Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Registry Modification
Related Articles: Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Registry Modification
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Registry Modification. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Registry Modification
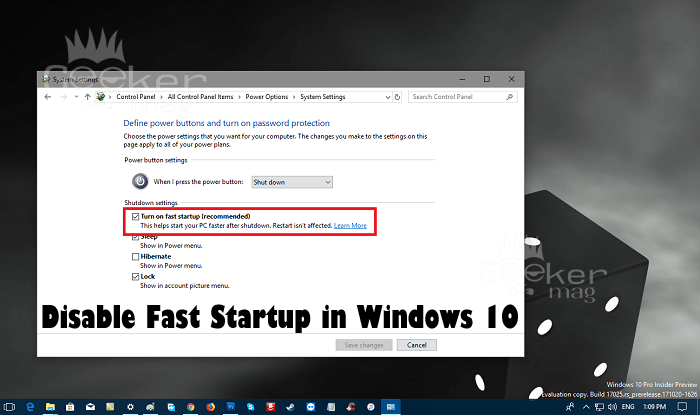
Fast startup, a feature introduced in Windows 8, is designed to expedite the boot process by utilizing a hybrid shutdown approach. While this generally results in faster boot times, it can sometimes lead to unexpected behavior and compatibility issues. For users who prioritize stability, data integrity, or specific system configurations, disabling fast startup may be necessary. This article provides a comprehensive guide to modifying the Windows 10 registry to disable fast startup, delving into the reasons behind this action and its potential implications.
Understanding Fast Startup and Its Impact
Fast startup, also known as "hybrid shutdown," is a power management feature that leverages a combination of hibernation and shutdown processes. When a user initiates a shutdown, the system does not fully power down but instead enters a hybrid state. The kernel and user mode drivers are saved to the hibernation file (hiberfil.sys), while other processes are closed. Upon restarting, the system quickly loads the saved data, bypassing the usual boot process and achieving a faster startup time.
While fast startup offers convenience, it can introduce certain drawbacks. These include:
- Potential Data Loss: In rare cases, unexpected power outages during the hybrid shutdown process can corrupt the hibernation file, potentially leading to data loss upon restarting.
- Compatibility Issues: Certain applications or hardware components may not function correctly with fast startup enabled. This can result in errors, instability, or even system crashes.
- Reduced Boot Options: Disabling fast startup provides access to more advanced boot options, such as safe mode and recovery environments, which may be crucial for troubleshooting or system repairs.
- Increased Disk Usage: The hibernation file can consume significant disk space, especially if the system has a large amount of RAM. This can impact available storage and system performance.
Modifying the Registry to Disable Fast Startup
Modifying the Windows registry requires caution, as incorrect changes can lead to system instability. It is highly recommended to create a system restore point before making any registry modifications.
To disable fast startup through the registry, follow these steps:
- Open the Registry Editor: Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box. Type regedit and press Enter.
-
Navigate to the Fast Startup Key: In the Registry Editor window, navigate to the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlPower - Modify the "HiberbootEnabled" Value: Locate the HiberbootEnabled DWORD value. Right-click on it and select Modify.
- Set the Value to 0: In the Value data field, enter 0 and click OK.
- Close the Registry Editor: Close the Registry Editor window and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Benefits of Disabling Fast Startup
Disabling fast startup can offer several advantages, depending on individual needs and preferences:
- Enhanced Data Integrity: Eliminating the hybrid shutdown approach reduces the risk of data loss due to unexpected power outages.
- Improved Compatibility: Disabling fast startup can resolve compatibility issues with certain applications or hardware components, leading to a more stable system.
- Access to Advanced Boot Options: Disabling fast startup provides access to a wider range of boot options, facilitating troubleshooting and system repairs.
- Reduced Disk Usage: Disabling fast startup removes the hibernation file, freeing up disk space and potentially improving overall system performance.
