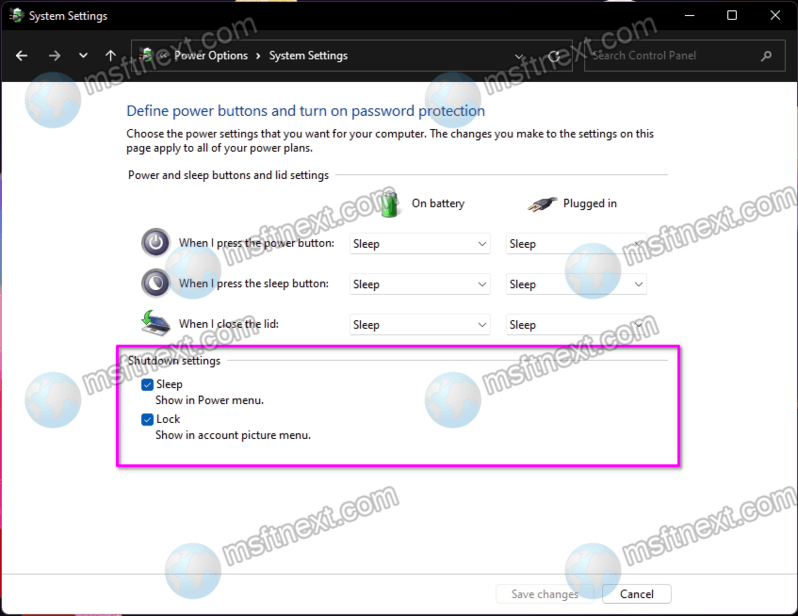
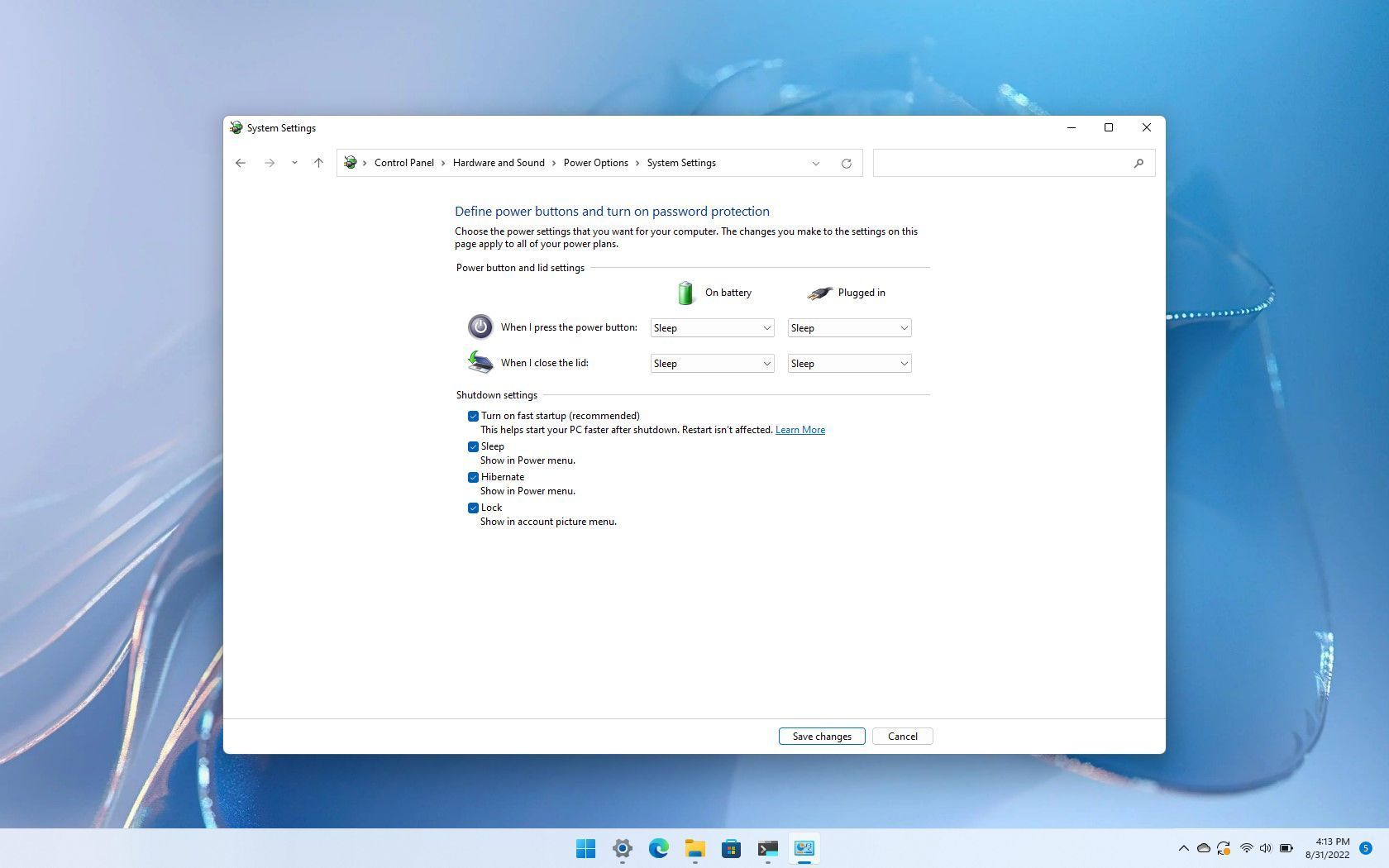
- Alternative Methods: Disabling fast startup can also be accomplished through the Windows Settings interface. Navigate to "System" > "Power & Sleep" > "Additional power settings" > "Choose what the power buttons do" > "Change settings that are currently unavailable". Uncheck the "Turn on fast startup" option.
FAQs: Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11
Q: Is disabling fast startup necessary for all users?
A: Disabling fast startup is not essential for all users. If you experience no issues with the boot process or troubleshooting, keeping fast startup enabled is generally recommended for its speed benefits. However, if you encounter specific problems or need full access to files during startup, disabling it can be beneficial.
Q: Can I re-enable fast startup after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable fast startup by using the following command:
powercfg /h onAlternatively, you can re-enable it through the Windows Settings interface as described above.
Q: What are the potential downsides of disabling fast startup?
A: The primary downside is a slightly longer boot time. However, this difference is often minimal and should not significantly impact most users.
Tips: Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11
- Backup Your System: Before making any changes to your power settings, it’s always advisable to create a system backup to ensure data recovery in case of unexpected issues.
- Check for Updates: Ensure your Windows 11 system is up-to-date with the latest updates, as older versions might have compatibility issues or require additional steps to disable fast startup.
- Monitor System Performance: After disabling fast startup, monitor your system’s performance, including boot time and general responsiveness, to ensure no significant degradation.
Conclusion:
Disabling fast startup in Windows 11 can be a valuable tool for users who require full access to files and processes during startup or experience specific issues related to the boot process. While this action might slightly increase the boot time, it offers greater control over the shutdown and startup processes, potentially improving troubleshooting capabilities and system integrity. Users should carefully consider their individual needs and circumstances before deciding whether to disable fast startup.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!