Delving into the Distinction: Windows and Windows NT
Related Articles: Delving into the Distinction: Windows and Windows NT
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Distinction: Windows and Windows NT. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Distinction: Windows and Windows NT
The term "Windows" has become synonymous with personal computing, but within its history lies a significant distinction: the difference between the original Windows operating system and its successor, Windows NT. While both are graphical user interfaces (GUIs) designed to make computers more user-friendly, their core functionalities, underlying architectures, and target audiences diverge considerably.
The Genesis of Windows: A User-Friendly Revolution
The original Windows, released in 1985, was a revolutionary step towards simplifying computer usage. It introduced a graphical interface, replacing the text-based command prompts that dominated the computing landscape. This interface, with its intuitive icons and windows, made computers more accessible to a wider audience. However, Windows was built on top of MS-DOS, a single-tasking operating system designed for simpler tasks. This foundation limited Windows’ capabilities, particularly in multi-user environments and network-intensive scenarios.
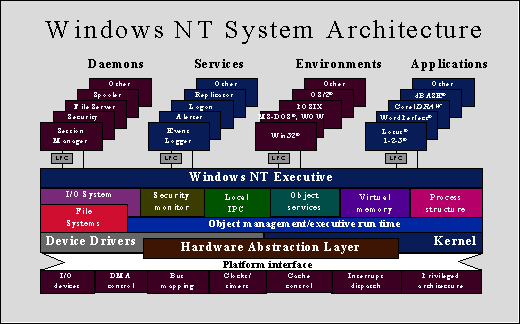
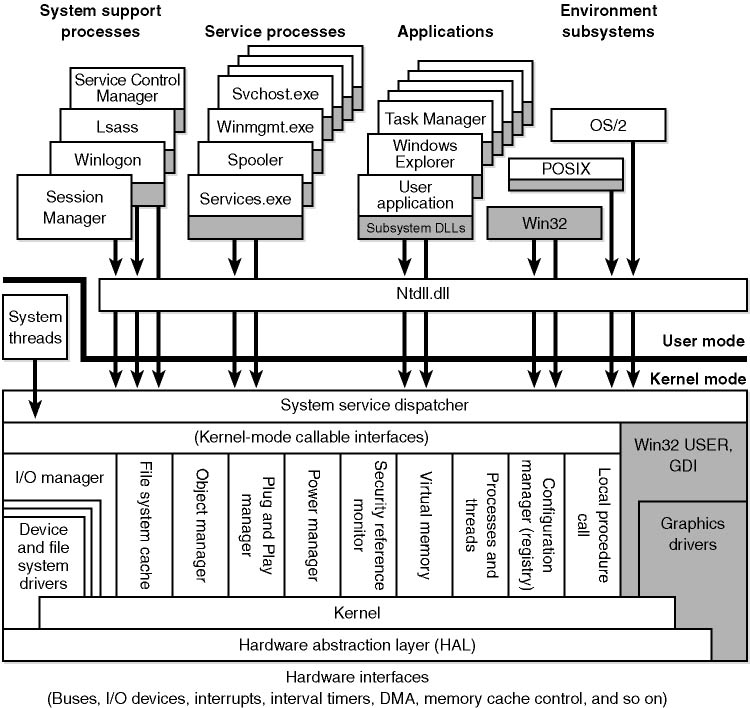
Windows NT: A New Paradigm for Power and Stability
Windows NT, released in 1993, represented a significant departure from its predecessor. It was built from the ground up with a new architecture, designed to address the shortcomings of the original Windows. Key features of Windows NT included:
- Preemptive Multitasking: Windows NT allowed multiple applications to run concurrently, efficiently utilizing system resources and ensuring smooth performance.
- Multi-User Support: Windows NT enabled multiple users to access the system simultaneously, each with their own workspace and security privileges.
- Robust Security: Windows NT incorporated a sophisticated security model, allowing for granular control over user access and data protection.
- Network Focus: Windows NT was designed with networking in mind, providing powerful tools for managing and connecting to network resources.
- Hardware Independence: Windows NT was designed to be portable across various hardware platforms, ensuring compatibility and flexibility.