FAQs Regarding Disabling Fast Startup
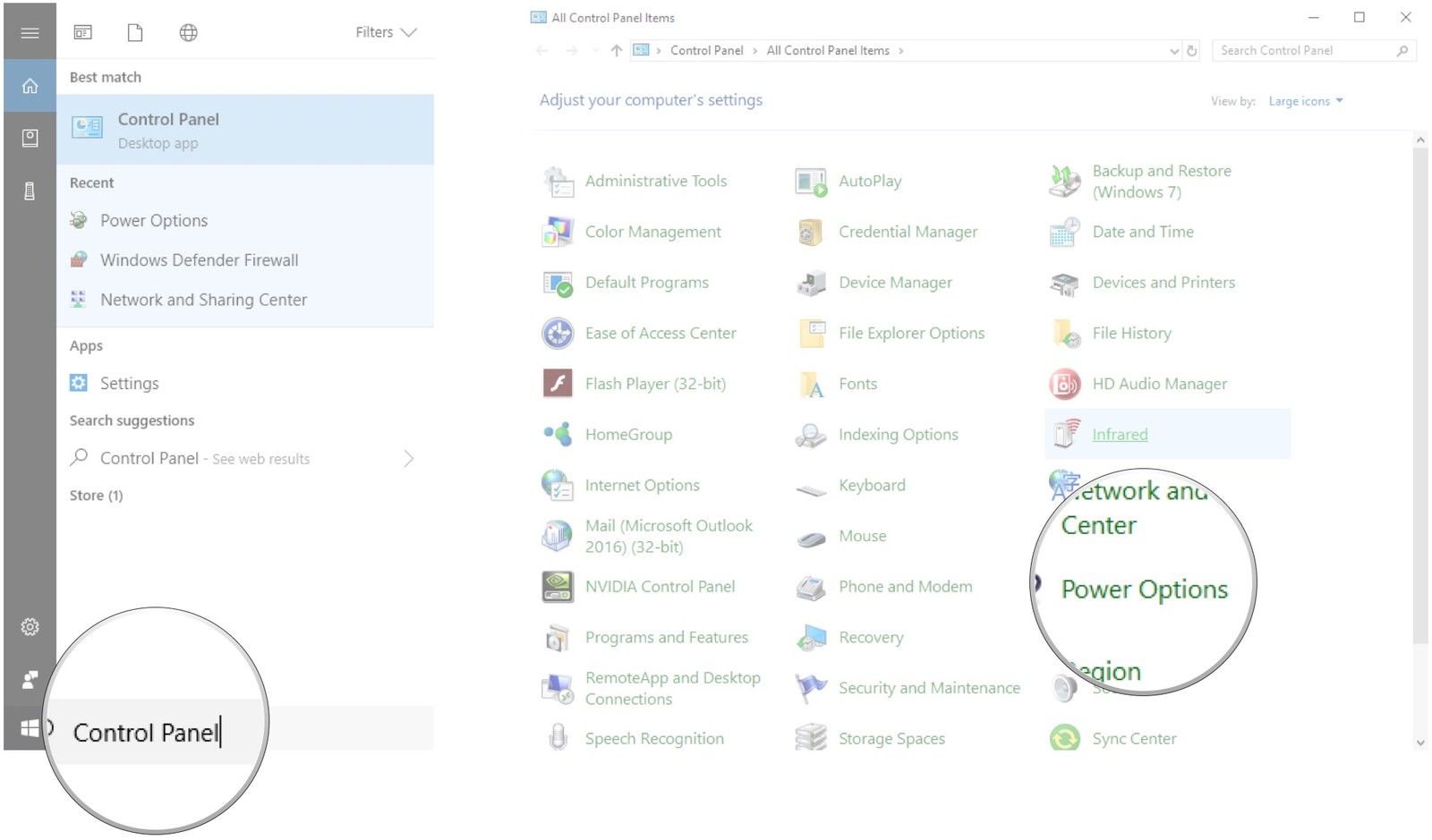
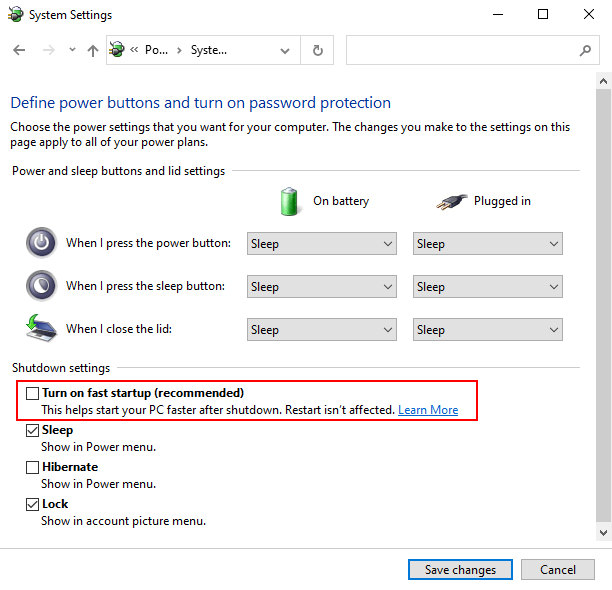
Q: Can I disable fast startup through the Control Panel?
