Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows 11, like its predecessor, features a "Fast Startup" mode that aims to expedite system boot times. While effective in reducing boot durations, this feature can sometimes lead to unexpected behavior, particularly for users who rely on specific functionalities or troubleshoot system issues. Disabling Fast Startup provides a solution for such scenarios, enabling a more traditional boot process with potential benefits for system stability, troubleshooting, and specific software functionalities.
Understanding Fast Startup
Fast Startup is a hybrid shutdown mode that combines elements of a traditional shutdown with a hibernation state. Upon shutdown, the operating system saves the current system state to a hibernation file, known as "hiberfil.sys". When the system restarts, Windows loads this file, effectively resuming from the saved state, thus skipping the full boot process.
Why Consider Disabling Fast Startup
While Fast Startup generally enhances the boot experience, it can lead to complications in certain situations. Some common reasons for disabling Fast Startup include:
- Troubleshooting Issues: When encountering system errors or difficulties, disabling Fast Startup allows for a cleaner boot process, potentially aiding in identifying and resolving the root cause.
- Compatibility with Specific Software: Certain software applications, particularly older programs, might not function correctly with Fast Startup enabled. This can manifest as unexpected behavior or errors.
- Enhanced System Stability: Disabling Fast Startup can improve system stability, especially for users experiencing frequent crashes or blue screen errors.
- Security Concerns: Some security experts argue that Fast Startup, due to its reliance on a hibernation file, might present a potential vulnerability if the file is compromised.
