Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
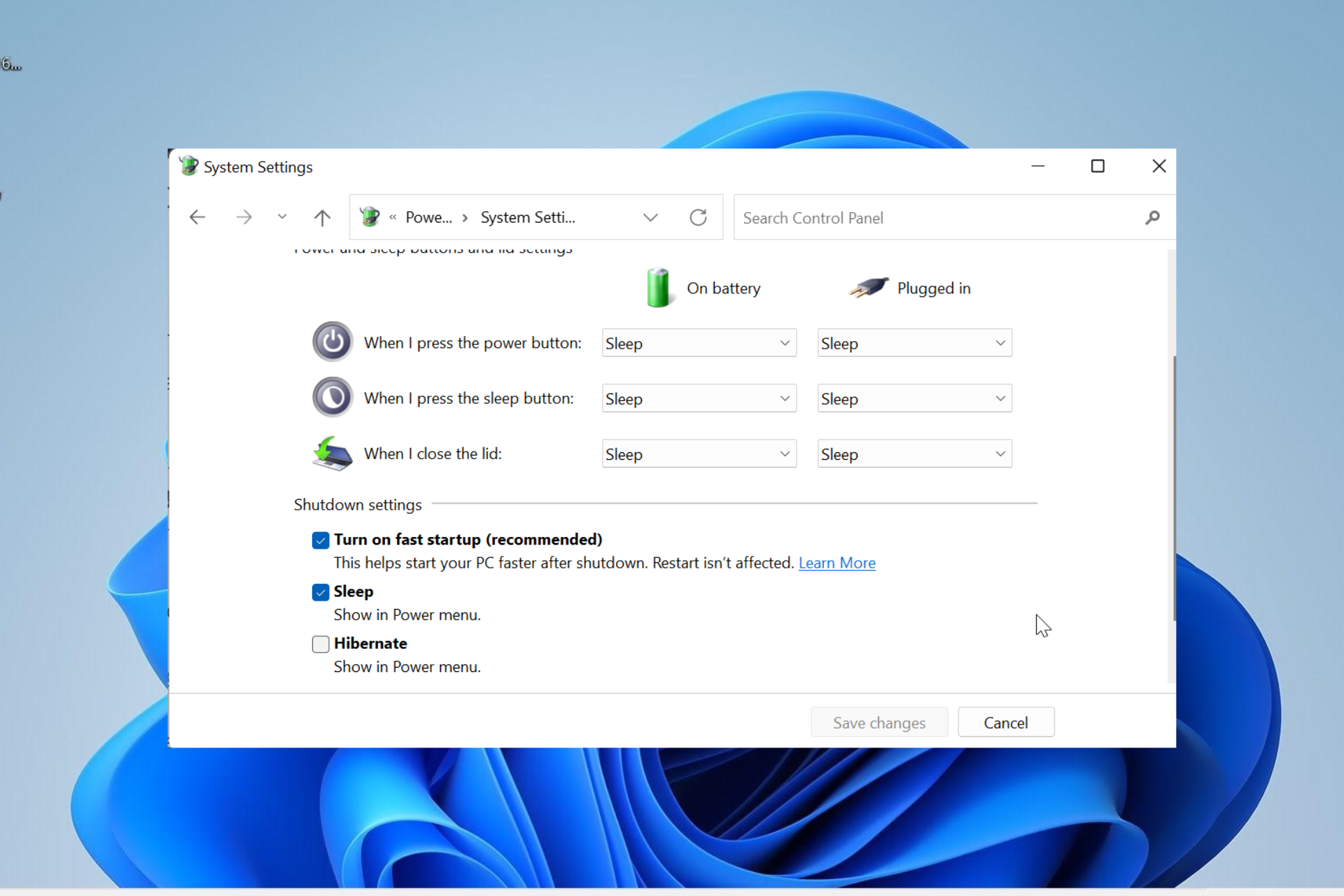
Windows 11’s Fast Startup feature aims to expedite system boot times, offering a quicker return to the desktop. However, this optimization comes with certain trade-offs, potentially impacting system stability, data integrity, and troubleshooting capabilities. This article delves into the intricacies of Fast Startup, outlining the circumstances where disabling it proves beneficial, and providing a comprehensive guide to achieving this through PowerShell.
Understanding Fast Startup: A Hybrid Approach
Fast Startup, also known as "Hybrid Shutdown," blends traditional hibernation and cold shutdown functionalities. Upon initiating a shutdown, the system does not fully power down. Instead, it saves the current user session state, including open applications and system settings, to a hibernation file, known as "hiberfil.sys." This file is stored on the system’s hard drive. When the system is restarted, it loads the saved state from this file, effectively bypassing the traditional boot sequence and significantly reducing startup time.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Fast Startup
While Fast Startup offers a noticeable improvement in boot speed, it introduces certain drawbacks:
- Potential Data Loss: As the system does not fully shut down, the saved session state might be incomplete or corrupted, leading to data loss in certain scenarios. This is particularly relevant when dealing with unsaved files, open programs, or ongoing system operations.