A: While disabling fast startup through the registry is the most direct method, it is also possible to disable it through the Control Panel. However, this option may not be available in all Windows 10 versions.
Q: Will disabling fast startup affect my boot times?
A: Disabling fast startup will likely result in slightly longer boot times compared to using the fast startup feature. However, the difference may be negligible for most users.
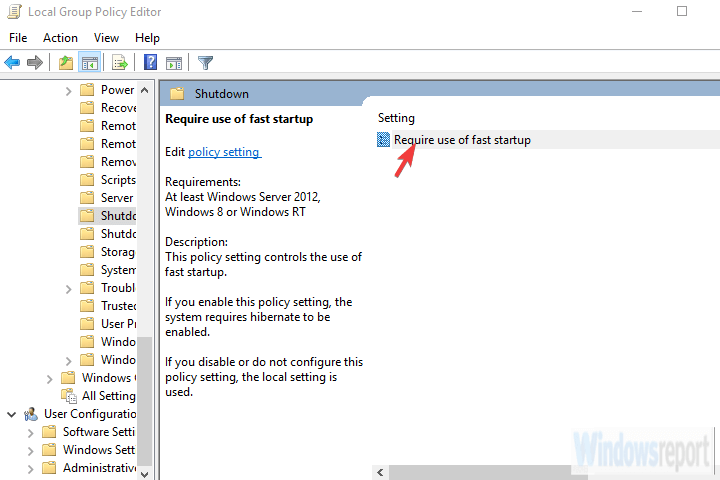
Q: Can I disable fast startup without modifying the registry?
A: While modifying the registry is the most common method, there are alternative solutions. Some third-party utilities offer options to disable fast startup without direct registry modifications. However, using such utilities may introduce other potential risks or compatibility issues.
Q: Does disabling fast startup affect sleep mode?
A: Disabling fast startup does not affect sleep mode. Sleep mode utilizes a different power management mechanism and remains unaffected by changes to the fast startup settings.
Q: Is it necessary to restart my computer after modifying the registry?
A: Yes, it is necessary to restart your computer for the registry changes to take effect. This ensures that the new settings are applied to the operating system.
Tips for Disabling Fast Startup
- Back Up Your System: Before making any changes to the registry, create a system restore point to ensure you can revert to a previous state if necessary.
- Consider Alternatives: Explore alternative solutions for faster boot times, such as optimizing system startup programs or using a solid-state drive (SSD).
- Monitor Performance: After disabling fast startup, monitor your system’s performance and stability. If you encounter any issues, consider re-enabling fast startup.
- Research Compatibility: If you experience compatibility problems with specific applications or hardware, research whether disabling fast startup is a potential solution.
Conclusion
Disabling fast startup in Windows 10 can be beneficial for users who prioritize data integrity, system stability, or access to advanced boot options. While it may slightly increase boot times, the potential advantages, such as improved compatibility and reduced disk usage, may outweigh this minor inconvenience. Remember to exercise caution when modifying the registry and to create a system restore point before making any changes. By carefully considering the pros and cons, users can make informed decisions about whether disabling fast startup is the right choice for their specific needs.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Registry Modification. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!