- Data Integrity: While rare, there are instances where data integrity might be compromised during the Fast Startup process, leading to data loss or corruption.
Disabling Fast Startup using Command Prompt (CMD)
The Command Prompt (CMD) offers a straightforward method to disable Fast Startup in Windows 11. This approach provides a more granular control over system settings, making it ideal for advanced users.
Steps to Disable Fast Startup using CMD:
-
Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Press the "Windows" key + "X" to open the Quick Access menu.
- Select "Command Prompt (Admin)" from the list.
-
Execute the Command:
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /h off
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
-
Verify the Change:
- To confirm the change, type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg /h - The output will display the current hibernation settings, confirming that Fast Startup is now disabled.
- To confirm the change, type the following command and press Enter:
Disabling Fast Startup using Settings
For users seeking a more visual approach, the Windows 11 Settings app provides an alternative method to disable Fast Startup.
Steps to Disable Fast Startup using Settings:
-
Open Settings:
- Press the "Windows" key + "I" to open the Settings app.
-
Navigate to System:
- Select "System" from the left-hand pane.
-
Choose Power & Battery:
- Click on "Power & Battery" from the right-hand pane.
-
Access Additional Power Settings:
- In the "Related Settings" section, click on "Additional power settings."
-
Open Power Options:
- The "Power Options" window will open.
-
Choose "Choose what the power buttons do":
- Select "Choose what the power buttons do" from the left-hand pane.
-
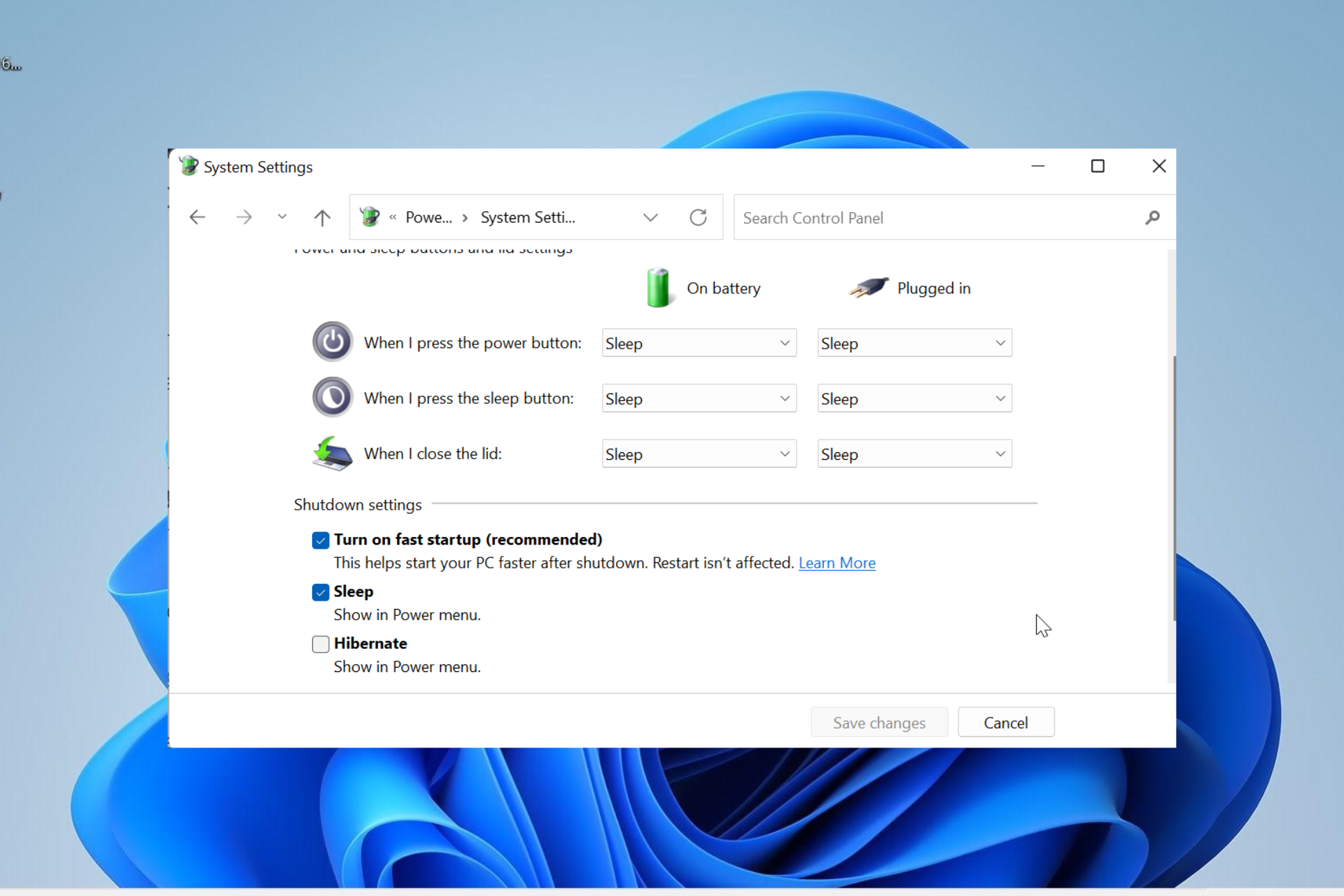
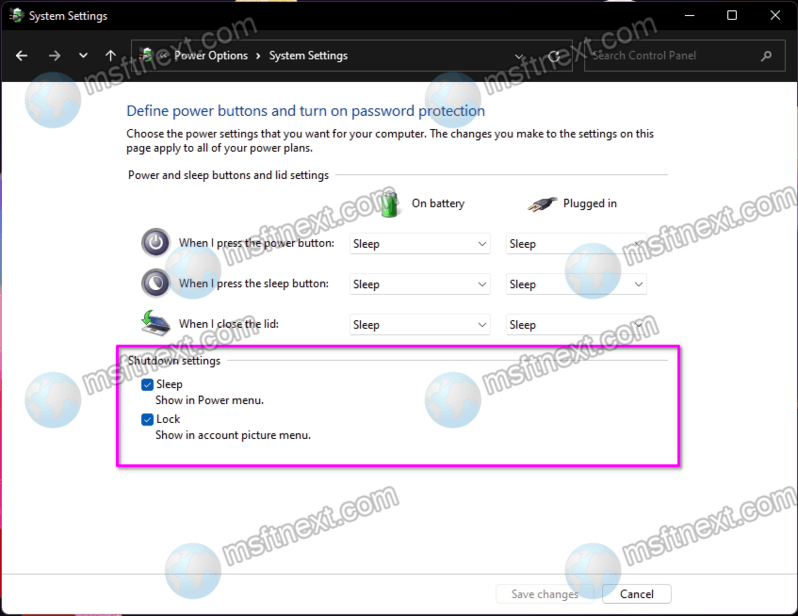
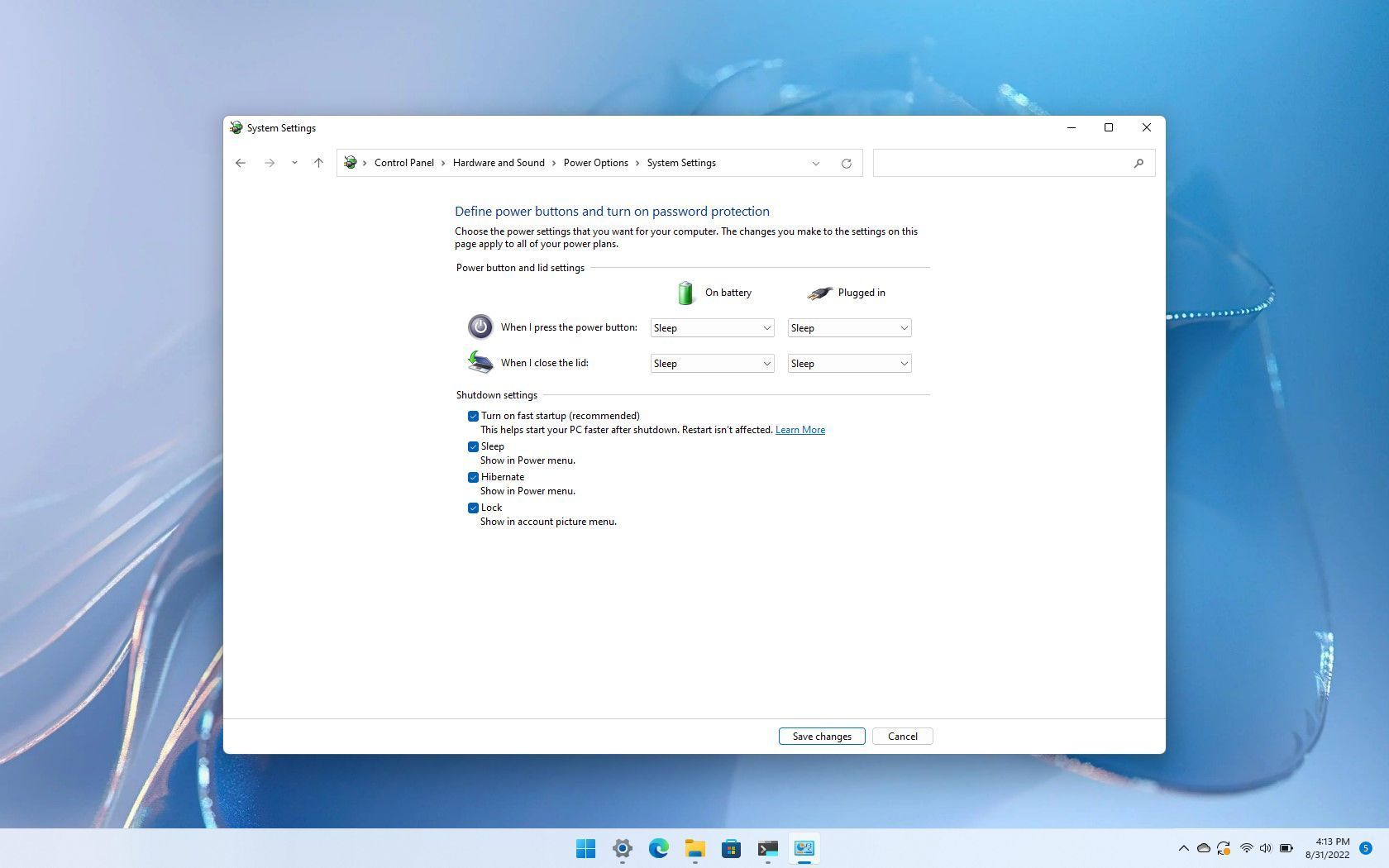
Disable Fast Startup:
- Under "Shutdown settings," uncheck the box labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