- Troubleshooting Limitations: Fast Startup can hinder troubleshooting efforts, as the system does not undergo a complete shutdown, potentially masking issues related to boot processes, drivers, or system configuration.
- Increased System Complexity: The hibernation file can occupy significant disk space, potentially impacting system performance and storage availability.
Circumstances Warranting Fast Startup Disablement
Disabling Fast Startup is advisable in specific scenarios:
- Data Integrity Concerns: Users handling critical data or requiring absolute data integrity should consider disabling Fast Startup to minimize the risk of data loss during system restarts.
- Troubleshooting Complex Issues: When encountering persistent system errors or difficulties during the boot process, disabling Fast Startup allows for a thorough system shutdown and restart, potentially revealing the root cause of the issue.
- Limited Storage Space: Users with limited storage capacity may find that the hibernation file consumes excessive disk space, impacting overall system performance. Disabling Fast Startup eliminates this file, freeing up valuable storage space.
Disabling Fast Startup Through PowerShell
PowerShell provides a robust and efficient method for managing system settings, including disabling Fast Startup. This approach offers granular control and allows for scripting and automation.
Steps to Disable Fast Startup:
-
Open PowerShell: Navigate to the Windows Search bar, type "PowerShell," and select "Windows PowerShell" from the search results.
-
Run as Administrator: Right-click on the PowerShell icon and select "Run as administrator." This ensures necessary permissions to modify system settings.
-
Execute the Command: In the PowerShell window, execute the following command:
powercfg /h off -
Confirm the Change: The command will execute silently. To verify the change, run the following command:
powercfg /hThis command will display the current Fast Startup status. If the output states "Hybrid Sleep is disabled," Fast Startup has been successfully disabled.
Important Notes:
- Rebooting the System: After disabling Fast Startup, it is recommended to reboot the system for the changes to take effect fully.