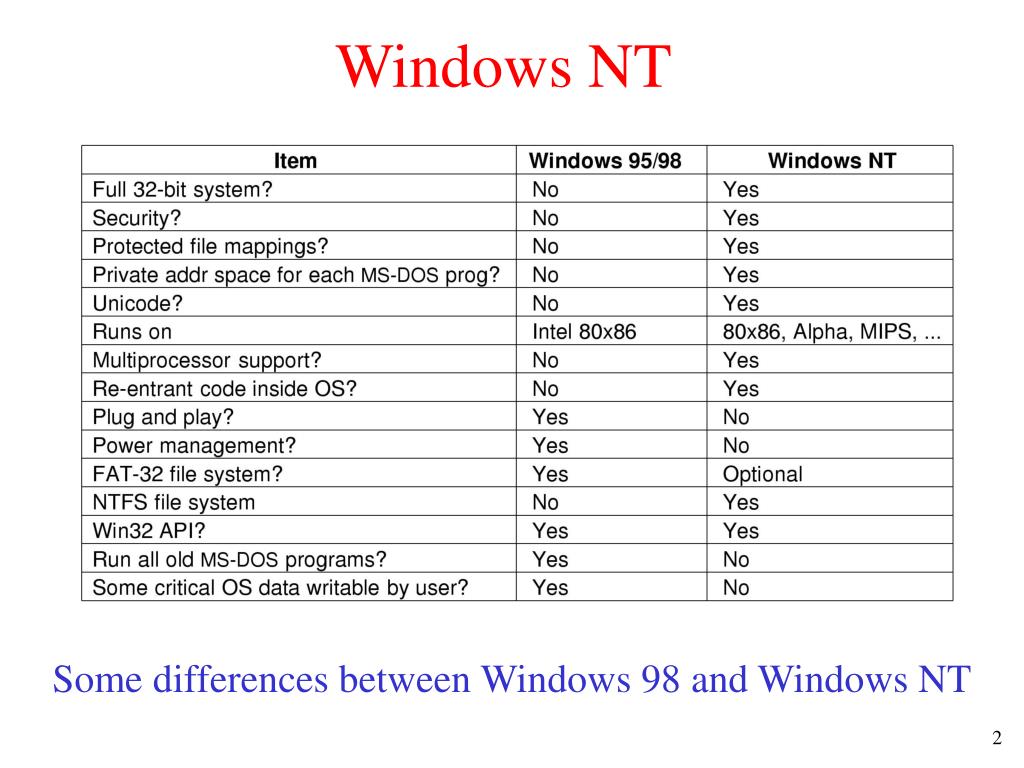
A Comparative Analysis: Unveiling the Differences
The following table summarizes the key differences between Windows and Windows NT:
| Feature | Windows | Windows NT |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Built on MS-DOS | New, independent architecture |
| Multitasking | Cooperative | Preemptive |
| Multi-user Support | Limited | Supported |
| Security | Basic | Advanced |
| Network Capabilities | Limited | Extensive |
| Hardware Compatibility | Limited | Broad |
| Stability | Less stable | More stable |
| Target Audience | Home users | Businesses, power users |
The Legacy of Windows NT: A Foundation for Innovation
Windows NT’s success laid the groundwork for the future of Windows. Subsequent versions, including Windows 2000, Windows XP, and later iterations, were based on the robust architecture established by Windows NT. This foundation enabled Microsoft to deliver operating systems that were increasingly powerful, stable, and secure.
Understanding the Impact: Why the Distinction Matters
The distinction between Windows and Windows NT is crucial for understanding the evolution of personal computing. While the original Windows democratized access to computers, Windows NT ushered in an era of enterprise-grade operating systems that powered the burgeoning internet and fueled the growth of the digital age. This distinction is reflected in the naming conventions used by Microsoft:
- Windows 95, 98, and ME: These versions were based on the original Windows architecture, primarily targeting home users.
- Windows NT 3.1, 4.0, 2000, XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, 11: These versions were based on the Windows NT architecture, designed for both home and enterprise use.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: Why is Windows NT considered more stable than the original Windows?
A: Windows NT’s preemptive multitasking architecture allowed for better resource management, preventing applications from crashing the entire system. Additionally, its robust security features minimized the risk of malicious software compromising the system.
Q: What are the advantages of using Windows NT for businesses?
A: Windows NT provided features crucial for enterprise environments, including multi-user support, advanced security, network management capabilities, and stability, making it a reliable platform for critical business operations.
Q: Is Windows NT still relevant today?
A: While Windows NT is no longer actively supported by Microsoft, its legacy lives on in the architecture of modern Windows operating systems. The principles of preemptive multitasking, multi-user support, and robust security, established by Windows NT, remain fundamental to the Windows experience today.
Tips: Navigating the Legacy of Windows NT
- For historical context: Understanding the evolution of Windows from its MS-DOS roots to the Windows NT architecture provides valuable insight into the history of personal computing.
- For technical understanding: Exploring the technical differences between Windows and Windows NT deepens the understanding of operating system architecture and its impact on performance and security.
- For business perspective: Recognizing the role of Windows NT in the rise of enterprise computing sheds light on the importance of robust and secure operating systems for businesses.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Innovation
The distinction between Windows and Windows NT represents a pivotal moment in the history of personal computing. While the original Windows made computers accessible to the masses, Windows NT laid the foundation for powerful, stable, and secure operating systems that have shaped the digital landscape for decades. By understanding this distinction, we gain a deeper appreciation for the evolution of computing and the enduring legacy of Windows NT.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Distinction: Windows and Windows NT. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