-
Save Changes:
- Click on "Save Changes" to apply the changes.
FAQs
Q: Will disabling Fast Startup significantly impact boot times?
A: While disabling Fast Startup might increase boot times slightly, the difference is typically minimal. Modern hardware and operating systems are optimized to minimize the impact of this change.
Q: Can I re-enable Fast Startup after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable Fast Startup by following the same steps outlined above but checking the "Turn on fast startup" option instead of unchecking it.
Q: Does disabling Fast Startup affect the hibernation feature?
A: No, disabling Fast Startup does not affect the hibernation feature. You can still choose to hibernate your system, which saves the current state to a hibernation file, allowing for a faster resume.
Tips
- Consider using a system restore point: Before disabling Fast Startup, it’s recommended to create a system restore point to allow for easy rollback if any issues arise.
- Monitor system performance: After disabling Fast Startup, observe your system’s performance and boot times to assess any potential changes.
- Consult system documentation: If you encounter specific issues after disabling Fast Startup, refer to the documentation for your software or hardware for potential solutions.
Conclusion
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11 offers a potential solution for users encountering specific issues or seeking enhanced system stability. While the feature generally enhances the boot experience, its impact on certain software compatibility, troubleshooting, and security concerns might warrant its deactivation. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks, users can make an informed decision regarding Fast Startup, ensuring a more optimized and reliable system experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!