-
Enabling Fast Startup: To re-enable Fast Startup, simply replace "off" with "on" in the initial PowerShell command:
powercfg /h on
FAQs
Q1: What is the impact of disabling Fast Startup on boot times?
A: Disabling Fast Startup will result in slightly longer boot times compared to the Fast Startup enabled state. However, the difference is typically minimal and should not significantly impact the user experience.
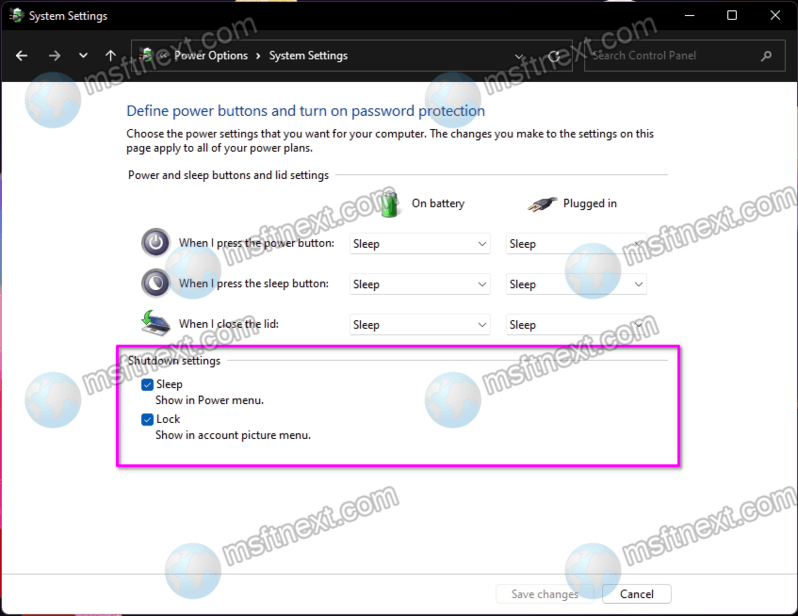
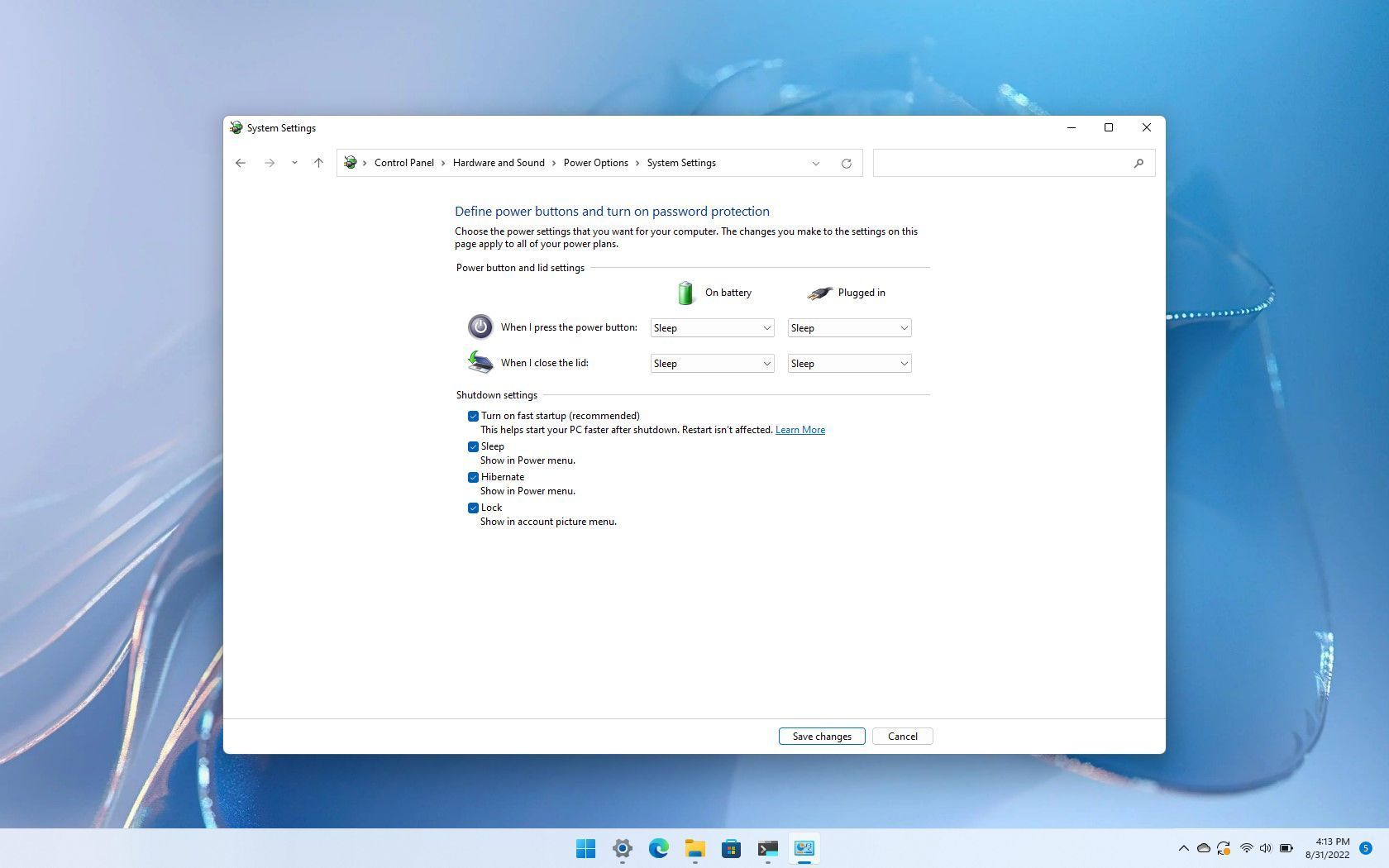
Q2: Can I disable Fast Startup through the Control Panel?
A: While the Control Panel offers an option to disable "Hibernate," this does not directly disable Fast Startup. The PowerShell approach is the most reliable method to achieve this.
Q3: Does disabling Fast Startup affect the performance of my system?
A: Disabling Fast Startup generally has a negligible impact on system performance. The primary performance impact comes from the hibernation file, which is no longer created when Fast Startup is disabled.
Q4: Will disabling Fast Startup affect the use of hibernation?
A: Disabling Fast Startup also disables hibernation. However, you can re-enable hibernation separately using the following command:
powercfg /hibernate onTips
- Monitor System Performance: After disabling Fast Startup, closely monitor system performance and boot times to assess any changes.
- Consider System Configuration: For systems with limited storage space, disabling Fast Startup can be beneficial to free up disk space.
- Explore Alternative Optimization Options: If boot times remain a concern, explore other system optimization options, such as disabling unnecessary startup programs or upgrading system hardware.
Conclusion
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11 is a decision that requires careful consideration, weighing the potential benefits against the potential drawbacks. While it may increase boot times slightly, it offers advantages in terms of data integrity, troubleshooting capabilities, and system stability. By utilizing the PowerShell approach, users can effectively manage Fast Startup settings, ensuring optimal system performance and data security.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!